* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War I - Humble ISD
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
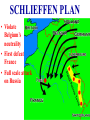
World War I: The War To End All Wars… or something. Early 1900’s: Alliances formed throughout Europe Two “isms” rear their heads: Nationalism: Militarism: Result: Europe is a powder keg! The Spark Who: Where: Why: Who else: Gavrilo Princip What happened: The leaders were unable to back away from their national "honor" and the entangling alliances they had agreed to. •Austria Hungary declared war on Serbia, who they believed had supported the assassins. •Russia, the traditional friend and ally of their fellow-Slavs, the Serbians, came to their support. •Russia's ally France also mobilized for war. •Germany, the ally of Austria Hungary, then came to the aid of their ally and invaded neutral Belgium to get to France. •When the French violated Belgian neutrality, Great Britain entered the fray. •Other nations followed. What should have been a small local war became the first world war. “Choosing Teams”: The Central Powers • • • • Germany Austria-Hungary Bulgaria Ottoman Empire (Turkey) “Choosing Teams”: The Allies • • • • • Great Britain France Russia Italy 20 other nations U.S. NEUTRALITY ADVANTAGES: CENTRAL POWERS • Germany, AustriaHungary-single connected territory • Efficient railroads • Rapid movement of troops and supplies • Submarines ADVANTAGES: ALLIES • Control of the seas • Blockaded Central Powers • Access to vital supplies • Number of troops THE GERMAN STRATEGY Schlieffen Plan: Delay the Russians in the East, hit the French HARD in the West, then focus on the Russians (Avoid fighting on two fronts) SCHLIEFFEN PLAN • Violate Belgium’s neutrality • First defeat France • Full scale attack on Russia THE WESTERN FRONT (“All Quiet on the Western Front”) • Stalemate-neither side able to gain land • Trench Warfare: 600 miles of ditches from the Alps to the North Sea • Distance between opposing ditches- “No Man’s Land” TRENCH WARFARE TRENCH WARFARE TRENCH WARFARE Meanwhile, back in the Batcave... U.S. positions: Official: Unofficial: Examples: Why Did The U.S. Enter The War? Two Major Reasons: Unrestricted Submarine Warfare International Rules: German Point of View: Goal: Starve the British and force them to release the British Navy blockade Sinking of Lusitania The Zimmerman Telegram What it said: What it did: Two Surprises For The Central Powers: 1. United States enters the War on the Allies’ side (Bad!) 2. The Bolshevik Revolution ends the Rominov (Anastasia) Dynasty, brings Marxism/ Leninism to Russia, and Russia exits the war. (Good!) WORLD WAR I WEAPONS OF WAR WEAPONS:CHLORINE GAS Had to wear gas masks Caused blindness, severe blisters, or death by choking First introduced by Germans; used by both sides WEAPONS: TANKS Introduced by the British Early tanks slow and clumsy Moved on a chain track WEAPONS: AIRPLANES •First time used in combat role •At first, used to take photographs •Soon, both sides used them to drop bombs. •Later guns were attached to fight in the air. WEAPONS: U-BOAT Submarine introduced by Germans Primary weapon-torpedo, self-propelled missile WEAPONS: MACHINE •Fired 400 GUN •Much improved by World War I rounds in a minute •Helped create a stalemate WEAPONS: HOWITZER First seen in fall of 1914 Austrian artillery