* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download consist of receptors and accessory organs. Skin, visual organ
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
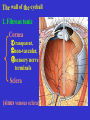
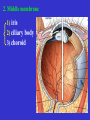
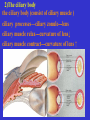
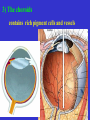
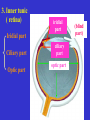
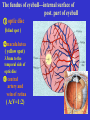
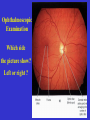
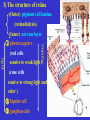
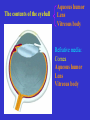
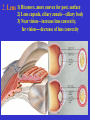
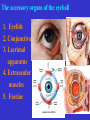
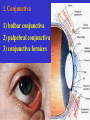
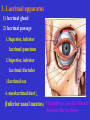
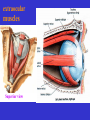
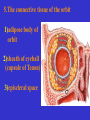
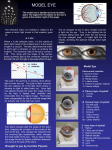
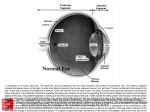
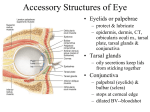
The sensory organs 1.General description 2.Visual organ 广西医科大学解剖学教研室 劳明 制作 Copyright @2003 lao ming All rights reserved General description Concept of receptors: ( are a structure) receive the stimulation from the external or internal environment of body, and convert it into nerve impulse. Classify: Exteroceptors: in skin,the mucous membrane of the nasal and oral cavity,visual and auditory organs Enteroceptors: in the wall of the viscera, the heart ,blood vessel Proprioceptors:in muscles,tendons,joint and ligaments Sensory organs: ~consist of receptors and accessory organs. Skin, visual organ, vestibulocochlear organ The visual Organs (eyes) 1.Composition 1) eyeball 2) accessory organs 2.Function to receive light , color. The eyeball The wall 1.Fibrous tunic cornea sclera 2.Middle coat iris ciliary body choroids 3.Inner tunic iris part blind part (retina ) ciliary part optic part The contents Aqueous humor Lens Vitreous body The wall of the eyeball 1. Fibrous tunic Cornea ①transparent, ②non-vascular, ③sensory nerve terminals Sclera (sinus venous sclera) 2. Middle membrane 1) iris 2) ciliary body 3) choroid 1) The iris pupil sphincter pupillae dilator pupilae 2)The ciliary body the ciliary body (consist of ciliary muscle ) ciliary processes—ciliary zonule---lens ciliary muscle relax---curvature of lens↓ ciliary muscle contract---curvature of lens ↑ 3) The choroids contains rich pigment cells and vessels 3. Inner tunic ( retina) iridial part Iridial part Ciliary part Optic part ciliary part optic part (blind part) The fundus of eyeball—internal surface of post. part of eyeball ① optic disc (blind spot ) ②macula lutea ( yellow spot) 3.5mm to the temporal side of optic disc ③ central artery and vein of retina ( A:V=1:2) Ophthalmoscopic Examination Which side the picture show? Left or right ? 3) The structure of retina (Outer) pigment cell lamina (retinodialysis) (rod cells light impulse (Inner) nervous layer ① photoreceptors sensive to weak light) (cone cells sensive to strong light and color ) ② bipolar cell ③ ganglion cells The contents of the eyeball Aqueous humor Lens Vitreous body Refrative media: Cornea Aqueous humor Lens Vitreous body 1.Aqueous humor form: Ciliary body Route: Post. Chamber ↓ Pupil ↓ Ant.chamber ↓ Iridocorneal angle ↓ Sinus venous sclera Function: supply nutrient, Maintain normal intraocular pressure 2. Lens 1) Biconvex ,more convex for post. surface 2) Lens capsule, ciliary zonule—ciliary body 3) Near vision—increase lens convexity, far vision----decrease of lens convexity 3.Vitreous body 1)Jelly-like substance 2)supporting the retina 3.Clinically practice / Cornea--- sensitive to pain stimulating, / Aqueous humor---if circulation blocked, pressure of eyeball increase, glaucoma / Lens---if became opaque, senile cataract / Vitreous body---If supporting role weakened, retinodialysis The accessory organs of the eyeball 1. Eyelids 2. Conjunctiva 3. Lacrimal apparatus 4. Extraocular muscles 5. Fasciae 1. The eyelids Morphology upper eyelids lower eyelids palpebral fissure Medial angle Lateral angle Lateral angle Medial angle Structures of the eyelid 1) skin--thin 2) subcutaneous loose, no fat 3) muscles orbicularis oculi levator M Mǚller muscle 4) tarsus 5) Conjunctiva 2. Conjunctiva 1) bulbar conjunctiva 2) palpebral conjunctiva 3) conjunctiva fornices 3. Lacrimal apparatus 1) lacrimal gland 2) lacrimal passage 1.Superior, inferior lacrimal punctum 2.Superior, inferior lacrimal ductules 3.lacrimal sac 4. nasolacrimal duct ↓ (Inferior nasal meatus) The pathway, you feel bitter in pharynx after eyedrops 4. Extraocular muscles ( the name and the function of the muscles ) Sup. Rectus--superomedially Inf. Rectus--inferomedially Med. Rectus--medially Lat. Rectus--laterally Sup. Oblique--inferolaterally Inf. Oblique—superolaterally Levator palpebral superior— elevate the superior eyelid extraocular muscles Superior view 5.The connective tissue of the orbit 1)adipose body of orbit 2)sheath of eyeball (capsule of Tenon) 3)episcleral space ▲strabismus(cross-eye) medially ▲conjunctivitis(red eye) ▲closed eye”—orbicularis oculi “open eye”---levator palpebrae superioris (only upper eyelid move upper) voluntary ▲pupil diminish--- sphincter pupillae pulpil dilate----dilator puillae (unvoluntary, adjusted by light) ▲tuyan (one of the symptons of hyperthyroidism)