* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human papillomaviruses
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Cervical cancer wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Candidiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
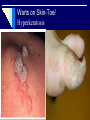
Human Papillomaviruses Prof. Dr Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan General Introduction Human Papillomaviruses (HPVs).. Small ds DNA.. Capsid,72 Capsomers with 2 surface major Proteins (L1,L2)..Responsible for invasion, widely distributed in nature.. Infect Human, Animals, Birds. Infect basal layers of squamous /columnar epithelium ..Viral DNA multiply in nucleus of cells.. cause no cell lyses. infectious virus DNA found in upper cell layers of epithelium (keratinocytes) ..causes Hyperkeratosis in horny layer.. Viral DNA can integrate in host chromosome. Viral infection establish in epidermis & mucous membranes.. Mostly benign Skin Warts.. Few virus types progress to malignant lesions..less than 0,01%. HPVs 200 types classified according homology of their genomes.. Types are categorized as low, intermediate & high risk according to their Oncogenic potential. /2 About 15 most common HPVs cause skin infections .. Viruses found in dead & living epidermis cells.. Transmitted from one infected person to another through direct skin contact, swimming floors, showers/ baths ..less clothes, dust particles. Cutaneous warts: Common types HPVs (1-8,10) grow in keratinized epithelium.. Face, hands, feet..other body parts. -Common skin /oral wart (Verruca vulgaris).. Types 2,4,7 -Deep Plantar warts (Verruca Plantaris).. Types 1,4.. Hard grainy growths appear on soles the feet . -Flat Warts.. Types 3,10.. Smooth colored face, legs fingers ..persist short / long time. Children are more susceptible to HPVs than adults. Skin HPV types are different from those that cause malignant growths in the throat or genital area. Warts on Skin-Toe/ Hyperkeratosis Genital HPV-1 Both humoral & cell-mediated immune responses develop.. Following skin infection.. Persistent & recurrent warts increased with cell mediated immunodeficiency. Genital HPV infections are very common and mostly associated with sexual contact & sexually transmitted diseases. Anogenital warts/ Condylom acuminatum affect any part of the sexual organs.. Penis, Vulva, Vagina, Cervix.. Perianal skin , common in sexually active adults. Types 6,11 cause 90% of benign anogenital infections.. mostly Cervical warts (Flat Condyloma/ squamous intraepithelial neoplasia)..may affect oral cavity Genital HPV-2 Genital warts often occur in clusters and can be very tiny lesion or spread into large masses in the extragenital or rectal area.. Rarely in anal colon HPV types 16+18 are associated with high risk of malignancy..mostly found inside vagina & cervix. Most HPV genital infections occur without any symptoms and may disappear without any treatment over few years. Genital HPV infection sometimes persists for many years, without causing cell abnormalities.. This mimic its present infection & increase a woman’s risk of developing cervical cancer.. Each year nearly 1 million women worldwide.. killing 250000 lives. Genital HPV-3 Increase risk factors of cervical cancer in women with HPV infection include young age, smoking, use immune suppressed drugs, oral contraceptive drugs, sexually transmitted diseases. Precancerous HPV lesions in cervix can progress to invasive cervical cancer.. usually takes 15–20 years Persistent HPV genital infections ( types 16,18) cause 70% of cervical cancer/endocervical Adenocarcinoma in Western countries.. Still less incidence in Jordan & most Arab countries.. Screening should be done for every woman using Colposcopy & Pap-smear H PV-4 Respiratory Papilloma .. mostly benign lesions on mucosa respiratory tract.. Larynx ( Laryngeal Papilloma).. Children and adults .. May cause obstruction if not removed early as possible ..Caused mostly by HPV types 6 & 11.. Less types 16 & 18.. It is unknown if immunological conditions contribute for infection.. Common among middle age (30-50) years. Squamous oral papillomas & Oral Hyperplasia .. (Types 6,11) are considered benign growths of the surface epithelium ..The lesions found on oral mucosa, lips, tongue base..small & large..may spread to soft palate, throat, tonsils.. Past HPVs exposure is increasing the risk of oral lesions.. old age, Common in association tobacco and alcohol use. Lab Diagnosis & Treatment A Pap smear test is used to detect abnormal cells in cervix .. Atypical squamous & glandular epithelial cells .. A Pap test is recommended at least once every 2-3 years. Detection of HPV DNA from suspected lesions by PCR is more accurate and detect early infection. There is currently no antiviral drugs against Papillomavirus infection.. the lesions should be removed. Treatment: Cryotherapy/ Cryosurgery.. Removing the lesions does not necessary eradicate the virus completely.. reoccurrence of warts is common. New Vaccine is available against HPV types 16,18.. Effective up 90% and safe. Detection and typing of common human papillomaviruses among Jordanian patients. S.bdour, L. AkKash, A.A> Shehabi J Medical Virology, 2013, 85:158-63 The epidemiology of human papillomaviruses (HPVs) genotype distribution of cutaneous warts in Jordanian patients were studied. A total of 200 samples were collected using skin swabs from patients with warts attending the dermatology clinic at the J U Hospital (2010 -2010). Another 100 control samples were taken from healthy Jordanian with no current or previous history of warts Methods: Wart samples collected using..DNA extraction and sequencing was carried out using PCR with the specific primer pair to detect HPV DNA, followed by multiple-type-specific (Multiplex) PCR combined with DNA sequencing. Results: The prevalence of HPV among Jordanian patients tested with warts diagnosed clinically was 82% . Conclusion: Alpha HPV types (2, 27, 57).. are mostly detected in Cutaneous warts of Jordanian patients with skin warts..These types rarely associated with malignancy.