* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Eyes and Ears MT 11
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
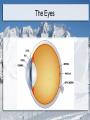
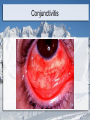
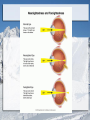
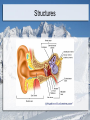
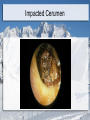
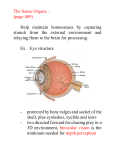
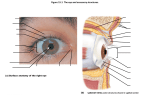
Special Senses: The Eyes and Ears MT Ch. 11 Adonis K. Lomibao 11/23/11 Objectives Identify the basic function and structures of the Eyes. Identify the basic function and structures of the Ears. The Eyes Function- receive images and transmit them to the brain. Structures include the eyeball and adnexa The Eyes The Adnexa of the Eyes The structures outside of the eyeball They include the: Orbit (eye socket), eye muscles, eyelids, eyelashes, conjunctiva, and lacrimal apparatus. Adnexa-means appendages or accessory structures of an organ. Lacrimal Apparatus:produce, store, and remove tears The Eyeball Aka globe, 1-inch sphere with only 1/6 of surface visible. Sclera: (whites of the eye) maintains shape and protects inner tissue. Choroid:middle layer, vascular: provides blood supply for eye. Retina:converts light images into electrical impulses and transmits them to the brain. The Uveal Tract The pigmented layer of the eye. Consists of the: -Choroid:provides blood supply for the eye. -Ciliary body:in the choroid-muscles and ligaments that adjust the thickness of the lens to refine focus of light rays on the retina. -Iris:controls the amount of light entering the eye. Cornea, Pupil, Lens Cornea: transparent outer surface—focuses light rays entering the eye. Pupil: the black circular opening in the center of the iris that permits light to enter the eye. Lens: clear, flexible, curved structure that focuses images on the retina. Common Conditions Conjunctivitis (pink eye)-inflammation of the conjunctiva Corneal abrasion-a scratch or irritation to the outer layers of the cornea Cataract-loss of transparency of the lens Glaucoma-increased intraocular pressure Macular degeneration-damage of the maculaloss of central vision. Conjunctivitis Cataract Central Vision Loss Peripheral Vision Loss Refractive Disorders Focusing problem that occurs when the lens and cornea do not bend light so it focuses properly on the retina. Astigmatism-impoper focus due to uneven curvatures of the cornea Hyperopia-(farsightedness) light rays focus beyond retina Myopia-(nearsightedness) light rays focus in front of the retina The Ears Function- receive sound impulses and transmit them to the brain Auditory-pertaining to the sense of hearing Acoustic-relating to sound or hearing Major structures The outer ear-includes the pinna, the external auditory canal, & cerumen. The middle ear- transmits sound to the inner ear. Includes the tympanic membrane or eardrum. The inner ear- contains sensory receptors for hearing and balance. Structures Common Conditions Impacted Cerumen Otitis-inflammation of the ear Vertigo- whirling, dizzynesss, loss of balance Tinnitus-a ringing, buzzing, or roaring sound in ears. Impacted Cerumen