* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Greece
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
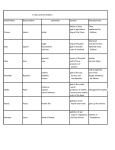
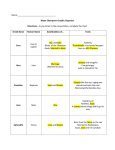
Ancient Greece Religion, Gods, and Mythology Key Terms • Myths • Titans Myths • The Ancient Greeks developed myths, or traditional stories, about their gods • Greeks tried to explain the mysteries of nature and power of human passions through stories of the gods • Epics written by Homer and Hessiod Creation of Earth • Chaos created Earth and the heavens • Mother Earth, Gaea, and Father Heaven, Uranus, had children called the Titans • Head Titan, Cronus, and his sister-queen, Rhea, had 6 children who became gods • Battle of Titans and Gods cleared Earth of monsters for humans • Video (3:16-24:40) Zeus Zeus Parents: Cronus, Rhea God of: Heaven, Earth, Men Symbol: Eagle, Oak Origin of Zeus: Cronus the Titan was told that one day, his son would overthrow him. In fear, he swallowed his children right after his wife Rhea gave birth. After swallowing five children, Rhea became angry. She hid Zeus at birth and switched his body with a rock to fool Cronus into thinking he had swallowed his newborn son. Rhea had a nymph care for Zeus until he came of age. He married the Titaness, Metis, and rescued his brothers and and sisters from Cronus, then killing his father. Poseidon Poseidon Name: Poseidon Parents: Cronus, Rhea God of: The Sea Notes: Although mainly a god of the sea, Poseidon created the horse as a gift for a nymph who he loved. The horse became his favorite animal, and he even created a flock for himself in the ocean. Hades Hades Name: Hades Parents: Cronus, Rhea God of: Underworld Notes: Being with dead people doesn't improve one's disposition much. Although he was one of the major gods, Hades didn't even have a throne on Olympus. He spent most of his time in the Underworld. Hades marriage to Persephone causes seasons, due to Demeter’s mourning of her daughter being gone. Demeter Demeter Name: Demeter Parents: Cronus, Rhea Goddess of: Agriculture, Plants Notes: Demeter tended to the plants and crops of all mankind. Without her constant care, nothing would grow. When her daughter, Persephone, leaves her for half the year to rule the Underworld, she weeps and ignores the plants therefore causing the seasons. Hera Hera Name: Hera Parents: Cronus, Rhea Goddess of: Women, Childbirth Symbol: Peacock Notes: A very powerful goddess, Hera did not take nicely to her husband, Zeus, and his many love affairs. Unable to kill Zeus, she often persecuted his lovers instead. Hestia Hestia Name: Hestia Parents: Cronus, Rhea Goddess of: The Hearth Notes: The only virgin goddess other than Artemis, Hestia was the most honored goddess of all, but the least talked about. As the goddess who guarded the hearth and the home, she was not to be gossipped about, so she rarely appears in myths. Aphrodite Name: Aphrodite Parents: Unknown Goddess of: Love, Beauty, Laughter, Pleasures Symbol: Rose, Swan, Dove, Myrtle Aphrodite was born from the foam of the sea and the blood of Zeus's father. All the gods wanted Aphrodite as their wife, but Zeus gave her to Hephaestus because he would make a good, loving, solid husband. Hephaestus Name: Hephaestus Parents: Zeus, Hera God of: The Forge, Fire Origin of Hephaestus: Hephaestus was one of the few children of Zeus and Hera. When he was born, Hera was so disgusted by his ugliness that she threw him off of Mount Olympus. He landed in the sea where a sea nymph took pity on him and cared for him. His half-sister, Athena taught him how to forge metal and make jewelry. He became such a skilled craftsman that Zeus finally allowed him to come back to Olympus. Apollo Name: Apollo Parents: Zeus, Leto God of: The Sun, Fine Arts, Medicine, Poetry, Eloquence, Prophecy Symbol: Laurel Tree Artemis Name: Artemis Parents: Zeus, Leto Goddess of: The Moon, Hunting, Wild Things, Childbirth, Virginity Notes: Young and free, Artemis did not think it right that girls should be forced to marry and have children. Strangely enough, she is also the goddess of childbirth. This comes from the fact that when she was born, she caused her mother no pain. Ares Name: Ares Parents: Zeus, Hera God of: War (Cruel War, Bloodshed, Violence) Notes: Unlike Athena, Ares loved war and reveled in violence. His constant companion was Eris, goddess of discord. Ares also romanced Aphrodite from a distance, enthralling her with tales of his victory and might. Unfortunately, he was actually a big coward, and often ran to his mother, Hera, when he was hurt. Athena Name: Athena Parents: Zeus, Metis Goddess of: Wisdom, War, Weaving, Skill Symbol: Owl Origin of Athena: When Zeus's first wife, Metis, became pregnant, an oracle prophesied that the son of Metis would overthrow Zeus just as Zeus had overthrown his father. In fear, Zeus challenged his wife to a contest of magic. Whoever could turn into a smaller animal won. Metis turned herself into a fly, and Zeus swallowed her. Soon after, he had a terrible headache. It felt like someone was in his head stabbing at all the soft spots in his brain. He called for Hephaestus to help him. The god of the forge lay Zeus's head down on his anvil and broke the skull with a hammer. Out of Zeus's head sprung Athena, dressed for battle and armed with a spear. Dionysus Name: Dionysus Parents: Zeus, Semele God of: Wine, Revelry Origin of Dionysus: Zeus had gone to see Semele every night, and she soon became pregnant with a boy. In anger, Hera tricked Semele into asking Zeus to reveal his godly self: certain death for any mortal. Zeus did so, and Semele died, but Dionysus survived. When he arrived at Olympus, he created quite a stir. There were only 12 thrones, and he wanted a throne for himself. The gods began to argue over who should give up their throne, but Hestia quietly stood up from her throne and sat on the floor in the ashes to tend the hearth. Thus, Dionysus took the throne of the most humble goddess of all. Hermes Name: Hermes Parents: Zeus, Maia God of: Trade, Travelers, Tricksters, Thieves, The Wind Notes: Best known as the messenger god, Hermes was a clever boy ever since his birth. He often acted as a messenger between gods and mortals. Legends • The Illiad and The Odyssey by Homer • 12 labors of Heracles • Monsters like Cyclops, Medusa, Pegasus, Centaurs, etc. • Pandora’s Box • King Midas • Oedipus