* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 4 Lecture
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
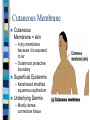
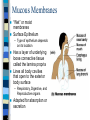
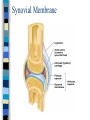
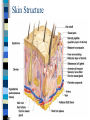
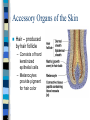
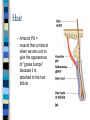
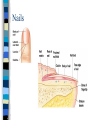
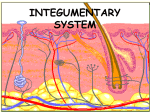
CHAPTER 4 Skin and Body Membranes Function of Body Membranes Line or cover body surfaces Protect body surfaces Lubricate body surfaces Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes – are simple organs – Cutaneous membranes – Mucous membrane – Serous membrane Connective Tissue Membranes Cutaneous Membrane Cutaneous Membrane = skin – A dry membrane because it is exposed to air – Outermost protective boundary Superficial Epidermis – Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Underlying Dermis – Mostly dense connective tissue Mucous Membranes “Wet” or moist membranes Surface Epithelium – Type of epithelium depends on its location Has a layer of underlying loose connective tissue called the lamina propria Lines all body cavities that open to the exterior body surface – Respiratory, Digestive, and Reproductive organs Adapted for absorption or secretion Serous Membranes Serous Membranes = “Serosa” Surface simple squamous epithelium with underlying areolar connective tissue Lines open body cavities that are closed to the exterior of the body Serous membranes occur in pairs: – Parietal = lines the cavity wall – Visceral = covers the outside of the organ contained in the cavity Serous Membranes Serous layers are separated by serous fluid which helps to reduce friction between organs. Specific Serous Membranes: – Peritoneum = covers the abdominal cavity – Pleura = surrounds the lungs – Pericardium = surrounds the heart Connective Tissue Membrane Synovial Membrane – Made of connective tissue only – Lines fibrous capsules surrounding joints Synovial Membrane Integumentary System Components include: – Skin = cutaneous membrane – Sweat glands – Oil glands – Hairs – Nails Integumentary System Protects deeper tissues from: – Mechanical Damage – Chemical Damage – Bacterial Damage – Thermal Damage – UV Radiation – Drying Out Integumentary System The skin aids in: – Heat Regulation – Excretion of urea and uric acid – Synthesizing vitamin D Skin Structure Has 3 layers: – Epidermis = outermost layer • Stratified squamous epithelium • Often keratinized (hardened by keratin) – Dermis = middle layer • Dense connective tissue • Firmly connected to epidermis – Hypodermis = aka “subcutaneous” tissue; deep to the dermis • Not part of the skin • Anchors skin to underlying organs • Composed mostly of adipose tissue Skin Structure Layers of the Epidermis Stratum Basale – Layer lying next to the dermis and is undergoing mitosis Stratum Spinosum Stratum Granulosum Stratum Lucidum – Occurs only in thick skin Stratum Corneum – 20 to 30 cell layers thick – Shingle-like dead cells – Have a totally “new” epidermis every 25-45 days Melanin Pigment produced by melanocytes Color is yellow to brown to black Found mostly in the stratum basale Amount produced depends upon genetics and the exposure to sunlight Layers of the Dermis Papillary Layer – Have projections called dermal papillae – Contain pain receptors (Meissner’s corpuscles) and capillary loops Reticular Layer – Deepest skin layer – Contains blood vessels, glands, and pressure receptors (Pacinian corpuscles) Normal Skin Color Determinants Melanin = yellow, brown, or black pigments Carotene = orange-yellow pigment from some vegetables Hemoglobin = red coloring from blood cells in the dermis capillaries; oxygen content determines the extent of red coloring Accessory Organs of the Skin Sebaceous Glands = produce oil – Acts as a lubricant for skin and kills bacteria – Most have ducts that empty into hair follicles – Glands are activated at puberty Accessory Organs of the Skin Sweat Glands = widely distributed in skin – 2 types: • Eccrine = open via duct to pore on skin surface • Apocrine = ducts empty into hair follicles – Composition of sweat: • Mostly water, some metabolic waste • Only in apocrine glands – fatty acids & proteins – Function: • Helps get rid of excessive heat • Excretes waste products • Its acidic nature inhibits bacteria growth – Odor is from associated bacteria Accessory Organs of the Skin Hair – produced by hair follicle – Consists of hard keratinized epithelial cells – Melanocytes provide pigment for hair color Hair – Has a central medulla, a cortex that surrounds it, and a heavily keratinized cuticle on the outside of the cortex Hair – Arrector Pili = muscle that contracts when we are cool to give the appearance of “goose bumps” because it is attached to the hair follicle Accessory Organs of the Skin Nails = scale-like modifications of the epidermis that are heavily keratinized – Have a lack of pigment that makes them colorless – Stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed so that the nail grows Nails Skin Homeostatic Imbalances Infections (page 107): – Athlete’s Foot = caused by fungal infection – Boils & Carbuncles = caused by bacterial infection – Cold Sores = caused by a virus – Contact Dermatitis = exposures cause an allergic reaction – Impetigo = caused by bacterial infection – Psoriasis = cause is unknown but is triggered by trauma, infection, and stress Burns (pages 108 – 109) Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV radiation, or chemicals Dangers of burns include dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and circulatory shock “Rule of Nines” is a way to determine the extent of burns – Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation and each area represents about 9% Severity of Burns 1st Degree Burns = only epidermis is damaged – Skin is red and swollen 2nd Degree Burns = epidermis and upper dermis are damaged – Skin is red with blisters 3rd Degree Burns = destroys entire skin layer – Burn is gray-white or black Burns Burns are considered critical if: – Over 25% of the body has 2nd degree burns – Over 10% of the body has 3rd degree burns – There are 3rd degree burns of the face, hands, or feet Skin Cancer Skin Cancer = most common type of cancer; abnormal cell mass; 2 types: – Benign – does not spread – Malignant – metastasized (moves) to other parts of the body Basal Cell Carcinoma Least malignant Most common type arises from stratum basale Squamous Cell Carcinoma Early removal allows a good chance of cure Arises from stratum spinosum Metastasizes to lymph nodes Malignant Melanoma Most deadly of skin cancers Cancer of melanocytes Metastasizes rapidly to lymph and blood vessels Detection of Skin Cancer Uses ABCD rule: – A = Asymmetry • 2 sides of pigmented mole do not match – B = Border irregularity • Borders of mole are not smooth – C = Color • Different colors in pigmented area – D = Diameter • Spot is larger than 6mm in diameter