* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System and Puberty
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
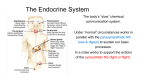
The Endocrine System System of ductless glands that secrete hormones or other substances which produce/activate/excite other cells into action. The Endocrine System is the workhorse for the Nervous System Endocrine System The pituitary gland works from the principle of bio-feedback. Problems with this system stem from either too much (HYPER) or too little (HYPO) production of a hormone. Pituitary Gland The pituitary gland is the master gland of the endocrine system that controls activity of all other glands. Regulates many physiological body responses such as stress, growth, energy levels and reproduction Thyroid Gland Proper thyroid gland functions include • Body metabolism & Energy • Blood calcium levels • Oxygen absorption of tissues • Thyroid also impacts other glands Parathyroid Glands Sole function of these glands is to monitor levels of calcium in the blood steam and bones Adrenal Glands Function Helps the body deal with stress. Hormones Cortisol - (Sugar Level) Adrenaline - (Fight or Flight Response) Disorders Addison’s Disease – hypo-cortisol Cushing’s Disease – hyper-cortisol Pancreas Dual Functions Endocrine System Gland Hormones Insulin – reduces blood sugar Glucagons – increases blood sugar Exocrine (digestive) Pancreatic/digestive juices are released into the small intestines to further breakdown carbs, fats and proteins in chyme Disease/Disorder Diabetes Gonads/Sex Glands Female The ovaries are the female sex glands Female Hormones - Estrogen and Progesterone Sex Cell - Ovum/Ova Male The testicles are the male sex glands Male Hormone – Testosterone Male Sex Cell - Sperm The Process of Puberty 1. 2. 3. The pituitary gland secretes gonadotropic hormones LH & FSH into the bloodstream. LH initiates the sex glands to produce the sex hormonesestrogen (Female Ovaries) and testosterone (Male Testicles). These hormones bring about the secondary sex characteristics and are continual produced throughout an adults life. FSH initiates the production of sex cells in the sex glands/gonads – ovum/ovaries & sperm/testicles. Female Reproductive System Internal Structure Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus/Endometrium Cervix Vagina/Birth Canal External Structure/Vulva Mons Pubis Clitoris Labia – majora/minora Vaginal opening - Hymen Internal Structures Ovaries Female sex gland Produces estrogen and progesterone Store egg follicles Internal Structures Fallopian Tubes Tubes that connect the ovaries with the uterus/womb Where fertilization takes place. Where an ectopic pregnancy can occurs Internal Structures Uterus/Womb Strong muscular organ. Shape: upside down pear Size of a fist Implantation occurs here Lining is called - The Endometrium Internal Structures • • • • • Cervix Narrow opening between the uterus and the vagina Mucous helps with infection control Child birth cannot occur until it dilates to 10 cm. Vagina/Birth Canal Muscular tube about 6 inches in length After baby passes through cervix baby passes through this External Structures (Vulva) • Clitoris – tissue in front of the vaginal opening which produces sexual arousal • Labia – folds of tissue on either side of vaginal opening providing protection from pathogens • Mons Pubis – rounded fatty tissue located directly on top of the pubic bone • Vaginal Opening/Hymen Menstrual Cycle Four Phases of the Menstrual Cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. Menstruation – 5-7 days Pre-Ovulation – lining thickens Ovulation – 14 days prior to the next cycle Post-Ovulation – unfertilized egg exits and the lining starts to die Male Reproductive System Functions of the System 1. To produce a sex cell – sperm 2. To produce the male hormone - testosterone Pathway of Sperm STEVSPCUP Scrotum Sac of skin used to hold the testicles. It’s purpose is to keep the testicles cooler for proper sperm production Testicles Produce Testosterone & Sperm Seminiferous Tubes This is where the sperm are produced within the testicle Epididymis Place where mature sperm wait Vas Deferens Two tubes that leave each testicle/epididymis And bring sperm to the seminal vesicles Seminal Vesicles The seminal vesicles add a fructose fluid to help nourish the sperm Prostate Gland Seminal gland that provides a basic solution to semen, which helps to neutralize the acidity of the vagina, which in turn protects sperm. Acidity and Heat kill sperm Cowper’s Glands Seminal gland that secretes a lubricant that cleanses the urethra prior to ejaculation. Again, Acidity kills sperm Urethra/Penis Urethra is the tube by which either urine or semen are released from the male body Reproductive Health Concerns Male • • • • • Testicular Cancer Prostate Cancer/Enlarged Inguinal Hernia Sterility STI’s – Sexually Transmitted Infections Female • Menstrual Cramps/PMS • TSS – Toxic Shock Syndrome • Cancers – Breast, Cervical, Uterine, & Ovarian • Amenorrhea/Dysmenorrhea • Ovarian Cysts • Sterility • STI’s – Sexually Transmitted Infections