* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War SS8H6a UPDATED 1516
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
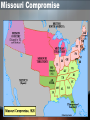
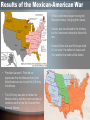
Issues Leading to the Civil War Standard SS8H6a Differences in 1800s Economy NORTH • Factories – Produced finished goods • Paid workers SOUTH • Agriculture – Produced mainly cotton • Slaves States’ Rights • States’ Rights – STATES are sovereign (only rules are from Constitution), and have the RIGHT to ignore laws they feel are unconstitutional. • South – favored (supported) states’ rights • North – opposed (against) states’ rights. • To ignore laws means to nullify them – Nullification is to make void or to deprive of value or effectiveness. • “If it ain’t in the Constitution, we ain’t gotta do it” • Georgians were split over the issue. Nullification • Southern states had fewer factories and therefore bought many cheaper manufactured goods from foreign countries instead of from the north. • Congress passed tariffs in 1828 & 1832 to force southern states to trade with them. – Many southern states opposed these tariffs and threatened to nullify them and secede from the union – Secession is to break apart from a group or a body The Unoccupied West • After the LOUISIANA PURCHASE, the North & South argued about how to use unoccupied territory (land that had not become a state yet) in the West. • The South wanted to distribute western lands as cheaply as possible; more agrarian & rural. • The North wanted to sell the land at a high price; more industrial & urban. Slavery Divides The Nation • As more western territories became states, would they become free states or slave states? • After Alabama became a state in 1819 (slave state), there were an equal number of slave and free states (11). – The North was upset. • Missouri Compromise (1820) – Congress stated that Missouri would be admitted as a “slave” state &Maine would be admitted as a “free”. Also, slavery would be prohibited north of latitude 36 30’. – Keeps the balance of free & slave states equal Missouri Compromise Results of the Mexican-American War • President James K. Polk did not appreciate that the Mexican Army had killed Americans so he sent the US Army into Mexico. • The US Army was able to defeat the Mexican Army, and the result was that all territories north of the Rio Grande River became ‘Merica. • White southerners began moving into Mexican territory, bringing their slaves. • Slavery was not allowed in the territory, but the Americans refused to follow this law. • General Santa Ana and his troops tried to “convince” the settlers to leave and this resulted in a battle at the Alamo. Compromise of 1850 After the US gained the former Mexican territories, Congress had to determine how the land would be distributed. Congress decided: • California would be admitted to the Union as a free state • The territories of New Mexico & Utah would be allowed to choose whether they wanted to be a slave or free state (STATES RIGHTS) – Both states voted (POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY) to become slave states • Congress would pass a law (Fugitive Slave Act) stating that runaway slaves would be returned to their owner • Georgia Platform • Many Georgian’s were not happy with Compromise of 1850 • The Georgia Platform was a statement that urged citizens to accept it to preserve the Union – Howell Cobb, Alexander Stephens & Robert Toombs • States’ Rights party formed – protest accepting any compromise until Congress agrees to protect slavery & state’s rights Kansas-Nebraska Act • 1854, Stephen Douglas (Illinois) got the KansasNebraska Act passed • Created territories of Kansas & Nebraska • Each state could decide to be Free or Slave state • This changes the Missouri Compromise the North is angered • Kansas = Slave state • Nebraska = Free state • Bloody Fighting breaks out between “Free Soilers” & Pro-slavery people – “Bleeding Kansas” • Congress accepts Nebraska as a (free) state but denies statehood to Kansas (slave state) – Southern states realize Northern votes can keep slave states from the Union Dred Scott Case • The case went to the Supreme Ct. • The Court said: • Dred Scott was born into slavery in Missouri – He went on a trip with his owner took him to Illinois (f) then to Wisconsin (f) 1. Scott could not sue b/c he was a slave and slaves were not citizens 2. Congress could not stop slavery in states • This issue further • After returning from the trip, divides North & South his owner died. • Scott sued his owner’s wife for his freedom Election of 1860 • 4 Candidates emerged – New Republican Party • Abraham Lincoln – Democrats • Northern Dems support Stephen Douglas • Southern Dems support John Breckenridge – Constitutional Union Party • Abraham Lincoln – Against slavery, but will not try to remove it from south – Supports protective tariff – Wants to give free land in the west to settlers – Supports building the Transcontinental Railroad with one end in the north and the other out west. • John Bell of Kentucky • To the South, the Republicans & Lincoln appear to be against everything the south wants Election of 1860 – Lincoln, Douglas, Breckenridge & Bell Election Results 1860 • http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/national.ph p?year=1860 Debate over GA secession & Alexander Stephens • Immediately after Lincoln’s election, Georgians began to discuss secession – Most Georgians support the Union, but more strongly support State’s Rights • Alexander Stephens argues strongly against secession • Gov. Joe Brown, Robert Toombs & Thomas Cobb strongly support secession and outweigh Stephens’ pleas The Union Breaks • South Carolina secedes in Dec. 1860 • Confederate States of America formed, Feb. 4, 1861 • Georgia secedes in Jan. 1861 – Jefferson Davis (Mississippi) elected President – Alexander Stephens elected Vice President • Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Texas all secede by Feb. 1861 • against secession now VP?!?! – Robert Toombs named Secretary of State United States no longer…