* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
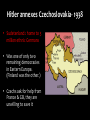
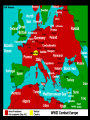
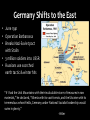
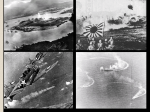
World War II 1939-1945 Japanese Aggression • Economic hardship—desire for more colonies • Japanese military leaders and ultranationalists thought Japan should have an empire equal to those of the Western powers. • Invade Manchuria- 1931 – Withdrew from the League of Nations (1933) • Anti-Comintern Pact with Germany 1936 Italian Aggression • Mussolini invades Ethiopia, 1935 • A reaction to Italy’s defeat by the Ethiopians in 1896 • League of Nations powerless to stop Italy – The League stopped selling weapons, but sanctions did extend to petroleum German Aggression • Lebensraum • Hitler violates Treaty of Versailles: – Remilitarizes • By 1935 550,000 men in the German Army • New air force – Invade the Rhineland, March 7, 1936 – His success made him more popular at home • Reaction: – Appeasement: or giving in to the demands of an aggressor in order to keep the peace. Why Appeasement? • Policy of Great Britain, France, US • Saw Fascism as the lesser of two evils • Impact of the Great Depression • Pacifism: opposition to all war Why did the Western democracies respond to aggression with a policy of appeasement? The Western democracies wanted to avoid the horrors of another war. Neville Chamberlain Hitler annexes Austria- 1938 • Anschluss – Union between Germany & Austria – Prohibited by Treaty of Versailles – Hitler threatened invasion – Eventually Germans annexed Austria in March of 1938 with ease because the Western democracies took no action Hitler annexes Czechoslovakia- 1938 • Sudetenland= home to 3 million ethnic Germans • Was one of only two remaining democracies in Eastern Europe. (Finland was the other.) • Czechs ask for help from France & GB, they are unwilling to save it Munich Conference, Sept. 29 1938 • Reaction to the invasion of Sudetenland • GB, France, Germany, Italy meet – (Who’s missing???) • What was the response? – APPEASEMENT again – Munich Pact • Signed by Hitler, Chamberlain, Daladier (France) – Agreed Hitler can take Sudetenland but must respect Czech borders Chamberlain (left) and Hitler (right) Six months later...Hitler takes Czechoslovakia Check for Understanding How was the Munich Pact an act of appeasement? A. Western democracies gave in to Hitler’s demands of annexing the Sudetenland. B. Czechoslovakia went to war with Germany to protect its lands. C. Hitler was given permission to annex Austria. D. Hitler gave in to Western democracies’ demands for an end to aggressive actions. German-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact: August 23, 1939 • Stalin distrusts Hitler, but distrusts Western allies more • Pact based on mutual need (Hitler feared communism and Stalin feared Fascism) • Agreement that neither would attack if the other invaded Poland • Gave Stalin the opportunity to expand in Eastern Europe “Wonder how long the honeymoon will last?” Hitler invades Poland- September 1, 1939 • “Official” start to WW2 • Blitzkrieg – “Lightning War” • Two days later, Britain and France declared war on Germany. World War II had begun German soldiers in Warsaw Soviets annex Baltic States- 1939 • Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania • Military bases Sitzkrieg- The Phony War • The Maginot Line – French built defensive line to protect themselves from German attack in 1930s • Stretched over 200 miles • VERY expensive The Maginot Line was France’s fortification at the French-German border. Britain and France, anticipating a German attack, armed the line with soldiers. Sitzkrieg- The Phony War continued… • Winter, 1940 – No movement or battles – French / Nazis Kept waiting for the other to attack – Ends April 9, 1940 when Germany turns attention towards… German Expansion • Denmark (April 1940) – 4 hours • Norway (May 1940) – Two months Why this territory? Oslo, April 10, 1940 German Expansion • May 1940 – Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg – Surprise French by going through Ardennes Forest (BELGIUM) – Push through France trapping 100,000s off beaches at Dunkirk German Expansion- the Fall of France • June 22, 1940, Germans enter Paris (with help of Mussolini) • French form a “government in exile” in England • France divided into Northern France (controlled by Germany) and Vichy France (German puppet state) A Frenchman weeps as German soldiers march into the French capital, Paris, after the Allied armies had been driven back across France. Who’s Left? • Britain • Winston Churchill becomes new prime minister (May 1940) • "We shall not flag or fail. We shall go on to the end. We shall fight in France, we shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our island, whatever the cost may be. We shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender." Battle of Britain • Hitler offered Churchill a truce, Churchill promptly rejected it • Hitler sent the Luftwaffe to lead the attack on Britain (Operation Sea Lion) – Needed air dominance in order to stage an invasion of Britain • London Blitz – Break British morale • Hitler stopped by the RAF – Radar- track German planes – Enigma- machine to break down German codes – Hitler’s first major defeat! