* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Girding For War - The North & The South
Arkansas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Red River Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Big Bethel wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Texas in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lancashire Cotton Famine wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union blockade wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
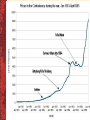
Chapter 20 Girding for War: The North and the South, 1861–1865 I. The Menace of Secession • Lincoln’s inaugural address – Was firm yet conciliatory, no attack unless attacked • Secession would create new controversies – EG: federal debt, western lands, fugitive slaves p419 II. South Carolina Assails Fort Sumter • Seceding states seized Federal property • Fort Sumter, in Charleston, SC harbor – SC bombards Ft. Sumter. • Lincoln calls for militiamen, blockade of ports • 4 more states ‘rebel’ (succeed) III. Brothers’ Blood and Border Blood • Border states: Union states with slaves • Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware • West Virginia -“mountain whites” split from Virginia(1861) • Lincoln used martial law & politics • Official goal = save the Union, not end slavery • Most Indians were Confederate allies POP ESSAY = 50 words in 5 minutes At what point did the Civil War become Inevitable? p421 IV. The Balance of Forces • Southern (Confederacy) advantages • • • • Could fight defensively behind interior lines South didn’t have to win, a draw was independence South fought for self-determination & preservation More talented officers, southern military culture • Advantages for the North (Union) • • • • Many supplies compared to the South The economy (farm, factory, & population) Controlled 75% of wealth and railroads Controlled the seas (superior navy), more trade IV. The Balance of Forces (What ifs…) • The might-have-beens are fascinating: – If the Border States had seceded. • “Butternut Region” of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois ? – If the uncertain states of the upper Mississippi Valley had turned against the Union. – If a wave of Northern defeatism had demanded an armistice. – And if Britain and/or France had broken the Union’s naval blockade of Southern ports. p422 p423 p424 V. Dethroning King Cotton • Successful revolutions have foreign intervention – Europe’s aristocracy, wealthy pro-South – Europe’s working class anti-slavery • Why did ‘King Cotton’ fail the South? – Less demand for American cotton • More cotton from Egypt and India • Imported grains from the North important – King Wheat and King Corn more important p426 p427 VI. The Decisiveness of Diplomacy • Major crisis in Anglo-American (North) relations • Trent affair— – 1861 Union warship stopped British ship (Trent) • Removal of two Confederate diplomats bound for Europe • CSS Alabama (and others) – “British pirate” captured over 60 vessels (1862-1864) • British built CSA ship, CSA officers, manned by Britons • Britain could not remain neutral – Union looked north, talked about grabbing Canada CSS Alabama Ship’s motto – “Help yourself and God will help you” Captain Raphael Semmes and First Lieutenant John Kell aboard CSS Alabama 1863 VII. Foreign Flare-ups • Third and final Anglo-American (North) crisis – Laird rams—GB build two CSA ramming warships • North threaten war w/ GB. GB never let South get ships • French-American (North) crisis – French Emperor Napoleon III invades Mexico (1862) • United States gave aid to Mexico – French government collapses (1866) The Execution of Maximilian I by Edouard Manet (1867) First painting, executioners wearing traditional Mexican clothes The Execution of Maximilian I by Edouard Manet (1869) Third and final completed painting, soldiers wearing generic uniforms (possibly French uniforms), man in red cap painted to look like Napoleon III VIII. President Davis Versus President Lincoln • President Davis – Serious talk of impeachment • President Lincoln – Tactful, quiet, patient, yet firm – Forbearance towards South & backbiting colleagues – Able to interpret and lead a fickle public opinion IX. Limitations on Wartime Liberties • During war, Congress usually supports POTUS • Honest Abe usurped Constitutional powers – Lincoln orders blockade – Increased Fed army size – Directed $2 million to military – Suspended writ of habeas corpus • Davis unable to expand his power – Opposition from states’ righters X. Volunteers and Draftees: North and South • Northern armies manned by volunteers (1861-63) – Congress passes first conscription law (1863) – Pay $300 for exemption rights ($5,774 in 2014) • The South relied mainly on volunteers – Started draft as early as 1862 – Exemptions for $, large slaveowners, specific areas NYC Anti-Draft Riots (1863) Poor Irish and Anti-Lincoln forces (Democrats) protested Civil War draft law and attacked blacks and others until federal troops arrived. p430 p430 XI. The Economic Stresses of War • Northern economies: a lion’s share of the wealth – – – – Excise taxes, income tax, Morrill Tariff Act (1861) Greenbacks: paper money Bonds – North netted $2.6 trillion National Banking System (1863-1913) • Financial landmark of the war • Southern financial woes – – – – Custom duties were cut off by Union blockade Confederate bonds sold $400 million Increased taxes , ‘bluebacked’ paper money print “Runaway inflation” - 9000% inflation rate Bluebacked Confederate money worth 1.6% of face value by April 1865 XII. The North’s Economic Boom • New factories, protective by tariffs mushroomed – Manufacturers raked in “the fortunes of war.” • Other industries were humming – Discovery of petroleum (1859) – Homestead Act (1862), caused westward movement • The Civil War was also a women’s war – Women often took men’s jobs as they went to war – U.S. Sanitary Commission trained nurses p432 p432 XIII. A Crushed Cotton Kingdom • The South fought to the point of exhaustion – Blockade (Atl & Miss R) caused economic suffocation – Loss of wealth (30% in 1860 to 12% in 1870) – Transportation collapsed • Destruction & cannibalism of rails • Northern industry conquered Southern manors