* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
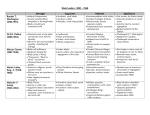
Reconstruction Objective: Interpret reconstruction’s impact on south/north relations post civil war Review: Main Causes of Civil War • State’s Rights • Slavery • Cotton Gin by Eli Whitney in 1793 • Preserving the Union • Uncle Tom’s Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe • Slave vs. Free States • Economics Review: Lincoln’s Aims and Actions • PRESERVE THE UNION – “Nothing more than Shay’s Rebellion or the Whiskey Rebellion” – Constitutional issue – Not a war over slavery • • • • Calls out state militias Increases the size of the Navy Naval Blockade of South Increased military spending without Congress’ okay The Soldiers: Human Devastation Problems after the war: • • • • • • • • • Unemployment Starvation Illiteracy War torn communities Homelessness Hatred and resentment towards Blacks State governments in the South Punishment: southern whites Economic breakdown in southern (agricultural) states White Control in the South • • • • • • Sharecropping Black Codes Poll Tax Literacy Tests Grandfather Clause Jim Crow – Laws that separate blacks and whites Sharecropping/Tenant Farming Sharecropping • A white plantation owner provide a Black family with: – seeds – Tools – shack to live in • Blacks work the land and grow the crops • Sell them and split the earnings • Blacks would go in debt with storeowners – never leave the plantation. Segregation Black Codes • Old slave codes aimed at keeping blacks at conditions close to slavery • Laws passed after the Civil War – In Southern States • The laws controlled – Freedmen – Enabled plantation owners to exploit African Americans. • (Example: curfews and contract work) Military Districts: 1867 • Divided the southern states into 5 military districts • Each district was assigned a Union general – maintain peace – protect the rights of Blacks. Freedman’s Bureau • Government program – helped to feed – Clothe – educate Blacks – helped to find jobs for them. Literacy Tests • Southern state tests designed to keep Blacks from voting – the tests were really really hard! • Had to prove you could read & write before you voted. – Had to interpret the Constitution Poll Tax • Southern state laws that required registered voters to pay to vote – kept the poor away from the polls. Grandfather Clause • If your father or grandfather was eligible to vote in 1866/1867, then you could vote even if you were illiterate or poor. Jim Crow laws • Racial caste system (segregation) • Preachers – White is choosen – Black cursed to be servents • Whites superior to all blacks • No interracial “crossbreeding” – Create a race that destroys America • Use violence if necessary to keep blacks down Jim Crow Examples • A Black male could not offer his hand (to shake hands) with a White male because it implied being socially equal. Obviously, a Black male could not offer his hand or any other part of his body to a White woman, because he risked being accused of rape. • Blacks and Whites were not supposed to eat together. If they did eat together, Whites were to be served first, and some sort of partition was to be placed between them. • Under no circumstance was a Black male to offer to light the cigarette of a White female -- that gesture implied intimacy. • Blacks were not allowed to show public affection toward one another in public, especially kissing, because it offended Whites. Jim Crow Examples • • • • Never assert or even intimate that a White person is lying. Never impute dishonorable intentions to a White person. Never suggest that a White person is from an inferior class. Never lay claim to, or overly demonstrate, superior knowledge or intelligence. • Never curse a White person. • Never laugh derisively at a White person. • Never comment upon the appearance of a White female. Plessy v. Ferguson • Separate railroad cars for blacks and whites was constitutional – “Separate but equal” • Segregation was legal as long as the separate facilities were equal • Solidified Jim Crow as law Booker T. & Du Bois Booker T. Washington’s Views • Concentrate on Vocational Education – Learn a trade or skill – Tuskegee Institute Created • Accept “second class citizenship” – DO NOT fight against segregation – DO NOT fight for suffrage • Concentrate on economics – Work hard – Your rights will come later W.E.B. DuBois’ Views • You deserve your rights now – Political, social and economic equality • You need to send people to college • Fight for you rights! – Use the law to guarantee your rights • NAACP Established • Court Cases 13th Amendment • Section 1. Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction. • Section 2. Congress shall have power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation. 14th Amendment • Section 1. All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. 15th Amendment • Section 1. The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude. • Section 2. The Congress shall have power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation. Ku Klux Klan • A southern secret society organization that terrorized African Americans and anyone else that was sympathetic towards the Blacks.