* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Middle East: A Brief Modern History
Land of Israel wikipedia , lookup
Interfaith marriage in Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on religious pluralism wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Jewish military history wikipedia , lookup
Faisal–Weizmann Agreement wikipedia , lookup
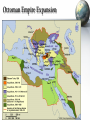
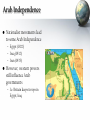
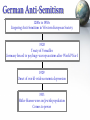
Monday, October 31 1. This Week: Earth’s Population will hit 7 BILLION 2. Notes: The Middle East – Brief History 3. Choose Countries tomorrow… The Middle East: A Brief Modern History World Geography Mr. Thomsen Fall 2011 Main Tenants of Islam • Arabian Peninsula: Known as one of the “Cradles of Civilization – Many of the first civilizations arose in this area • Mesopotamia (between Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) • Muhammad founds religion of Islam ~600AD • Islamic Core Beliefs – Allah is the only God (same God as Jews and Christians) – Muhammad is the final Prophet (Jesus, Abraham also Prophets) – 5 Pillars • Profession of Faith (Shahada) • Prayer 5 times Daily (Salat) • Almsgiving – Charity (Zakat) • Holy Month of Ramadan (Sawm) • Pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) • Divisions of Islam: – – – – Sunni (Largest Segment) and Shia, or Shi’ite Differences in Leadership, some religious practices Sunni-dominated countries: Saudi Arabia, Jordan Shia-dominated countries: Iran, Iraq Main Tenants of Judaism • Oldest organized religion (8,000 BCE) • Main Figures: – Abraham, Isaac, Ishmael – Jesus a prophet, but not “Messiah” • Main text: Torah (Old Testament) • Divisions within Judaism: – Reform – Orthodox – Conservative • Important Holidays: – Yom Kippur, Chanukah, Main Tenants of Christianity • Jesus as “Son of God”, Messiah • Old Testament = Judaism; New Testament = Jesus & Disciples • Main Text: Bible • Catholic Church dominant until 1500s – then Protestant groups (Calvinism, Lutheranism, etc.) The Crusades, Revisited • What were the causes for the Crusades? – Christian Church attempt to conquer Holy Lands; Muslims defend • What were the outcomes of the Crusades? – Christian, Muslim, and Jewish mutual distrust The Ottoman Empire • Centered around modern-day Turkey • Osman I consolidated power in late 13th century • At height, Ottoman Empire encompassed: – Southeastern Europe, Anatolia (Turkey), Iraq, Western Iran, Greater Syria, Egypt, West Arabian Peninsula & Northern Africa Source: MSN Encarta Online Ottoman Empire Expansion European Expansion Britain, France expand colonial territories Extensive colonization in Africa; deals made with Ottomans for trade, resources In Middle East, Arab Nationalism grows In Europe, the Jewish “Zionist” Movement gains strength Jewish Homeland in Palestine Jews had been driven out of Palestine in 200s World War I Effect on Middle East • Ottoman Empire sides with Central Powers (Germany, Austro-Hungarian Empire) • Allied Powers (Britain, France, Italy, USA) devise Picot-Sykes Agreement – Secret plan to divide Middle East after war – Balfour Declaration • Letter from British government declaring support for Zionist Movement Post World War I • Mandate system in Middle East – “Supervisory” control over territories • England: Iraq, Palestine, Transjordan (now Jordan) • France: Syria & Lebanon – Turkey – resists Europe, Ätaturk creates modern secular state Israel.org Ataturk.com Zionism and Arab Resistance Jewish Immigration Into Palestine 66,472 70,000 60,000 37,337 39,195 34,386 50,000 40,000 30,000 8,223 20,000 4,592 10,000 0 19 20 19 25 19 33 19 35 19 39 19 41 • Due to Balfour Declaration, Jewish immigration into Palestine rose dramatically from 1920 to 1935 • Beginning in 1936, Arabs revolted and fought against the immigration • Britain issues “White Paper” of 1939, which limits Jewish immigration into Palestine Arab Independence • Nationalist movements lead to some Arab Independence – Egypt (1922) – Iraq (1932) – Iran (1935) • However, western powers still influence Arab governments – I.e. Britain keeps troops in Egypt, Iraq World War II •Allied Powers – England – France – Russia – United States – Italy (1943-45) •Axis Powers – Germany – Austria – Japan – Italy (1940-1943) German Anti-Semitism 1200s to 1930s Lingering Anti-Semitism in Western European Society 1920 Treaty of Versailles Germany forced to pay huge war reparations after World War I 1929 Onset of world-wide economic depression 1933 Hitler blames woes on Jewish population Comes to power The Holocaust • By 1945, approximately 6 million Jews had been killed across Europe – Nazi Death Camps such as Auchwitz – Stalin purges Jewish Communities in Soviet Union Encarta.com Encarta.com World Reaction • United Nations founded in 1945 • Britain steps up plans to create Jewish Homeland – Jewish settlers begin armed attacks versus British occupation and Arab groups • United States, now a dominate world power, lends support to movement as well • United Nations Partition Plan of 1947 The Creation of Israel • Jewish immigrants approve of UN Partition Plan • Arab population does not approve • Britain turns mandate over to United Nations, withdraws from Palestine on May 14, 1948 • David Ben-Gurion, leader of Jewish settlers, declares the state of Israel on May 15, 1948 • Arabs flee across Jordan River; Egypt, Syria attack new nation Worlgeography.abc-clio.com Discussion . . . • Argument for Israel – Followed UN Partition Plan (I.e. world support) – Historic Homeland, right to exist – Horror of the Holocaust – needed specific place – Defended against Arab invasions • Argument for Arab Palestinians – Under British Occupation – no control in Jewish Immigration – Majority of land in UN Partition plan went to minority Jews – Historic Homeland, – No military support Which do you believe has the stronger claim?