* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download America Remains Neutral
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
List of World War I memorials and cemeteries in Artois wikipedia , lookup
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
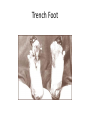
America Remains Neutral I. Reasons a. Economic reasons = Foreign investments b. Peacemakers ‘moral diplomacy’ c. 1/3 of US population 1st or 2nd generation immigrants d. Mexican Revolution/Pancho Villa II. Fighting starts (Bloody stalemate in Europe) a. German plan for war Schlieffen Plan – attack France first through Belgium, then turn to Russia with both armies - By September Germany within 30 miles of Paris on the Western Front - Also winning on the Eastern Front against Russia; looks like it will be a quick war… wrong! b. Allies stop German on Western Front by end of 1914 - Huge casualties (Trench Warfare begins) IMPORTANT EARLY BATTLES - 1st Battle of the Marne – Sept. 5-12, 1914 (Allied Victory) - Verdun – Feb. 21, 1916 (major German offensive) - Battle of the Somme – July 1st-Mid November, 1916 (Bloodiest battle) Only 7 miles change hands – Bloody stalemate c. Modern Weaponry - automatic machine guns, hand grenades, mechanized cannons, poison gas, tanks, fighter planes Trench Warfare Trench Warfare – Long concentrated artillery bombardments, followed by all out charges at the enemy across “no man’s land” (area between the trenches) Diagram of Trenches Trench Dugouts Going “Over the Top” Trenches of Somme Automatic Machine Guns Life in the Trenches a. Living conditions were horrible 1. Horrible smell, filled w/ dead bodies and stricken with flies 2. Filled with mud up to the knees, wet conditions led to diseases 3. 4. 5. 6. Trench foot – led to amputation Rats fed on the dead Shell shock – mental breakdowns “lousey” – lice that ate away at the scalp – loss of hair 7. Boredom 8. Poison Gas – Chlorine, Sulfur, Mustard Boredom in Trench Shell Shock Shell Shock Trench Foot U.S. remains neutral? 1. People horrified – American Red Cross and American Ambulance Corp. see trench warfare firsthand. 2. French Foreign Legion – volunteer 3. U.S. Gov.t trades with both sides a. British naval blockade – USA still supplies Allies with food, weapons, supplies b. American banks give Allies billions of dollars through war bonds c. Central powers upset and notice unfair neutrality Reasons US pushed toward war 1. German U-boats and Unrestricted Submarine Warfare a. To fight British naval blockade b. Unrestricted warfare – all seas around GB considered a “war zone” and subs would fire without warning. c. By May 1915 Italy leaves the Central Powers and joins the Allies 2. Sinking of the Lusitania a. May 7th, 1915 U-boat sinks Lusitania in 18 minutes, 1,200 die; 128 Americans b. Secret cargo on board = 4,200 cases of gun cartridges c. US remains neutral = American people upset = Wilson refused to repeal neutrality 3. Zimmerman Note a. Jan. 1917 intercepted by British intelligence said: - - Germany would continue unrestricted submarine warfare Proposed Mexico to join Germany should US enter the war Promised Mexico financial aid to re-conquer NM, TX, and ARZ US Declares War 1. Wilson outraged, breaks diplomatic relations with Germany 2. Zimmerman Note published in US papers on March 1st 1917 3. German U-boats sink 3 American ships on March 16th 4. US declares war on April 6th at 3 AM 5. More support war than oppose (Jeanette Rankin). Senate 82-6, House 373-50 US mobilizes for war 1. Not prepared for war at first, send 14,000 led by John Pershing. More needed! 2. Selective Service Act; May 1917 a. 3 million enlisted, 5 million volunteer (AEF = American Expeditionary Force) b. Included 11,000 women (Am. Red Cross, etc.) John Pershing Total War Total War = All Resources of a nation used for the war effort 3. US agriculture and industry increased 4. Propaganda campaigns by Gov.t a. “War to end all wars” b. CPI led by George Creel c. Against anything German = hamburgers, beers, music. d. Discrimination against Germans Objectives of Wartime Propaganda 1. Recruitment of soldiers, draft or voluntary enlistment 2. Financing the war effort, sale of war bonds, loans, new taxes 3. Eliminating dissent and unifying the country 4. Conservation of resources, food, oil, steel 5. Participation in home-front organizations Common tools used in Wartime Propaganda 1. Demonization, portray the enemy as purely evil, menacing, murderous, and aggressive 2. Emotional Appeals, playing on people’s emotions to promote the war effort 3. Name Calling, using loaded labels to encourage hatred of enemy 4. Patriotic Appeals, using patriotic language or symbols to appeal to national pride 5. Half-Truths or Lies, deception or twisting the truth 6. Catchy Slogans, memorable phrases to foster support for the war effort 7. Evocative Visual Symbols, using symbols to appeal to people’s emotions 8. Humor or Caricatures, capturing the viewer’s attention through the use of humor to promote the war effort US Prepares for War 5. Gov.t Acts a. Espionage Act 1917 – treason, hunt out spy's b. Sedition Act 1918 – cannot criticize gov.t for war 6. Convoy system a. Destroyers with depth charges to fight U-Boats 7. American Soldiers in Europe a. 2 million cross Atlantic and join Pershing b. Infantry called “doughboys” c. African Americans segregated 300,000 volunteered or drafted - Most never saw combat did menial work Harlem Hell Fighters – awarded the Croix de Guerre Fighting and the end of the war 1. New Factor changes face of war = Civil War in Russia led by Vladimir Lenin successful a. Bolshevik/Communist take-over Nov. 1917 b. Calls peace with Germany c. Germany can now focus totally on Western Front Lenin Czar Nicholas The Romanov Family 2. By June 3, 1918 Germans push within 50 miles of Paris a. US troops enter war in full force and hold Paris against German offensive at Chateau-Thierry. - Allied victories at Belleau Wood, & the 2nd Battle of the Marne - Within 7 weeks Germany is pushed out of France b. Sensing defeat Kaiser Wilhelm seeks concessions from Allies in return for peace, the Allies refuse, will only accept total surrender. c. Sept. 26-Oct. 9, 1918 One million AEF fought Germans back on a 200 mile front at the MeuseArgonne (Lost Battalion) - Central Powers crumble = Bulgaria, Turkey, AustriaHungary all surrender - Armistice finally comes when Kaiser Wilhelm flees country due to uprising on Nov. 9th, Armistice signed on Nov. 11th, 1918…fighting stops Bloodiest War in History a. Approximately 8.5 million are killed or die (this does not include civilians) b. Approximately 21 million additional people wounded c. Approximately 8 million prisoners or missing in action d. War creates approximately 10 million additional refugees e. Total cost of war about 350 billion dollars (direct economic costs) Approximately 57.6% of all men mobilized end up casualties of war France lost 20% of its men ages 20-44 Germany 15% Young people that lived became known as the “lost generation”.