* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 33-the walls & joint..
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
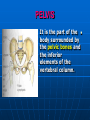
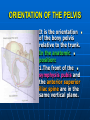
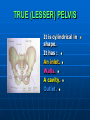
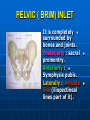
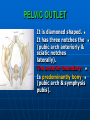
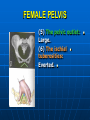
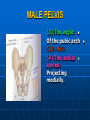
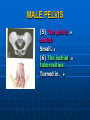
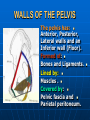
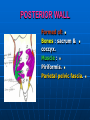
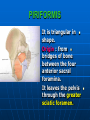
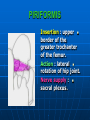
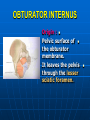
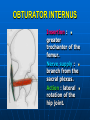
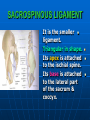
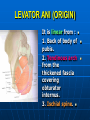
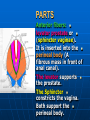
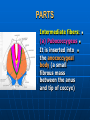
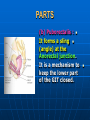
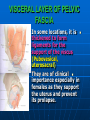
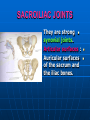
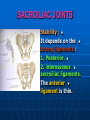
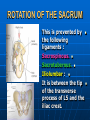
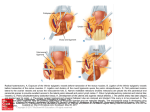
PELVIS It is the part of the body surrounded by the pelvic bones and the inferior elements of the vertebral column. FUNCTIONS OF BONY PELVIS 1.Transmittion of body weight from the vertebral column to the femora. 2. Protection and support of the pelvic viscera. 3. Gives attachment to the muscles of the lower limb and trunk. ORIENTATION OF THE PELVIS It is the orientation of the bony pelvis relative to the trunk. In the anatomic position: 1.The front of the symphysis pubis and the anterior superior iliac spine are in the same vertical plane. ORIENTATION OF THE PELVIS 2. The pelvic surface of the symphysis pubis faces upward and backward. 3. The anterior surface of the sacrum is directed forward and downward. SUBDIVISIONS OF THE PELVIS It is divided into two parts by the pelvic brim (pelvic inlet) : Upper large part (false) pelvis : above the brim. Lower (true) pelvis. FALSE (GREATER) PELVIS It is of little clinical importance. It is considered part of the abdominal cavity. It is bounded by : Posteriorly : lumbar vertebrae. Laterally : iliac fossae and iliacus muscles. Anteriorly : lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. TRUE (LESSER) PELVIS It is cylindrical in shape. It has : An inlet. Walls. A cavity. Outlet. PELVIC ( BRIM) INLET It is the opening between the abdominal and the pelvic cavities, through which structures can pass between them. It is opened. PELVIC ( BRIM) INLET It is completely surrounded by bones and joints. Posteriorly : sacral promontry. Anteriorly : Symphysis pubis. Laterally : Arcuate line (iliopectineal lines part of it). PELVIC OUTLET It is closed by the pelvic floor. It separates the pelvic cavity above from the perineum below. The terminal parts of the urinary & gastrointestinal tracts and the vagina pass through it. PELVIC OUTLET It is diamoned shaped. It has three notches the (pubic arch anteriorly & sciatic notches laterally). The anterior boundary: Is predominantly bony (pubic arch & symphysis pubis). PELVIC OUTLET Posterior boundary: Is predominantly ligamentous: (sacrotuberous ligaments & (coccyx ). Lateral boundary: Elements of the pubic arch. FEMALE PELVIS It should have the following criteria to allow the passage of a baby during labour. (1) Pelvic inlet : Transversly oval (less distinct promontry and broader alae). FEMALE PELVIS (2) The angle: Between the two rami of the pubic arch : (80-85). (3) The ischial spines: Do not project so far medially. (4) The false pelvis: Is shallow. FEMALE PELVIS (5) The pelvic outlet: Large. (6) The ischial tuberosities: Everted. MALE PELVIS (1) Pelvic inlet : Heart shaped. (2) The false pelvis: Deep. MALE PELVIS (3) The angle: Of the pubic arch (50 – 60). (4) The ischial spines: Projecting medially. MALE PELVIS (5) The pelvic outlet: Small. (6) The ischial tuberosities: Turned in. WALLS OF THE PELVIS The pelvis has: Anterior, Posterior, Lateral walls and an Inferior wall (Floor). Formed of: Bones and Ligaments. Lined by: Muscles . Covered by: Pelvic fascia and Parietal peritoneum. ANTERIOR WALL It is the shallowest wall. It is formed of (bones) : The posterior surfaces of the bodies of pubic bones. pubic rami. symphysis pubis. POSTERIOR WALL Formed of: Bones : sacrum & coccyx. Muscle : Piriformis. Parietal pelvic fascia. PIRIFORMIS It is triangular in shape. Origin : from bridges of bone between the four anterior sacral foramina. It leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. PIRIFORMIS Insertion : upper border of the greater trochanter of the femur. Action : lateral rotation of hip joint. Nerve supply : sacral plexus. LATERAL WALL It is formed of : Bones : hip bones below the pelvic inlet. Ligaments : sacrotuberous and sacrospinous. Muscle : obturator internus and its covering