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fg85ggZSHMw The first attack took place on September 7, 1940. German bombers darkened the skies over London and other cities. After a sleepless night, Londoners found parts of their city in ruins. Families built shelters in their yards and cellars. When the sirens blared, thousands of Londoners whose homes did not have shelters took shelter in the Underground (subway) stations. The British government organized “Operation Pied Piper,” which sent more than 3 million children to safer homes in rural areas. Each child boarded a train with a gas mask and a nametag. Germany Shifts to the East • June 1941 • Operation Barbarossa • Breaks Nazi-Soviet pact with Stalin • 3 million soldiers into USSR • Russians use scorched earth tactic & winter hits “If I had the Ural Mountains with their incalculable store of treasures in raw materials,” he declared, “Siberia with its vast forests, and the Ukraine with its tremendous wheat fields, Germany under National Socialist leadership would swim in plenty.” -Hitler Pacific Theater--Pearl Harbor • Japan attacks French Indochina – US cuts off oil shipments • Japan attacks US naval base, Pearl Harbor – Dec. 7 1941 – Japan claimed that its mission was to help Asians escape Western colonial rule. In fact, the real goal was a Japanese empire in Asia. USS Arizona Memorial US Casualties Service Navy Killed 2,008 Wounded 710 Total 2,718 Army 218 364 582 Marines 109 69 178 Civilians 68 35 103 Total 2,403 539 3,581 • 200 aircrafts destroyed • All 8 battleships destroyed Pearl Harbor • US breaks isolation – Declares war December 8, 1941 – “Day of Infamy” – On December 11, Germany and Italy, as Japan’s allies, declared war on the United States. Journal Entry 1. Read the Article The Pro and Con of Dropping the Bomb 2. In your journal, answer the following question: Do you think the United States should have used the atomic bomb on Japan? Why or why not? Cite evidence from the lists above to support your answer. Allied Response Allied Powers Strategize • “Big Three” – FDR, Churchill, Stalin – Goal: Finish war in Europe first, then focus on Pacific – Stalin wants 2nd front in Germany – FDR, Churchill not enough resources Turning Point in European TheaterStalingrad June 1941 Nazi Invasion • Siege of Leningrad – Winter 1941- 1942 – 3,000-4,000 Soviets starve each DAY • Battle of Stalingrad – 250,000 Germans sent in – Soviets assemble 1 million – Soviets surround Germans • Cut off from supplies • Outcome: – German generals surrender despite Hitler’s orders – Feb 1943– Soviets regain city – Significance of battle? • Proves that Hitler could be stopped! Victory in Europe D-Day (June 6, 1944) • Allied invasion of France (Germany controlled France) – Organized by the United States – Goal was to force Germany for fight a two-front war • Invasion was successful – Germans were overwhelmed, and by August 1944 Allies entered Paris Yalta Conference February 1945 (in Soviet Union): the “Big Three” met to plan the final stages of the war and post-war Europe. Goals: 1. Divide Germany into 4 zones; occupied by Britain, France, U.S., Soviet Union 2. The Soviet Union would get to keep much of eastern Europe 3. Agreed to create the United Nations Victory over Germany • Summer of 1944: Soviets pushed Germans out of Soviet territory. • March 1945: U.S. and Britain pushed into Germany through France • March 1945: Soviets enter Berlin from the east. – Hitler committed suicide in an underground bunker. • May 7, 1945: Germany Surrendered—officially war in Europe ended the next day May 8th= V-E Day (Victory in Europe) Potsdam Conference August 1945: Allies met in Potsdam, Germany (Truman had replaced the deceased Roosevelt) Outcomes: 1. Officially issued “unconditional surrender” demand to Japan. 2. Tensions began to arise between the U.S. and Soviet Union; disagreement over the future of Europe (Truman did not trust Stalin as much as Roosevelt did). Victory in the Pacific War in the Pacific • Up until Mid 1942 = Japan won an interrupted series of victories controlled much of Southeast Asia + Many Pacific Islands. • (May 1942) Japan gained control of Philippines = Killed several hundred American soldiers + 10,000 Filipino soldiers Bataan Death March. – 60+ mile march in blazing heat to POW camps – Over 10,000 died US Strategy “Island Hopping” • Dilemma: taking over each island would be very costly • Solution: “Hop” past Japanese strongholds – Cut off supplies for bypassed islands – Build bases – Recapture some Japanese held islands + bypass others Defeat for Japan Mid 1945: Allied poured resources into defeating Japan. – Most of Japanese navy and air force had been destroyed, although the Japanese army still had 2 million men February to March 1945: Bloody battles on the islands of Iwo Jima and Okinawa showed that the Japanese would fight to death rather than surrender. Defeat for Japan Invasion or Bomb? Manhattan Project • Allied scientists discovered that splitting atoms could create an explosive far more powerful that any known bomb. • After consulting with advisors and other Allied leaders, Truman, determined to save tremendous numbers of American lives, decided to use the new weapon against Japan (The Atomic Bomb) Truman issued warning to Japan to surrender or face “complete destruction and utter devastation” Utter Devastation • August 6, 1945: An American plane dropped and atomic bomb over the city of Hiroshima – Bomb flattened four square miles+ instantly killed 70,000 people. – In month to follow many more would die from radiation sickness Utter Devastation • August 8, 1945: Soviet Union declared war on Japan= invaded Manchuria. • Japanese leaders again did not respond. • August 9, 1945: United States dropped second atomic bomb on city of Nagasaki. – Bomb killed 40,000 people August 10, 1945: Emperor Hirohito intervened and forced government to surrender. August 14, 1945: V-J Day (Victory in Japan)