* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nasal cavity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
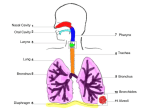
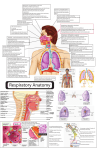
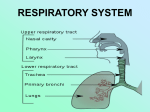
Respiratory system 广西医科大学人体解剖教研室 The respiratory system 1. respiratory tract 2. lung/pulmo nose pharynx upper respiratory tract larynx trachea principal bronchi branches of principal bronchi lower respiratory tract Section 1 nose The Nose The external External nose Root of nose Back of nose Apex of nose Alae nasi Nares Left nasal cavity Nasal cavity Nasal root Nasal back Apex of nose Nasal Alae septumnasi Reft Rightnasal nasalcavity cavity Paranasal cavity Cartilages Frontal sinuses Maxillary sinuses Ethmoidal sinuses Sphenoidal sinuses Nares Nasal cavityplate Olfactory region Perpendicular of ethmoid bonenasal vestibule lined by skin The part Nasal bone proper nasal cavity lined by mucosa. The mucosa has two region: olfectory Septal cartilage region and respiratory region. The medial wall: Nasal septum Vomer Respiratory region The lateral wall: Superior, middle ,inferior nasal concha Superior, middle ,inferior nasal meatus The paranasal sinuses are some air spacesSphenoethmoidal lying in the bone recess around Frontal the nasalsinus cavity. Frontal sinus The place of the oppenings of paranasal sinuses. The place of the openings of paranasal sinuses. frontal sinus maxillary sinus middle nasal meatus anterior group ethmoidal sinus middle group posterior group sphenoidal sinus superior nasal meatus sphenoethmoidal recess Section 2 The larynx 1. The position and relation 2. The composition Laryngeal cartilages Laryngeal joints larynx Laryngeal muscles The sagittal section of the skull and neck Laryngeal cavity 1. Laryngeal cartilages thyroid cartilage 1 cricoid cartilage 1 epiglottic cartilage 1 arytenoid cartilage 2 2. The laryngeal joints quadrangular membrane vestibular ligament Thyrohyoid membrane Quadrangular membrane Conus elasticus Cricotracheal membrane Cricothyroid joint Cricoarytenoid joint Epiglottic cartilage Hyoid bone Thyrohyoid membrane Thyroid cartilage Arytenoid cartilage Cricoarytenoid joint Cricothyroid joint Conus elasticus Lamina of cricoid cartilage Conus elasticus extend upward from the cricoid cartilage to Tracheal cartilage Vocal ligament the arytenoid cartilages and the posterior surfaceConus of elasticus the Vocal ligament thyroid cartilage. Annular lig. Vocal ligament is the superior of the conus elasticus. Thethe laryngeal cavity and joint Vocal fold is the mucosa covering vocal ligament. 3. The muscle of larynx Posterior cricoarytenoid Crinothyroid Transverse arytenoid Thyroarytenoid Transverse arytenoid Oblique arytenoid Thyroarytenoid Lateral cricoarytenoid Posterior cricoarytenoid Posterior cricoarytenoid can open the glottis. cricothyroid Oblique arytenoid Transverse arytenoid and oblique arytenoid close the glottis. Posterior cricoarytenoid and crinothyroid can tense and lenghten the vocal fold. Thyroarytenoid can relax and shorten the vocal fold. 4. The laryngeal cavity Epiglottis Laryngeal vestibule Aperture of larynx The inlet: aperture larynx Aryepiglottic fold Rima vestibuli The vestibular folds Interarytenoid notch The mucous fold Vestibular fold Oblique arytenoid VentricleThe of larynx vocal fold Vocal fold Transverse arytenoid Fissure of glottis Posterior cricoarytenoid Infraglottic cavity Cricothyroid joint The laryngeal vestibuleThyroid cartilage The parts The intermedial cavity of larynx Tracheal cavity The infraglottic cavity Cricoid cartilage Tracheal cartilage The fissure glottis Conus elasticus The fissure glottis Section Larynx 3 The trachea and bronchi 1.Trachea The trachea The composition: The tracheal cartilages, smooth muscle, connective tissue and epithelium. R principal bronchus principal bronchus The position of theL bifurcation of trachea: the sternal angle or the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra The carina of trachea: 2. The bronchi Bifurcation Principal bronchi, lobar bronchi, segmental bronchi, The carina of trachea bronchioles and terminal bronchioles. Section Larynx 3 The trachea and bronchi 1. TheTrachea trachea The composition: Right principal bronchus Bifurcation of tracea The position of the bifurcation of trachea: Left principal bronchus carina of trachea: Superior lobar bronchus Middle lobar bronchi bronchus 2. The Principal bronchi bronchioles lobar bronchi lobar bronchus segmental Sup. bronchi terminal bronchioles. Inf. lobar bronchus The lobar differences Inferior bronchus of right and left principal bronchus: shorter, wider, more vertical Section 4 lung/pulmo Larynx Apex of lung Apex of lung trachea lobar bronchus Superior Hilum lung Rightofprincipal bronchus Oblique fissure Pulmonary a. Apex 1. The external features Apex Pulmonary a.of lung Hilum Superior lobe Apex left principal bronchus Superior pulmonary v. Posterior border Superior lobe Costal surface Superior lobe Base or Anterior border Posteriorfissure border Horizontal Superior pulmonary v. diaphragmatic suface Horizontal fissure Two surface: Oblique fissure Oblique fissure v. Right inf. pulmonary costal and medial surface cardiac notch Superior lobe Right inf. pulmonary v. oblique fissure Cardiac impression inferior lobe Cardiac notch inferior lobe Oblique fissure Three border: Middle Middle lobelobe inferior lobe Inferior base of lobe lung Hilum of lung base of lung Root of lung: medial surface The bronchi, pulmonary artery and veins, nerves, Inferior border bronchial vessels, lymphatics and lyph nodes Medial surface of right