* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BS 14
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Substance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Anorexia nervosa wikipedia , lookup
Controversy surrounding psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
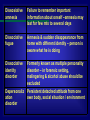
BS 7 OTHER PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Cognitive disorders Personality disorders Dissociative disorders Obesity & eating disorders I Cognitive disorders Involve problems with memory, orientation & level of consciousness These are due to abnormalities in neural chemistry, structure / physiology originating in the brain secondary to systemic illness These pts may show secondary psychiatric symptoms – depression, anxiety, paranoia, hallucinations & delusions The major cognitive disorders are: delirium, dementia & amnestic disorder. Delirium A temporary state of mental confusion and fluctuating consciousness resulting from high fever, intoxication, shock, or other causes. It is characterized by anxiety, disorientation, hallucinations, delusions, and incoherent speech. Delirium tremens: An acute, sometimes fatal episode of delirium that is usually caused by withdrawal or abstinence from alcohol following habitual excessive drinking and that is characterized by sweating, trembling, anxiety, confusion, and hallucinations. Etiology: CNS trauma, infection, high fever, substance abuse / withdrawal . Sometimes hepatic diseases More common in children / in elderly Commonest psychiatric manifestation in hospitals Associated with acute medical illness, autonomic dysfunction & EEG changes- fast wave activity Symptoms worse in the nights (sundowning ) Develop quickly – fluctuating course – alternating with lucid intervals Treatment: is to treat underlying medical problem Dementia Loss of memory & intelligence Cause: Alzheimers is major cause 55%, vascular diseases10%, CNS diseases like Huntington’s & parkinsonism, CNS trauma / infection like HIV More common in elderly 20% over 65 yr have it Not associated with medical illness / autonomic dysfunctions Normal EEG, normal consciousness, no psychotic symptoms Develops slowly – progressive course No effective treatment – pharmaco & supportive therapy Not reversible Amnestic disorder Loss of memory with few cognitive problem Thiamine deficiency due to long term alcohol abuse, temporal lobe trauma, vascular disease & infection (herpes simplex encephalitis) No medical illness / no autonomic dysfunction – normal EEG Normal consciousness, no psychotic symptoms Confubulation (lieing to hide memory loss) Slow & progressive No treatment – pharmaco supportive therapy Alzheimer's disease Most common dementia Gradual loss of memory & intellectual function, lack of judgment, depression & anxiety Later psychosis- progress to coma & death Should be differentiated from psudodementia & normal aging Genetic association: abnormalities in chromosome 21 (trisomy / down synd / mongolism), 1 & 14 (early onset), apolipoprotein E4 gene on chromosome 19 More common in women Decreased activity of Ach, abnormal processing of amyloid precursor protein Brain ventricles enlarged Diffuse atrophy of cortex & flattened sulci Loss of cholinergic neurons, senile amyloid plaques, neuro fibrillary tangles, neuronal loss in hippocampus & cortex Progressive, irreversible, downhill course Treatment: Acetylecholinestrase inhibitors (e.g tacrine - cognex) psychotropic agents used to treat anxiety, depression & psychosis) Dementia of alzhiemer’s type: Brain dysfunction, Severe memory loss, other cognitive problems, decrease in IQ, disruption of normal life Management: Structural environment, cholinestrase inhibitors (tacrine), nursing home Pseudodementia: Depression of mood, few cognitive problems, Moderate memory loss, no decrease in IQ, disruption of normal life Treatment: Antidepressants, ECT, Psychotherapy Normal aging: minor changes in the normal brain, minor forgetfullness, reduction in the ability to learn new things quickly, no decrease in IQ, no disruption of normal life Treatment: no medical intervention, practical & emotional support from physician II Personality disorders Chronic life long rigid unsuitable patterns of relating to others that cause social & occupational problems They do not realize their own problems – no insight – do not have frank psychotic symptoms & do not seek psychiatric help According to DSM IV, PDs are classified in to: Cluster A Cluster B Cluster C Cluster A Hall mark: Avoids social relationship – is peculiar, but not psychotic Genetic / familial association: Psychotic illness may be there among other family members They may be Paranoid – distrustful, suspicious / litigious – blame others for their own problems Schizoid: long term voluntary social withdrawal Schizotypal –peculiar appearance, magical thinking, odd thought patterns behavior Cluster B Hall mark: dramatic., emotional & inconsistent Genetic / familial association: mood disorders & substance abuse Histrionic : theatrical (overly dramatic), extroverted, emotional & sexually provocative life of the party – cannot maintain intimate relationship Narcissistic: self admiration, vanity & pompous – lack respect to others Antisocial: no concern for others, criminal behavior Borderline: impulsive, unstable behavior & mood, self mutilation, mini psychotic episodes suicidal attempt for trivial reasons Cluster C Hall mark: Fearful, anxious Genetic / familial association: anxiety disorders Avoidant: socially withdrawn, inferiority complex, sensitive to rejection Obsessive-compulsive: perfectionist, orderly, inflexible & indecisive Dependent: poor self confidence, allow others to decide Passive-aggressive: procrastinates (lazy, careless), inefficient – shows outward compliance, but inward defiance Treatment Individual / group psychotherapy – if they seek help Drugs are useful to treat symptoms like depression & anxiety III Dissociative disorders Short temporary amnesia / identity due to psychological factors Due to disturbing emotional experience in recent / remote past Classified in to 4 types Dissosiative amnesia Failure to remember important information about onself –amnesia may last for few mts to several days Dissociative fugue Amnesia & sudden disappearance from home with different identity – person is aware what he is doing Dissociative identity disorder Formerly known as multiple personality disorder – in forensic setting, malingering & alcohol abuse should be excluded Depersonaliz ation disorder Persistent detached attitude from one own body, social situation / environment Treatment: Hypnosis, amobarbitol sodium interview & long term psychotherapy IV Obesity & eating disorders Obesity: More than 20% over weight 25% adults are overweight in US Genetic factor + More common in lower socio economic group – associated with increased risk of cardiorespiratory problems, hypertension, diabetes & orthopedic problems Treatment: sensible dieting & exercise is most effective way Eating disorders: Anorexia nervosa & bulimia nervosa More common in women of higher socio economic groups in US than in any other country Anorexia Extreme nervosa weight loss >15% Amenorrhea, hypercholeste rolemia, anemia, lanugos (fine infant hair on body) Refusal to eat despite normal appetite, lack of interest in sex, excessive exercising – was a perfect child in the beginning Hospitalizati on, family therapy, psychoactiv e drugs like periactin Bulemia nervosa Normal body weight, esophageal varices, menstrual disorders Binge eating, vomitting, poor self image, depression & excessive exercise Cognitive & behavior therapy, anti depressants , psychothera py