* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drugs used in hypothyroidism
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
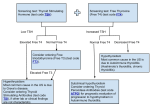
DRUGS USED IN HYPOTHYROIDISM by Dr.Abdul latif Mahesar Objectives At the end of the lecture the students will be able to : Classify common drugs used for treatment of hypothyroidism Details the drugs regarding , mechanism of action , pharmacological effects , clinical uses & side effects Recognize treatment of special cases of hypothyroidism . 7 Hypothyroidism Thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones CAUSES Congenital ( cretinism , dwarfism) Autoimmune disorder ( Hashimotos thyroiditis) Irradiation Surgical removal of thyroid gland Thyroid carcinoma 8 CAUSES Congenital which results to ( cretinism , dwarfism) Autoimmune disorder ( Hashimotos thyroiditis) Irradiation Of the gland Surgical removal of thyroid gland Thyroid carcinoma 9 HYPOTHYROIDISM People who are most at risk include those over age 50 & mainly in females Diagnosed by low plasma levels of T3 & T4 and high levels of TSH. 10 Manifestations of Hypothyroidism Fatigue and lack of energy weight gain Dry and cold skin Dry hairs Constipation Slowed thinking Bradycardia Heavy menses 11 12 13 14 15 16 Treatment Replacement therapy with synthetic thyroid hormone preparations 17 Thyroid preparations LEVOTHYROXINE: (T4) A synthetic form of the thyroxine (T4) , is the drug of choice for replacement therapy . Stable and has a long half life ( 7 days) . Administered once daily. Oral preparations available from 0.025 to 0.3 mg tablets Absorption is increased when hormone is given on empty stomach Parentral preparation 200-500µg . 18 In old patients and in patients with cardiac problems , treatment is started with reduced dosage. Normal thyroid levels are restored within 2-3 weeks. levothyroxine(T4) is given in a dose of 12.5 – 25 µg/day for two weeks and then increasing it after every two weeks. 19 Clinical uses Hypothyroidism, regardless of etiology including : Congenital Autoimmune thyroiditis ( Hashimoto thyroiditis) Pregnancy Thyroid carcinoma 20 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF OVER DOSES CHILDREN : Restlessness, insomnia, accelerated bone maturation. ADULTS : Tachycardia, palpitation, cardiac arrhythmias, tremor , restlessness , heat intolerance , headache, muscle pain Change in appetite, diarrhea, weight loss 21 Adverse effects of under-dosing Sluggishness Mental dullness Feeling cold Muscle cramps 22 Liothyronine(T3) More potent (3-4 times) and rapid action than levothyroxine but has a short half life is not recommended for routine replacement therapy, it requires multiple daily doses. It should be avoided in cardiac patients. It is best used for short –term suppression of TSH. Oral preparation available are 5-50µg tablets Parentral use 10µg/ml 23 MYXEDEMA COMA: Life –threatening hypothyroidism The treatment of choice is loading dose of levothyroxine intravenously 300-400µg initially followed by 50µg daily. I.V liothyronine for rapid response but it may provoke cardiotoxicity I.V hydrocortisone may be used in case of adrenal and pituitary insufficiency. 24 HYPOTHROIDSM AND PREGNANCY. In pregnant hypothyroid patient 20-30 % increase in thyroxine is required because of elevated maternal TBG(thyroxine binding globulin) induced by estrogen and because of early development of fetal brain which depends on maternal thyroxine 25 Combination drugs LIOTRIX is a combination of synthetic T4 and T3 in a ratio of 4:1 that attempt to mimic the natural hormone secretions Major limitation to this product are high cost And lack of therapeutic rationale,because about 35% of T4 is peripherally converted to T3. 26