left lung lung Larynx 2. The lobe trachea Apex oblique Superior lobe Costal surface fissure Superior lobe Right lung Anterior border Horizontal fissure Oblique fissure horizontal fissure Left lung Superior lobe cardiac notch Middle lobe oblique fissure Inferior lobe inferior lobe Middle lobe Inferior lobeoblique Apex fissure Superior lobe medial surface Inferior lobeborder Inferior 3. The situation of lungs 4. The Thebronchopulmonary bronchopulmonary segments 4. segments Section 5 The pleura Costal pleura Diaphrgmatic pleura Parietal pleura 1. The parts Mediastinal pleura Cupula of pleura Visceral pleura 2. The pleural cavity and thoracic cavity 3. The pleural recess:costodiaphragmatic recess 4. The projection of inferior margins of lungs and pleura The inferior margins of lungs and pleura : midclavicular line midaxillary line scapular line inferior margin of lungs 6th rib 8th rib 10th rib inferior margin of pleura 8th rib 10th rib 11th rib Section 6 The midiastinum Superior mediatinum Sernal angle The subsection: Anterior mediastinum Superior mediastinum Posterior mediatinum Middle mediastinum Heart anterior mediastinum Diaphragm Inferior mediastinum middle mediastinum posterior mediastinum Sum up the main point of respiratory system 1. The respiratory system includes respiratory tract and pulmo. The upper respiratory tract includes the nose, pharynx, larynx; and the trachea, principal bronchi with their branches belong to the lower tract. The primary function of this system is to supply the body with oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide. 2. The nose includes the external nose, nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Each nasal cavity is divided into nasal vestibule and proper nasal cavity. The nasal vestibule is lined by skin, and the proper nasal cavity by mucous membrane. According to the function ,the mucous membrane is divided into two parts: olfectory and respiratory region. The paranasal sinuses includes the frontal, maxillary, ethmoidal and sphenoidal sinus. They all communicate with nasal cavity. The frontal, maxillary, the anterior and middle ethmoidal sinuses open into the middle nasal meatuses; and the posterior ethmoidal sinus into the upper nasal meatus; and the sphenoidal sinus into the sphenoethmoidal recess. The positions of the opening the maxillary sinuses are higher than its floor. 3. The larynx consist of a framework of cartilages that connected together by ligament, membrane and joint. There are five cartilages: one thyroid, one cricoid, one epigrottic, and a pair arytenoid cartilage. The laryngeal cavity may be divided into three parts by the vestibular folds and the vocal folds: the laryngeal vestibule, the intermedial cavity of larynx and the infraglottic cavity. Here, there are several names we must memorize: The conus elasticus: the membrane between the upper of the cricoid cartilage, the posterior of the thyroid cartilage, and arytenoid cartilage. The vocal ligament: the upper of the conus elasticus between the thyroid cartilage and the vocal projection of the arytenoid cartilage. The vocal fold: the mucosa covering the surface of the vocal ligament and the arytenoid cartilage. The fissure of glottis: the between the right and left vocal folds. The glottis: consists of the vocal folds and the fissure of glottis. 4. Trachea and bronchi are all composed of C-shaped ring of cartilages, smooth muscle and connective tissue. The lower end of the trachea is called the bifurcation. There is a carina of trachea on the inner surface of the bifurcation. The carina of trachea is the marker to guide the bronchoscope to the left or right bronchus. The right principal bronchus is shorter, wider, and more vertical in position than the left. 5. The lung/ pulmo is respiratory organ. The lung/ pulmo is conical and has an apex, a base, two surfaces and three borders. The apex of the lung extends to about 2~3 cm above the level of the medial one-third of the clavicle. The left pulmo is divided into superior and inferior lobes by oblique fissure; and the right pulmo is divided into superior, middle and inferior lobes by oblique and horizontal fissures The branches of the bronchi in the lungs: the principal bronchus lobar bronchi segmental bronchi bronchioles the terminal bronchioles. A bronchopulmonary segment: a unit of lung tissue, where the branches / ramifications of a segmental bronchus distributes to. There are 10 segments on each side lung. 6. The pleura are serous membrane, divided into the parietal and visceral pleura. The parietal pleura are divided into four parts: the costal pleura, the diaphragmatic pleura, the medial stinal pleura and the cupula of pleura. The pleural cavity is the potential space between the parietal pleura and visceral pleura. The right and left pleural cavity is separated from each other by mediastinum. The costodiaphragmatic recess is in the place of the reflection of the diaphragmatic and costal pleura. When the body is standing or sitting, the costodiaphragmatic recess is the lowest place of the pleural cavity. So if the pleural cavity has liquid, for example the blood or the pus, the liquid always fills in this recess first. The projection of the inferior margins of the lungs and the pleura, (on the midclavicular line, midaxillary line, and scapular line) are respectively in: The lung: 6th, 8th, 10th rib; the pleura: 8th, 10th, 11th rib 7. The mediastinum is divided into 4 regions by the level of sternal angle and the pericardium: the superior mediastinum, the anterior mediastinum, the middle mediastinum, and the posterior mediastinum.