* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
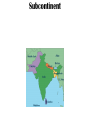
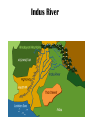
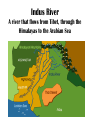
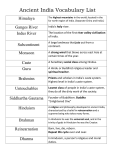
Ancient India Social Studies Vocabulary Words and Definitions Vocabulary– Ancient India subcontinent Indus River Himalayas Indus Plain citadel migrate Harappa Mohenjo-Daro Hinduism Vedas caste system reincarnation dharma Buddhism monk karma Four Noble Paths Eightfold Path Middle Way Siddhartha Gautama Kosala To review vocabulary: • Click your way through the slide show with your mouse or touchpad. • The vocabulary word will appear on the first slide. The definition will appear on the second slide, along with the vocabulary word. • Practice until you are able to give a good definition in your own words. It does not have to be “word for word” – it does need to be accurate and complete. • All pictures are of Indian historical figures, statuary, landscapes, maps, and buildings. • Good luck and have fun! Welcome to India Ch. 6 Vocabulary Subcontinent A large landmass that is geographically separated from the rest of the continent Subcontinent A large landmass that is geographically separated from the rest of the continent Indus Plain A vast, dry region south of the Himalayas that is made fertile by deposits of silt from the Indus River Indus Plain A vast, dry region south of the Himalayas that is made fertile by deposits of silt from the Indus River Indus River A river that flows from Tibet, through the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea Indus River A river that flows from Tibet, through the Himalayas to the Arabian Sea Himalayas Himalayas The world’s highest mountain range, forming the northern border of the Indian subcontinent Citadel walled fort that protects a city Citadel walled fort that protects a city Migrate to move from one place to another Migrate to move from one place to another Harappa city of the ancient Harappan civilization Harappa city of the ancient Harappan civilization Mohenjo-Daro City of the ancient Harappan civilization Mohenjo-Daro City of the ancient Harappan civilization Hinduism the religion of India that grew out of the beliefs of the ancient Aryan peoples; it stresses that one main force connects all of life Hinduism the religion of India that grew out of the beliefs of the ancient Aryan peoples; it stresses that one main force connects all of life Vedas In Hinduism, the ancient books of sacred songs on which much of which its religious beliefs are based Vedas In Hinduism, the ancient books of sacred songs on which much of which its religious beliefs are based Caste system the social system in Hindu society in which a person’s place is determined by the rank of the family into which he or she is born Caste system the social system in Hindu society in which a person’s place is determined by the rank of the family into which he or she is born Reincarnation a Hindu belief that people move in a constant cycle of life, death, and rebirth Reincarnation a Hindu belief that people move in a constant cycle of life, death, and rebirth Dharma laws and duties that instruct Hindus on how to live Dharma laws and duties that instruct Hindus on how to live Buddhism Buddhism A religion founded in India by Siddhartha Gautama which teaches that the most important thing in life is to reach peace by ending suffering. monk monk A man who devotes his life to a religious group, often giving up all he owns. karma karma In Hinduism and Buddhism, the end result of all of a person’s good and bad acts, which determines his or her rebirth. Four Noble Truths 1. Life means suffering. 2. The origin of suffering is attachment. 3. The cessation of suffering is attainable. 4. The path to the cessation of suffering. Four Noble Truths In Buddhism, the principles that rule life and promise an end to suffering. 1. Life means suffering. 2. The origin of suffering is attachment. 3. The cessation of suffering is attainable. 4. The path to the cessation of suffering. Eightfold Path 1. Right View 2. Right Intention Wisdom 3. Right Speech 4. Right Action Ethical Conduct 5. Right Livelihood 6. Right Effort 7. Right Mindfulness 8. Right Concentration Mental Development Eightfold Path In Buddhism, the basic rules of behavior and belief leading to an end of suffering. 1. Right View 2. Right Intention Wisdom 3. Right Speech 4. Right Action Ethical Conduct 5. Right Livelihood 6. Right Effort 7. Right Mindfulness 8. Right Concentration Mental Development Middle Way Middle Way In Buddhism, a way of life, neither too strict nor too easy, that results from following the Eightfold Path. Siddhartha Gautama Siddhartha Gautama 563? – 483? B.C. Ancient Indian religious leader known as the Buddha, or enlightened One, who founded Buddhism. Kosala Kosala An ancient kingdom in northern India where Siddhartha Gautama is said to have been born. Chapter 6 – Ancient India subcontinent Indus River Himalayas Indus Plain citadel migrate Harappa Mohenjo-Daro Hinduism Vedas caste system reincarnation dharma Buddhism monk karma Four Noble Paths Eightfold Path Middle Way Siddhartha Gautama Kosala