* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HINDUISM
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
Bhagavata Purana wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Vaishnavism wikipedia , lookup
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
Madhvacharya wikipedia , lookup
Vishishtadvaita wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu deities wikipedia , lookup
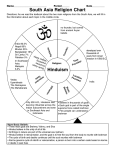
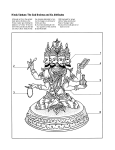
HINDUISM PART I I. INTRODUCTION A. In 1500 B.C. the Aryans from Persia and mixed with the people around the Indus River region. “Hindu” means “the people and culture of the Indus River region”. B. Aryan religion expressed in hymns and later collected in sacred texts called the Vedas. 1. language – Sanskrit 2. Veda means “knowledge” 3. Vedas collected from about 1400 B.C. to 400 B.C. MAP OF INDIA C. Brahmin priests established and social laws They established a caste system 1. Brahmins – priests 2. Ksatriyas – warriors, rulers 3. Vaisyas – merchants 4. Sudra – laborers, servants 5. Harijans – untouchables – impure “no group” D. Buddhism – born in India 1. rejected – sacrificial system of the Hindus 2. developed – yoga system; guru/student relationship E. Bhakti – devotion to a personal god 1. two most popular Hindu gods – Siva and Krishna F. 6 schools of Hindu thought – 1000 B.C. to 0 1. darsana – each developed their own way of looking at truth 2. Samkara (SHAN ka ra) born 788 A.D. founded a school of thought a. individual soul – each person has an individual soul that is related to the Universal Soul (Brahman) b. Universal Soul - Brahman II. CONTEMPORY HINDUISM A. bhakti – path of devotion B. two popular gods to worship – Siva and Vishnu 1. texts providing understanding of these gods Bhagavad-Gita Puranas C. Moksa – personal salvation; available as result of gracious love bestowed by the Adorable One to those who adore God in whatever forms most meaningful to them D. Radhakrishnan (1888 – 1975) – was one of the most important Hindu philosophers, He helped establish Hinduism in the West III. HINDUISM IN NORTH AMERICA A. Transcendentalism Movement – mid 1800’s 1. Ralph Waldo Emerson – pantheistic worldview 2. Henry David Thoreau – inspired by Bhagavad-Gita wrote Walden B. Maharishi Mahesh Yogi – developed idea of unity and oneness of all creation 1. 1959 – came to U.S. to impart meditation 2. 1960’s – taught TM to Beatles, Beach Boys 3. mid 1970’s a. scientifically proven method of achieving relaxation and inner peace b. could be practiced without violating own religious beliefs c. self-help technique for dealing with stress 4. decline a. couldn’t deliver on all benefits b. seekers wanted something more powerful c. legally a religion – couldn’t get into schools C. Hare Krishna Movement 1. Vishnu – god (preserver) 2. Avatars – incarnations of these gods a. Krishna – most popular 3. Prabhupada – founder of Hare Krishna a. 1944 – wrote religious views in Back to Godhead b. 1965 – came to NYC and established temples throughout the U.S. c. inherited leadership – several of his disciples d. bhakti dancing and chanting to Krishna – burn off ignorance and karma Indians laugh in amusement at Hare Krishna! D. Population of Indians between 1899 – 1907 – over 1900 in U.S. 1. population at 2000 – close to 1 million 2. Hindus in India – 700 million a. world population – 13% Hindu IV. THEOLOGY A. History of the world is cyclical 1. measure time – according to creator God, Brahma 2. when Brahma dies – we die 3. Brahma born again from a cosmic egg 4. Puranas, sacred texts a. division of world into 4 recurring ages b. increasing evil as ages progress c. we live in the last age (Kali), worst evil B. Sesa (SHA shu); lord of the snakes 1. destroyed the world with fire 2. Sesa pleased Brahma with his piety 3. Brahma gave Sesa the honor of bearing the earth 4. Sesa linked to the sustainer god Vishnu C. All humanity destroyed (Kali age) 1. 400,000 years longer before the end of this world 2. GREED – root of all suffering SELFISHNESS – source of war, disease, and death 3. Categories of sins a. violating social customs, dishonoring family, and no respect for Brahmin priests b. not maintaining purity of body (eating cow meat) c. evil behavior – stealing, killing, etc. 4. Decay of the world a. vegetation is gone, people starve b. sun scorches earth by drying up all water c. cosmic rain brings fire and floods d. cosmic ocean exists, absorbs spiritual remains of beings, waiting to be reborn e. Brahma’s life ends, but is reborn again and he creates a new universe V. JESUS CHRIST A. Christ did not suffer B. Jesus was not perfect 1. anger was a major flaw in Christ’s character – moneychangers in the temple C. Jesus Christ was one of many great men 1. admiration is expressed by Hindu leaders but He is not acknowledged as God or Savior D. Highest reverence should be offered to Brahman, who is the greatest among all gods 1. avatar – some believed Jesus was an avatar (reincarnation) VI. GOD A. Numerous gods protect humankind 1. Hindu pantheon includes many gods, but Brahman is the greatest B. Brahman is the creator of the world C. True enlightenment is knowing that we are one with god. That is, we are god. 1. by practicing spiritual disciplines (such as yoga) that help an individual seeker explore the hidden meaning of the inner self VII. SALVATION A. The cycle of death and rebirth is the fate of all unenlightened souls. B. Those who break free from the cycle of death and rebirth become immortal. They are delivered from the cycle of death and rebirth. C. An enlightened person achieves salvation and perfection through the efforts of one’s self D. Ultimate salvation of the soul is total absorption into Brahman.