* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diapositive 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
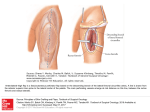
STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP FEATURES Lateral and oblique in the neck 2 bellies Course from manubrium and clavicle (head and medial 1/3) to occipital bone (mastoid process and superior nuchal line) 5 X 18 cm STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP MOTOR NERVE spinal portion of XI and 2sd and 3rd cervical nerves enter proximal portion of posterior muscle belly FUNCTION head rotation and bending expendable if remaining neck muscles are functionnals STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP VASCULAR ANATOMY type II of Mathes and Nahai Dominant pedicle: branch of occipital artery (D) enters on deep surface of upper 1/3 of muscle belly (3 cm x 1 mm) m1 D m2 m3 STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP VASCULAR ANATOMY 3 minor pedicles: branch of posterior auricular artery (m1; 2cm x 0.6 mm; close to mastoid insertion) branch of superior thyroid artery (m2; 2 cm x 0.6 mm; distal 1/3 of anterior muscle belly) m1 D m2 branch of suprascapular artery (m3; 2 cm x 0.5 mm; posteriorly near clavicular origin) m3 STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP FLAP TYPE muscular or musculocutaneous or osseomusculocutaneous POINT AND ARC OF ROTATION Based on the dominant pedicle: level of carotid bifurcation; anterior neck and lower face (anterior rotation) posterior neck and occipital area (posterior rotation) STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP ARC OF ROTATION Distally based flap: middle and lower neck STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP MUSCULOCUTANEOUS FLAP SKIN TERRITORY anterolateral skin of the neck located over the muscle 6 x 20 cm coverage of intraoral and lower facial defects SCM STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP FLAP MODIFICATIONS osseomusculocutaneous flap with the entire or partial medial third of the clavicle (mandibular reconstruction) also functional muscular flap (facial reanimation) STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP APPLICATIONS Coverage: anterior neck, posterior neck lower face, midlateral face oral cavity occipital scalp Reconstruction: mandible facial reanimation STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP GUIDELINES FOR FLAP ELEVATION Patient position: Lying on back with head turned to opposite side Markings : Mastoid, clavicle, suprasternal notch Skin islands: Standard flap: over the distal muscle closed to its origin Distally based flap: over the upper proximal muscle closed to its insertion STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP GUIDELINES FOR FLAP ELEVATION Pedicle location: Dominant pedicle: on deep surface of upper 1/3 of muscle Distal pedicle: deep to lower 1/3 of muscle STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP GUIDELINES FOR FLAP ELEVATION Incisions: Skin island isolated Muscle exposed through transverse neck incision or vertical incision STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP FLAP ELEVATION TECHNIQUES STANDARD FLAP Origin is divided More distal pedicle is divided Muscle is elevated from clavicle toward superior neck Remaining segmental pedicle are divided Dissection continues up toward dominant pedicle Dominant pedicle is identified and preserved XIth cranial nerve is preserved Dissection is completed at level of hyoid bone STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP FLAP ELEVATION TECHNIQUES DISTALLY BASED FLAP Muscle outlined by drawing a line from mastoid to manubrium Incision along that line and muscle identified Muscle divided at midway along its length Muscle mobilized from above toward distal pedicle STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP FLAP ELEVATION TECHNIQUES VASCULARIZED BONE Clavicle is cut with a saw, preserving the attachments of the origin of the muscle from the bone Distal pedicle is identified and ligated The combined flap is dissected from below upward STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP EXTENSION OF PEDICLE LENGHT rotation arc increases with release of insertion of SCM or extension of skin island inferior to clavicle for 1 or 2 cm TRANSPOSITION Tunnelled under mandible for intraoral reconstruction STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID FLAP DONOR SITE CLOSURE Directly PRECAUTIONS Spinal nerve: passing through SCM at upper and middle 1/3 junction Internal jugular vein: closed to SCM at its origin Great auricular nerve: closed to anterosuperior border of SCM RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY PRINCIPLES, ANATOMY AND TECHNIQUES S J MATHES F NAHAI CHURCHILL LIVINGSTON EDS 1997