* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy - Science Class Rocks!
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
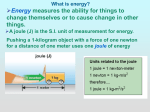
Energy The ability to do work Work is done when a force moves an object over a distance Potential Energy Stored energy an object has due to its position. – Ex: A rock on top of a cliff has potential energy because of its position above ground level – Ex: A lump of coal contains potential energy in its chemical bonds, causing fire when exposed to a flame Kinetic Energy Energy of motion – Ex: A rock falling off a cliff – The heat given off by a burning lump of coal – The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has Energy Potential energy may be changed into kinetic energy when an object begins to move – Ex: Water held back by a dam has potential energy but no kinetic energy. Releasing the water and letting it flow changes its potential energy into kinetic energy. Energy Kinetic energy may also be changed into potential energy – Ex: When a ball is thrown straight up in the air, its kinetic energy changes into potential energy as the ball rises higher above the ground. At the highest point, the ball is motionless and has only potential energy. As the ball falls back to the ground, the potential energy changes back into kinetic energy. Forms of Energy There are 6 forms of energy – Mechanical – Chemical – Nuclear – Heat (thermal) – Electric – Light (radiant, electromagnetic) Mechanical Energy Energy with which moving objects perform work – Ex: hammer striking a nail, a jack lifting a car, pedals turning the wheel of a bike – Sound is a type of mechanical energy Chemical energy Energy stored in certain substances because of the make up of their chemical bonds – Ex: coal, oil, natural gas, food Nuclear energy Energy stored within the nucleus of an atom – Joining small nuclei together or splitting large nuclei apart Heat Energy Produced by the molecular motion of matter – Ex: rubbing your hands together, cellular respiration, burning fuel oil in a home Electric Energy Produced by the flow of electrons through a conductor, such as a wire. – Ex: computers, light bulbs, washing machines all are operated with electric energy. – A generator produces electric energy. Light Energy Form of radiant energy that moves in waves – Ex: magnifying glass burns a hole in a leaf or using a laser beam to burn a hole in a steel plate. Conservation of Energy The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Energy can easily be transformed from one type of energy into another type of energy Conservation of Matter The law of conservation of matter states that matter can neither be created or destroyed. Energy and matter are interchangeable. The total amount of energy and matter in the universe is constant and each can be converted into the other. – Ex: The sun converts large amounts of matter into light and heat energy Energy Transformations Ex: when you take a bus to school, chemical energy in the gas is changed into mechanical energy that turns the wheels of the bus Ex: The bell rings between classes, electric energy is transformed into sound energy Ex: At night when you are reading, electric energy is changed into light energy Unusable Energy During energy transformation heat energy is produced that is not usable. – A cars motor changes chemical energy in gas into mechanical energy to move the car. The motor eventually becomes hot due to the burning of fuel and friction of the motors moving parts rubbing against one another Unusable Energy Ex: a vacuum cleaner contains a motor that transforms electric energy into mechanical energy. Run a vacuum cleaner for a few minutes and it gets warm. The electric energy entering the motor produced mechanical energy to operate the appliance and an unusable amount of heat energy.