* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Who`s Who on Mount Olympus
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
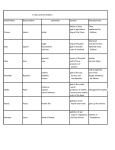
Who’s Who on Mount Olympus ARES • ARES (AIR-eez; Roman name Mars) • the god of war, or more precisely of warlike frenzy • Though an immortal deity, he was bested by Heracles in battle and was almost killed when stuffed into a jar by two giants. When another hero wounded him during the Trojan War, he received scant sympathy from his father Zeus. • He is often depicted carrying a bloodstained spear. APHRODITE • Roman name Venus • the goddess of love, beauty and fertility. She was also a protectress of sailors. • Dove, swan • Aphrodite cont. • Homer said that she was the daughter of Zeus • When the Trojan prince Paris was asked to judge which of three Olympian goddesses was the most beautiful, he chose Aphrodite over Hera and Athena. • Aphrodite offered the love of the most beautiful woman in the world. • This was Helen of Sparta, who became infamous as Helen of Troy when Paris subsequently eloped with her. In the ensuing Trojan War, Hera and Athena were implacable enemies of Troy while Aphrodite was loyal to Paris and the Trojans. Apollo • APOLLO (uh-POL-oh; Roman name Apollo) was the god of prophesy, music and healing. • As god of music, Apollo is often depicted playing the lyre. He did not invent this instrument, however, but was given it by Hermes in compensation for cattle theft. Some say that Apollo did invent the lute, although he was best known for his skill on the lyre. • Sun Artemis • ARTEMIS (AR-ti-mis; Roman name Diana) was the virgin goddess of the hunt. She helped women in childbirth but also brought sudden death with her arrows. Artemis is generally depicted as a young woman clad in buckskins, carrying a bow and a quiver of arrows. She is often accompanied by wild creatures such as a stag or she-bear. Athena • ATHENA (a-THEE-nuh; Roman name Minerva) • the goddess of crafts and the domestic arts and also those of war. • She was the patron goddess of Athens. Her symbol was the owl. • She was originally the Great Goddess in the form of a bird. By the late Classic, she had come to be regarded as a goddess of wisdom Demeter • DEMETER (dee-MEE-tur; Roman name Ceres) • the goddess of agriculture • Demeter as the sister of Zeus and the mother of Persephone. • When depicted in art, Demeter is often shown carrying a sheaf of grain. Dionysus • DIONYSUS (dye-oh-NYE-sus; Roman name Bacchus) • the god of wine Hephaestus • HEPHAESTUS (he-FEE-stus or he-FESS-tus; Roman name Vulcan) • the god of fire and crafts or the two together, hence of blacksmiths. • Hephaestus accomplished numerous prodigies of craftsmanship, such as the marvelous palaces that he built for the gods atop Mount Olympus • HAMMER Hera • HERA (HEE-ruh; Roman name Juno) was the goddess of marriage. • Hera was the wife of Zeus and Queen of the Olympians. • Peacock Hermes • HERMES (HUR-meez; Roman name Mercury) was the messenger of the gods and guide of dead souls to the Underworld. • A prankster and inventive genius from birth, Hermes aided the heroes Odysseus and Perseus in their quests. • Hermes was the son Zeus and a mountain nymph. • Winged shoes Poseidon • POSEIDON (puh-SYE-dun or poh-SYE-dun; Roman name Neptune) was the god of the sea, earthquakes and horses. • Although he was officially one of the supreme gods of Mount Olympus, he spent most of his time in his watery domain. • Trident Zeus • ZEUS (zoose or zyoose; Roman name Jupiter) was the supreme god of the Olympians. • Zeus was the youngest son of the Titans Cronus and Rhea. When he was born, his father Cronus intended to swallow him as he had all of Zeus's siblings: Poseidon, Hades, Hestia, Demeter and Hera. But Rhea hid the newborn in a cave in Crete. • Lightning bolt Others • Hestia (VESTA), goddess of the hearth, grew tired of the godly bickering and gladly gave her place to the god of wine, Dionysus. • Hades, god of the dead and brother of Zeus and Poseidon, isn't included in our assembly because he dwelt in the Underworld and not on Olympus. His Roman name was Pluto. CERBERUS Others cont. • Pan was a god of shepherds and flocks. Pan was the son of Hermes and a nymph. He was born with the legs and horns of a goat, which caused his own mother to spurn him. FATES • "These are Clotho, Lachesis, and Atropos, and they give mortals their share of good and evil." (Hesiod, Theogony, 905-6) Fates • Clotho was the spinner, Lachesis was the drawer of lots, and Atropos represented the inevitable end to life. This notion that human fate was spun around a person at birth by divine Spinners - in other words, the Fates was popular in Greek mythology, poetry, and literature. Indeed, there is a compelling scene in the Odyssey of Homer that alludes to this concept of spinning fate. Fates • The three goddesses who supervised the spinning of human fate evolved into a more concrete concept. The Fates came to be identified as three older females who handled the threads of human life. One of these threads was placed to every person, and each goddess took her turn in manipulating this thread. Clotho selected the thread, Lachesis measured it, and Atropos cut this thread to signify the end of a person's existence. Hebe • • • • • Juventas Goddess of youth Daughter of Zeus and Hera Married to Heracles (Hercules) Symbol: cup (because she is the cupbearer to the gods)