* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eye Presentation - Downey Unified School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
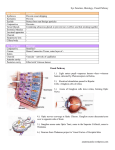
Sage Lee, Samantha Alvarez Layers of the Eye Outer layer Sclera Cornea Iris Lens Middle layer Uvea Contains the blood vessels Inner layer Retina Rods Cones Optic nerve Fibrous Tunic The outer, fibrous layer composed of the sclera and the cornea The cornea: smooth, clear glass-like transparent region made of loose connective tissue that protects the eye Corneasclera The Sclera: the “white of the eye”, forming a supporting wall for the eye Vascular Pigmented Tunic The iris: circular muscle that controls the size of the pupil Ciliary body: responsible for secretion of aqueous humor Ciliary Muscle: responsible for accommodating lens Ciliary body and Choroid Choroid: layer of blood vessels providing nutrients to the retina Pupil: controls amount of light entering the eye Lens: a structure that helps focus light on the retina The nervous tunic The retinas major regions consists of; Optic papilla: joint of optic nerve and retina Fovea centralis with macula lutea: area of greatest visual acuity Pigment Epithelium Cells of the eye Photoreceptors Neurons: Bipolar, Ganglion cells, Centrifugal cells, and amocrine Supporting cells: Muller’s cells and Neurological cells Cones Eye glands Meibomian glands Lacrimal Gland Components of Retina 9 layers: Layer of rods and cones Optic Nerve Fovea Macula Ganglion Layer Eye Muscles Inferior oblique muscle Inferior rectus muscle Lateral recuts muscle Medial rectus muscle Superior rectus muscle Superior oblique muscle Levator palpeprae muscle Eye Secretions Vitreous Drusen Aqueous Humor Neurons and Visual Process Photoreceptors Rods Cones Bipolar Neuron Amacrine Cells Ganglion Cells Optic Nerve Bipolar Neuron Axon extends from one side, dendrite from the other Found also in the nose and ear Used for sense of smell and hearing Form in middle layer of the retina Amacrine Cells Located at the inner plexiform of the retina (IPL) Transfer message between bipolar cells and ganglion cells Classified into two types By dendrite morphology and stratification (formation and appearance) Ganglion Cells and Optic Nerve Ganglion cells Transmit the message to the optic nerve Optic nerve Longest part of process Reaches a far part in the brain where the image is processed Processing is done in the lateral geniculate body Output is sent to the striate cortex so we can see the “picture” Visual Receptors Rods Cones Location: retina Location: retina Thin projection at terminal Short, blunt projections ends Approx. 100 million More sensitive to light Nerve fibers converge causing blurry outlines 3 different kinds to detect color Red, blue, green Approx. 3 million Single fibers, no convergence. Create sharp images Visual Receptors Cont. Vision and the receptors only stimulated by light Each receptor sends a small portion of the big picture to the brain The brain puts it all together Epithelial pigment absorbs light not taken in by receptors Epithelial pigment and pigment of choroid coat keep light from reflecting off of surfaces in the eye Pigment layer stores vitamin A Helps receptor cells to synthesize visual pigments Interpreting Sight ● Refraction ○ occurrs when light rays travel through through the curved, clear front surface of the eye(cornea). ● Convergent vs. Divergent waves ○ Converging waves: light waves that come together from different directions and have a common meeting point on the lens of the eye. ○ Divergent wave: light waves that come from different directions, and once it hits the lens, continues to travel in different directions. Interpreting Sight Cont. ● Convergent vs. divergent lenses ● Converging lens(convex) ● directs rays of light to a point at the optical center or axis of the lens ● thick across the middle and thin at the upper and lower edges ● Diverging lens(concave) ● directs light away from the optical center or axis of the lens ● thin across middle and thick at the upper and lower edges Interpreting Sight Cont. ● Dark vs. Light vision ○ Pupil expands and contracts depending on the amount of light, and could physically block out light form the eye ○ Cone cells can perceive color in bright light. ○ Rod cells perceive black and white images and work best in low light. ■ contains Rhodopsin ● it is the chemical that the rods use to absorb photons and perceive light. Interpreting Sight Cont. ● Stereoscopic vision ● The single perception of a slightly different image from each eye ● how we detect depth perception ● perceives distance, depth, height, and width of objects ● brain puts together the pictures from both eyes into one vision ● brings the three dimensional vision bibliography "The Neural Layer." Sight. N.p., n.d. Web. 10 August 2014.<http://teaching.pharmacy.umn.edu/courses/eyeAP/Eye_Anatomy/Sight/NeuralLayer.htm>. "Eye, Brain, and Vision." Eye, Brain, and Vision. N.p., n.d. Web. 07 May 2009.<http://hubel.med.harvard.edu/book/b6.htm>. N.p., n.d. Web. <http%3A%2F%2Fwww.getbodysmart.com%2Fap%2Fnervoussystem%2Fnervecells%2Fbipolar%2Ftu torial.html> "The Ottawa Hospital." Anatomy of the Eye. Ottowa Hospital, 08 June 2012. Web. 06 May 2015. <https://www.ottawahospital.on.ca/wps/portal/Base/TheHospital/ClinicalServices/DeptPgrmCS/Pro grams/EyeInstitute/AnatomyoftheEye>. Hubel, David.”Eye and Vision.” hubel.med.harvard.edu.N.p.,n.d.Web.28Apr.2015 <http;//hubel.med.edu/book/b14.htm>. "Bipolar Neurons-Structure and Function." getbodysmart.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Apr. 2015. <http://www.getbodysmart.com/ap/nervoussystem/nervecells/ bipolar/tutorial.html>. "Stereoscopic Vision." thefreedictionary.com. farlex, n.d. Web. 28 Apr. 2015. <http://medicaldictionary.thefreedictionary.com/stereoscopic+vision>. "The Anatomy of a Lens." physicsclassroom.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Apr. 2015. <http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refrn/Lesson-5/ The-Anatomy-of-a-Lens>. Heiting, Gary. "Refractive Errors and Refraction: How the Eye Sees.llaboutvision.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Apr. 2015. <http://www.allaboutvision.com/eye-exam/refraction.htm>.