* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Program revision 2
Monad (functional programming) wikipedia , lookup
Sieve of Eratosthenes wikipedia , lookup
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp syntax wikipedia , lookup
Fisher–Yates shuffle wikipedia , lookup
Standard ML wikipedia , lookup
C Sharp (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
CAL Actor Language wikipedia , lookup
Sorting algorithm wikipedia , lookup
Linked list wikipedia , lookup
Corecursion wikipedia , lookup
DT249-Information Systems
Research Practice-2015-16
Programming Revision Lecture 2
Lecturer: Patrick Browne
One-Dimensional arrays
• An array is an ordered collection, or numbered list, of
values. All of the values in an array must be of the same
type. The type of the array is the type of the values it
holds, followed by the characters []. An index is used
to refer to individual values in the array. If we have N
values, we think of them as being numbered from 0 to
N-1. Each cell of the array called num contains a value.
1 dimensional arrays
class ArrayApp1 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
// 8 elements indexed 0 to 7
int a[] = {17,3,60,128,11,11,2,8};
for (int i=0; i<8; i++)
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");}}
• Make the above program omit the last element.
• Make the above program omit the first element.
• If we have N values, we think of them as being
numbered from 0 to N-1.
Two dimensional array
Each cell of the array contains a value
Two dimensional array
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class ArrayApp2 {
//... Define named constants to centralize definitions
static final int ROWS = 2;
static final int COLS = 4;
•
•
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a2 = new int[ROWS][COLS];
String output = "";
// Accumulate text here
//Print array in rectangular form using nested for loops.
for (int row = 0; row < ROWS; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < COLS; col++) {
output += " " + a2[row][col];}
output += "\n";}
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, output);}}
Assign the row value to each element
Assign the column value to each element.
Functions
class FactApp {
static public void main (String [ ] args) {
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int f = factorial (a);
System.out.println("Factorial of " + a + " is " + f);
}
static public int factorial (int n ) {
int c = n - 1;
int r;
if (c > 0)
r = n * factorial(c);
else
r = 1;
return r; }}
•
The factorial of a number N, denoted by N!, is the product of all positive numbers less than or equal to N.
•
•
•
Takes input from command line. Change to take input from prompt.
Make a function to increment an integer
Make a function to add two integers
Procedures (methods)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MeanApp {
public static int numSamples;
// Number of samples to be computed.
public static float total=0.0f, // Total of all sample values.
mean =0.0f; // Mean of the sample values.
// Asks user for number of samples and gathers input from the keyboard.
public static void gatherInput()
{ // Create a new KeyboardInput object for input.
Scanner keyIn = new Scanner (System.in);
int count;
// Counts through samples.
System.out.print("How many samples? :");
numSamples = keyIn.nextInt();
for (count=1; count <= numSamples; count++)
{System.out.print("Sample number " + count + " :");
total += keyIn.nextFloat();
}
// Do the mean calculation.
mean = total / numSamples;}
// Displays the results of sample mean calculations.
public static void displayResults()
{ System.out.println("The mean of the " + numSamples + " samples is " + mean);
public static void main(String[] args){
gatherInput();
displayResults();}}
}
2D arrays
CSV2DArrayApp
• This program reads a comma separated file into
a two dimensional array.
• Copy the program and data files, called
male.csv and female.csv to your folder.
• The dimensions of the array are
int [][] numbers = new int[13][3];
• Change these to [20][20] and then to [12][3], and
then to [13][2]
Sorting
• public static void Sort()
•
{
•
int list[] = {10,7,19,5,16};
•
sortList(list);
•
}
•
Sorting
do
{ displayList(list);
listChanged = false;
for (int i=0; i<list.length-1; i++)
{ if (list[i] > list[i+1])
{temp = list[i];
list[i] = list[i+1];
list[i+1] = temp;
listChanged = true;}} }
while (listChanged == true);
Sorting swapping elements
temp = list[i];
list[i] = list[i+1];
list[i+1] = temp;
Sorting
do
{ displayList(list);
listChanged = false;
for (int i=0; i<list.length-1; i++)
{ if (list[i] > list[i+1])
{temp = list[i];
list[i] = list[i+1];
list[i+1] = temp;
listChanged = true;}} }
while (listChanged == true);
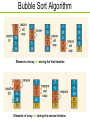
Bubble Sort Algorithm
Elements of array list during the first iteration
Elements of array list during the second iteration
Bubble Sort Algorithm
Elements of array list during the third iteration
Elements of array list during the fourth iteration
Location Quotients
• To load CSV files see program
CSVLocQuoApp.java
• Location quotients compare a local area's
business composition to that of a larger
area. In this case the two CSV files
(male.csv and female.csv) hold the
number of people employed in various
industries in the Dublin area. See notes
section below.