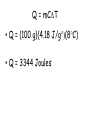* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Compressed air energy storage wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Micro combined heat and power wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
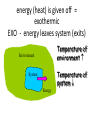
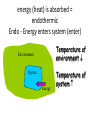
Do Now: TOPIC: ENERGY All physical & chemical changes are accompanied by change in energy The chemistry of energy changes is known as Thermochemistry! Stability and Energy • If energy is high, stability is low • If energy is low, stability is high Energy: Ability to do Work The SI unit for an energy measurement is called the Joule (J) EXAMPLE: 1 Joule = amount of energy required to lift a golf ball 1 meter Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy is neither created nor destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical change, rather it can be converted from one form to another - potential to kinetic - radiant to electric - electric to heat - chemical to kinetic - chemical to electrical Energy before = Energy after Energy Non-mechanical – too small to see Mechanical – large enough to see Kinetic Potential Chemical (Not a complete list!) Heat Light Electrical Nuclear Kinetic Energy (KE) – energy of motion • KE = ½ x Mass x Velocity2 = ½ mV2 • KE depends on how heavy and how fast Kinetic Molecular Theory: the atoms and molecules making up substances are in constant motion Potential Energy (PE): energy of position; stored energy of matter EXAMPLES stapler Rubberband • When Potential energy is released from matter it becomes kinetic energy Energy in Chemistry = chemical energy heat energy Chemical Energy • energy stored in bonds; it is released as the result of a chemical reaction Heat Energy Heat: energy that is in the process of flowing from warmer object to a cooler object Symbol for heat energy = Q or q The amount of heat required to raise the temp. of 1 gram of water 10C = a calorie Other Energy Units: calorie, Calorie, BTU’s 1 calorie = 4.18 Joules 1 Calorie = 1000 calories = 1 kilocalorie NOTE: When your body breaks down food, these reactions give off heat – which is measured in calories (That’s why your food is labelled in calories) energy (heat) is given off = exothermic EXO - energy leaves system (exits) Temperature of environment Environment Temperature of system System Energy energy (heat) is absorbed = endothermic Endo - Energy enters system (enter) Temperature of environment Environment System Energy Temperature of system Energy of Universe is conserved Universe EnvironmentEnvironment System Energy Energy can move between the system and the environment Calorimeter: an insulated devise used for measuring the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical or physical change “universe” is contained in Styrofoam cup “environment” is water**** “system” is whatever put in water Energy lost = Energy gained Difficult to monitor “system” Easy to monitor “environment” (water) Energy lost/gained by environment = Energy gained/lost by system The amount of heat transferred depends on 3 things Temperature change Mass of substance Specific Heat of substance Specific Heat • The amount of heat required to raise the temp of any given substance by 10C • Symbol = c • Specific heat = a physical constant • unique for each pure substance Found in Table B Calculating Heat Transferred Simple system: •pure substance in single phase •calculate heat gained or lost using: Q = mCT Q = amount of heat transferred m = mass of substance C = specific heat capacity of the substance. T = temperature change = Tfinal – Tinitial Calorimetry 10 grams of NaOH is dissolved in 100 g of water & the temperature of the water increases from 22C to 30C • was dissolving process endothermic or exothermic • how do you know? Exothermic – temperature of environment ↑ Dissolving • What’s happening when NaOH dissolves? Add H2O molecules close together, not interacting molecules pulled apart & interacting with H2O Calorimetry – Calculate energy released by NaOH as it dissolves in water Energy lost by NaOH = Energy gained by water Easier to calculate from H2O perspective Q = mCT Q = energy (joules) M = mass (grams) C = specific heat capacity (Table B) T = temperature change = Tf - Ti Calorimetry & Q = mCT temperature of water increased from 22C to 30C 30C -22C = 8C = T What mass to use? Well, temp change was for water, so want mass of water m = 100 g Same goes for specific heat capacity; calculate heat absorbed by water cH 0 = 4.18J/g 2 Q = mCT • Q = (100 g)(4.18 J/g)(8C) • Q = 3344 Joules