* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atomic Theory - Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
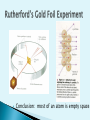
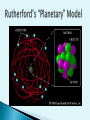
Democritus -400 B.C. - Coined the term “atom” Aristotle -384-322 B.C. - Believed matter is continuous 1627 – 1690 A.D. Introduced a scientific approach to chemistry All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element have the same properties. (mass, size, etc.) In a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed – Law of Conservation of Mass Compounds always contain elements in the same ratio by mass – Law of Definite Proportions Dalton 1810 A penny contains 2.4 x 1022 atoms. The radius of a single atom is around 2 x 10-10 m or 0.2 nm. Scanning tunneling microscopes can generate images of individual atoms. Showed electrons are negatively charged Every atom’s electrons have same charge Conclusion: most of an atom is empty space Dalton’s Model (1803) Rutherford’s Model (1909) Thomson’s Model (1897) Bohr’s Model (1913) Electron-cloud Model (present) Robert Millikan Oil Drop Experiment Determined charge of electron Max Planck E=h v Defined a quantum of energy James Chadwick Discovered Neutron in 1932 Nucleus ◦ Contains protons and neutrons ◦ Makes up most of an atom’s mass ◦ Is positively charged Proton (+ charge) Neutron (0 charge) Electron Cloud ◦ Contains electrons ◦ Makes up most of an atom’s volume Subatomic Charge Location Particles Mass Other Feature Proton + Nucleus 1 amu Defines the element -Atomic # Neutron 0 Nucleus 1 amu Change # to form isotopes Electron - Electron Cloud ~0 Atom’s volume -dictate’s reactivity Short-ranged forces that hold the nuclear particles together Between electrically charged particles Like charges repel Opposite charges attract Atoms of the same element that differ in mass ◦ Atomic # = # protons ◦ # protons = # electrons ◦ Mass # = # protons + # neutrons mass# atomic# X Nuclide Protons Neutrons Protium 1 0 Mass Number 1 Deuterium 1 1 2 Tritium 1 2 3 108 47 Ag 207 82 80 35 Pb Br Silver - 108 Lead - 207 Bromine - 80 Found in an e- cloud outside of the nucleus ◦ But NOT in paths like the planets 1st nrg level holds up to 2 e- 2nd nrg level holds up to 8 e- 3rd nrg level holds up to 18 e- 2n 2 Arranged by increasing atomic # Rows = Periods Columns = Groups OR Families