membrane. OBTURATOR MEMBRANE It is a fibrous sheet. It almost completely covers the obturator foramen. It leaves the obturator canal for the passage of the obturator nerve and vessels. OBTURATOR INTERNUS Origin : Pelvic surface of the obturator membrane. It leaves the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen. OBTURATOR INTERNUS Insertion : greater trochanter of the femur. Nerve supply : branch from the sacral plexus. Action : lateral rotation of the hip joint. SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT It is strong. Triangular in shape. It has an extensive attachment between the lateral part of the sacrum & coccyx, the posterior inferior iliac spine and the ischial tuberosity. SACROSPINOUS LIGAMENT It is the smaller ligament. Triangular in shape. Its apex is attached to the ischial spine. Its base is attached to the lateral part of the sacrum & coccyx. FUNCTION OF THE LIGAMENTS 1. They stabilize the sacrum on the pelvic bones by preventing the lower end of the sacrum & coccyx from upward rotation at the sacroiliac joint by the body weight. 2. They convert the greater and lesser sciatic notches into foramina. INFERIOR WALL (FLOOR) It is formed by the pelvic diaphragm It supports the pelvic viscera. PELVIC DIAPHRAGM It is formed by the levator ani & coccygeus muscles of both sides and their covering fascia. It is incomplete anteriorly to allow the passage of urethra and vagina. LEVATOR ANI (ORIGIN) It is linear from : 1. Back of body of pubis. 2. Tendinous arch from the thickened fascia covering obturator internus. 3. Ischial spine. PARTS Anterior fibers: levator prostate or (sphincter vaginae). It is inserted into the perineal body (A fibrous mass in front of anal canal). The levator supports the prostate. The Sphincter constricts the vagina. Both support the perineal body. PARTS Intermediate fibers: (a) Pubococcygeus It is inserted into the anococcygeal body (a small fibrous mass between the anus and tip of coccyx) PARTS (b) Puborectalis : It forms a sling (angle) at the Anorectal junction. It is a mechanism to keep the lower part of the GIT closed. PARTS (c) Posterior fibers: Iliococcygeus. Inserted into the anococcygeal body and the coccyx. ACTION OF LEVATOR ANI 1. It supports and maintains the pelvic viscera in position (especially the uterus). 2. Forms the sling around the anorectal junction. ACTION OF LEVATOR ANI 3. Resists the rise of the intrapelvic pressure during straining efforts of the abdominal muscles (cough & vomiting). 4. A sphincter of the vagina. NERVE SUPPLY 1. Perineal branch (4th sacral nerve). 2. Perineal branch (pudendal nerve) COCCYGEUS MUSCLE It is triangular in shape. It overlies the sacrospinous ligament. Origin : Ischial spine Insertion : Lateral margins of coccyx and lower part of sacrum. COCCYGEUS MUSCLE Nerve supply : From 4th & 5th sacral nerves. Action : Support the posterior part of the pelvic floor. PARIETAL PELVIC FASCIA It lines the walls of the pelvis. In many locations where it comes in contact with bone, it fuses with the periosteum. It is named according to the muscle it overlies. Obturator fascia. piriformis fascia. PARIETAL PELVIC FASCIA Superior fascial layer of pelvic diaphragm. As the pelvic diaphragm is deficient anteriorly, the fascia becomes continuous with the fascia covering the inferior surface of the pelvic diaphragm. VISCERAL LAYER OF PELVIC FASCIA It is a loose connective tissue that covers and supports all pelvic viscera. It fuses with the parietal layer when a viscus comes into contact with the pelvic wall. VISCERAL LAYER OF PELVIC FASCIA In some locations, it is thickened to form ligaments for the support of the viscus (Pubovesical, uterosacral) They are of clinical importance especially in females as they support the uterus and prevent its prolapse. SACROILIAC JOINTS They are strong synovial joints. Articular surfaces : Auricular surfaces of the sacrum and the iliac bones. SACROILIAC JOINTS Stability : It depends on the strong ligaments : 1. Posterior. 2. interosseous sacroiliac ligaments. The anterior ligament is thin. SACROILIAC JOINTS Function : Transmitting the weight of the body from the vertebral column to the bony pelvis. ROTATION OF THE SACRUM The weight of the body tends to thrust the upper end of the sacrum downwards and rotates the lower end upwards. ROTATION OF THE SACRUM This is prevented by the following ligaments : Sacrospinous. Sacrotuberous. Iliolumbar : It is between the tip of the transverse process of L5 and the iliac crest. SYMPHSIS PUBIS It is a secondary cartilagenous joint. The two pubic bones are covered by hyaline cartilage and connected together by a fibrocartilagenous disc. The joint allows no movement. SACROCOCCYGEAL JOINT It is a cartilagenous joint between the bodies of the last sacral vertebrae and the 1st coccygeal vertebra. It has a great amount of movement.