* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 5 Geocentric v Heliocentric Models
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
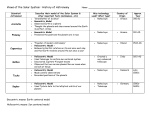
Trivia Question of the Day Astronomy Picture of the Day Review Questions (on a separate sheet of paper) 1. Write down ONE piece of evidence that supports the Big Bang Theory. Review Questions 2. List the following in order from OLDEST to YOUNGEST: - - Solar system Milky Way galaxy - Universe Review Questions 3. In which part of the H-R diagram do stars spend most of their lives? Review Questions 4. Review Questions 5. The 4 terrestrial planets include… 6. The 4 jovian planets include… Review Questions 7. How is rotation different from revolution? Review Questions 8. Which of the following are MORE eccentric? A. B. Review Questions 9. How could we move the foci to make this ellipse MORE round? 10. How could we move the foci to make this ellipse MORE eccentric? Review Questions 11. At what time of year is the Earth at perihelion? 12. At what time of year is the Earth at aphelion? Lesson 5: Geocentric vs. Heliocentric Models of Apparent Motions What are “Apparent Motions”? ►A motion that an object appears to make ► Can be real or an illusion ► For example, A person is spinning around = real motion The spinning person sees the room as spinning = apparent motion ► Earth’s rotation causes the apparent motions of celestial objects (the Sun, moon, stars, and planets) across our sky So what do apparent motions have to do with astronomy??? ► Every day and night throughout the year, when you look up in the sky, what do you see moving??? The Sun The Moon The Stars Some of the Planets For thousands of years, people have had ideas, theories and models to explain why these objects APPEAR to move the way they do… Geocentric Models ► Key Ideas: “Geo” = Earth “Centric” = Center ► “Earth-centered” Earth is the center of the solar system Earth is stationary (not moving) and everything is moving around us In your notes, draw a picture of what the geocentric model looks like… Geocentric Models ► Key Limitations: Did not explain the apparent motions of some planets (for example, Mars) Did not explain all of Earth’s motions, including how a freely-swinging pendulum moves Heliocentric Models ► Key Ideas: “Helio” = Sun “Centric” = Center ► “Sun-centered” The Sun is the center of the solar system Earth rotates on its own axis AND revolves around the Sun In your notes, draw a picture of what the heliocentric model looks like… Heliocentric Models ► Key Limitations: The early models used circular orbits did not explain the apparent motions of planets (BUT… once elliptical orbits and planets’ orbital speeds were added to the model, the planets’ apparent motions could be explained and even predicted!) Challenge Question ► Write down one SIMILARITY between the geocentric and heliocentric models ► Write down one DIFFERENCE between the geocentric and heliocentric models Practice Problems & Homework #4