* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 05 - pectoral region
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
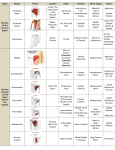
BREASTS They are modified sweat glands which are capable to secrete milk. They are present in both sexes. (A) Males and Immature Females: The nipples are small. BREASTS They are surrounded by a small colored area (areola). The breast tissue is formed of little duct system embedded in connective tissue that is restricted to the margin of the areola. BREASTS (B) At puberty in (Females): The mammary glands increase in size mainly by the deposition of fat and by the influence of the ovarian hormones. It protrudes forward from a circular base. POSITION Most of the gland lies in the superficial fascia. Its base extends from : A. 2nd -6th ribs. B. Lateral margin of the sternum to the midaxillary line. BREASTS Axillary Tail: It is the part of the gland in the deep fascia. It extends upward and laterally to enter the axilla. STRUCTURE (1) lobes : It is formed of (15-20) lobes radiating from the nipple. The lobes are separated by fibrous septa. In the upper part, they are well developed (suspensory ligaments) binding the skin to the deep fascia. STRUCTURE 2. Ducts : A main duct arises from each lobe. It opens separately on the summit of the nipple. Each duct has a dilatation (ampulla) prior to its termination. STRUCTURE Areolar glands: They produce tiny tubercles on the areola. Retromammary space: It is a loose connective tissue separating the breasts from the underlying deep fascia. BLOOD SUPPLY Arteries : 1. Internal thoracic & intercostal : perforating branches. 2. Axillary : lateral thoracic & thoracoacromial. BLOOD SUPPLY Veins : Correspond to the arteries. LYMPH DRAINAGE It is of considerable clinical importance because of the frequent development of cancer of the gland and the dissemination of the malignant cells along the lymph vessels. BREAST QUADRANTS Regarding the lymph drainage, the breast (mammary gland) is divided into four quadrants: Upper medial. Lower medial. Upper lateral. Lower lateral. LYMPH DRAINAGE 1.Lateral quadrants: To anterior axillary (pectoral) group of lymph nodes. 2.Medial quadrants: To internal thoracic lymph nodes along the internal thoracic artery within the thoracic cavity. LYMPH DRAINAGE 3. To the opposite breast. 4. To the anterior abdominal wall. 5. To the posterior intercostal nodes along the posterior intercostal arteries. CANCER BREAST Cancer occurring in the lateral quadrants of the breast spreads to the axillary lymph nodes which can be removed surgically. 60% of carcinomas of the breast occur in the upper lateral quadrant. CANCER BREAST Thoracic metastases (from carcinomas) of the medial quadrants are difficult to treat. PECTORAL MUSCLES They are four muscles that move the shoulder girdle and attach it to the thoracic wall. (1) PECTORALIS MAJOR It triangular in shape. It covers the upper chest. Its lower border forms the anterior wall of the axilla. Superiorly it is separated from deltoid muscle along the clavicle by the deltopectoral triangle. (1) PECTORALIS MAJOR Origin It has two heads : Clavicular : from the medial half of the clavicle. Sternocostal: Anterior sternum. Upper six costal cartilages. External oblique aponeurosis. (1) PECTORALIS MAJOR Insertion : Lateral lip of the bicipital groove of the humerus. Nerve supply : Medial and lateral pectoral nerves. Action : Adduction and medial rotation of humerus. Flexion of arm (clavicular head). (2) PECTORALIS MINOR It is a thin triangular muscle that is covered by pectoralis major. Origin : Anterior surfaces of 3rd -5th ribs. Insertion : Coracoid process. (2) PECTORALIS MINOR Nerve supply : Medial pectoral nerve. Action : Pulls the shoulder downwards and forwards. It elevates the ribs (acessory muscle of respiration) when the scapula is fixed. (3) SUBCLAVIUS Origin : 1st costal cartilage. Insertion : Inferior surface of the clavicle. Nerve supply : A branch from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. Action : Depresses the clavicle. CLAVIPECTORAL FASCIA It is a strong sheet of fascia. Attachment : Superiorly : It is attached to the clavicle and splits to enclose the subclavius muscle. Inferiorly : It encloses the pectoralis minor and continues as the suspensory ligament of the axilla and joins the CLAVIPECTORAL FASCIA Contents : 1.Nerve : lateral pectoral. 2.Artery : thoracoacromial. 3. Vein : cephalic. 4. Lymph nodes. CLAVICLE It is a long bone that lies horizontally across the root of the neck. It is subcutaneous throughout its length. CLAVICLE Articulations : Medially : Sternum. 1st costal cartilage. Laterally : Scapula (acromion). CLAVICLE Functions : 1.Holds the arm away from the trunk. 2. Transmits forces from the upper limb to the axial skeleton. 3. Gives attachment to muscles. CLAVICLE Shape : Its medial 2/3 are convex forward. Its lateral 1/3 is concave forward.