* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Great War
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
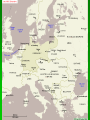
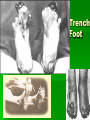
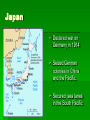
The Great War 1914 - 1918 The Pursuit of Peace By 1914 Europe had enjoyed a century of relative peace The support of Pacifism – opposition to all war 1899 the first Universal Peace Conference Hague Tribunal – World Court to settle disputes between nations Marching Toward War What was occurring in Europe that led to a rise in tensions? Causes of WWI Nationalism- a deep devotion to one’s country Imperialism- a policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, economically, or socially Militarism- a policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always ready for war. Rivalries Among European Powers Economic Rivalries Britain is threatened by Germany’s rapid economic growth Imperialism Causes Rivalries France and Germany compete for colonies i.e. Morocco Militarism and the Arms Race Militarism is the glorification of the military The “Great Powers” expanded their armies and navies Fierce competition in the “arms race” Military leaders became important figures Causes of WWI (cont.) Bismarck sees France as the greatest threat to peace in Europe and thought the French wanted revenge for their defeat in the FrancoPrussian War. What land did the French lose in the Franco-Prussian War? Alsace and Lorraine Otto von Bismarck Chancellor of Prussia Goal was to isolate France to maintain peace. In 1879 Bismark formed the Dual Alliance between Germany and Austria Hungary. 1881 made a treaty with Russia Causes of WWI (cont.) Kaiser Wilhelm forces Bismarck to resign allows treaty with Russia to lapse in return Russia forms an alliance with France Wilhelm begins a tremendous shipbuilding program and in return Britain forms an alliance with France Tangled alliances Triple Alliance Germany AustriaHungary Italy Triple Entente Great Britain Russia France Crisis in the Balkans What is happening in this region that adds to the tensions in Europe? Crisis in the Balkans Nationalism leads people to demand independence Austria-Hungary annexes Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia was home to many Slavic people Serbians were furious at the takeover Crisis in the Balkans (cont.) Archduke Ferdinand assassinated along with his wife Sophie June 28th, 1914 Ferdinand and his wife Sophie visit Sarejevo – Capital of Bosnia Shot was point blank range. Killer Gavrilo Princip 19 year old Serbian Member of the Black Hand (Serbian terrorist group) The Assassin: Gavrilo Princip A Harsh Ultimatum Austria sent Serbia an ultimatum - a final set of demands End all anti-Austrian agitation Punish any Serbian official involved in the assassination Austria must join the investigation Serbia only partly agreed – July 28th 1914 Austria declared war on Serbia The Great War Begins Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia This leads to a domino effect. Russia declares war on Austria-Hungary Germany declares war on Russia and France Great Britain declares war on Germany Nations Take Sides Central Powers: Allied Powers: Germany Austria-Hungary Ottoman Empire Great Britain France Russia Italy 20 The Two Fronts Western Front- Region in northern France where the Allies and Central powers battled each other. Eastern Front- Region along the GermanRussian border where Russians and Serbs battled Germans, Austrians, and Turks. German Problem: A Two Front War German officials did not want to fight a two front war Eastern Front vs. Russia Western Front vs. France What to do? Schlieffen Plan Germany would have to defeat France quickly then fight Russia Germany would have to march through Belgium – 8/3/1914 This causes Britain to declare war on Germany Germany’s defeat at the Battle of the Marne destroyed the Plan Why was this Germany’s battle strategy? Battle on the Eastern Front Russians launch initial attack on both Germans and Austrians. In the end Germans counter and crush the Russians, and the Austrians push the Russians out. How did Russia’s lack of industrialization affect its war efforts? Trench Warfare Trench warfare was a form of warfare in which both combatants occupied static fortified fighting lines, consisting largely of trenches, in which troops were largely immune to the enemy's small arms fire and were substantially sheltered from artillery. In the Trenches Warring armies burrowed into a vast system of trenches Rats, lice and heat became major problems “Over the top” orders were given and soldiers would leave their trenches and rush toward enemy lines In the Trenches In the Trenches Trench foot Many soldiers fighting in WWI suffered from trench foot This was an infection of the feet caused by cold, wet and unsanitary conditions. If untreated, trench foot could turn gangrenous and result in amputation. 20,000+ men in the British Army were treated for trench foot in one year!! Trench Foot Trench Foot Info.. The only remedy for trench foot was for the soldiers to dry their feet and change their socks several times a day. British soldiers were under orders to change their socks at least twice a day WWI Weapons Name some weapons used in WWI Explain how theses new weapons added to WWI deaths Technology in Modern Warfare World War I was very devastating due to new technology Rapid fire machine guns Poison gas The Tank Submarines Poison Gas "Our men were swallowed up by the mysterious cloud. At the same time, I felt its effect on my breathing. It burned in my throat. I felt a pain in my chest and could barely breathe any longer. I spit up blood and became dizzy. I thought I was lost." The Airplane Airplanes were primitive Had only 1- 2 seats With machine gun Mostly used for reconnaissance “Dog Fights” Air combat between planes Automatic Machine Gun Usually 2-man teams Provided a continuous stream of bullets This weapon was the main reason for the war settling into a STALEMATE Submarine German “U-Boats” To sink merchant ships Unrestricted Submarine Warfare Made the oceans unsafe for all Allied response – convoys Small groups of merchant ships protected by warships Zeppelins Gas filled balloons used by the Germans to bomb the English coast They were able to carry a much heavier load than airplanes The Tank Developed to end Trench Warfare Used a mounted machine gun Ran by a 8 man crew A Global Conflict Map of the World showing the Participants in World War I Green: Allies (some entered the war or dropped out later) Orange: Central Powers Grey: Neutral Countries War affects the world World War I was much more than a European conflict Fighting took place outside of Europe Every continent (except Antarctica) was involved Europe Asia Africa South America Australia North America Brazil The only South American country to enter the war. They assist the Allies in the naval war in the Atlantic Ocean Send troops to the Western front. Africa Japan Declared war on Germany in 1914 Seized German colonies in China and the Pacific. Secured sea lanes in the South Pacific Australia and New Zealand Both countries fight on the Allied side Contribute a significant amount of troops to the campaign in Gallipoli The Gallipoli Campaign Aim of the Gallipoli Campaign Attack and defeat the Ottoman Empire via the Dardanelles, a narrow sea straight that was the gateway to the Ottoman capital. Establish a supply line to Russia. Gallipoli Campaign Effort to take the region took place in 1915. Allies including Australia, New Zealand (ANZAC), British, and French forces battled Turkish troops Another bloody stalemate- 250,000 casualties on Allied side America joins the fight Germany seeks to control the Atlantic Ocean. Their aim is to cut off supplies to Britain, and slowly starve them Begin to use unrestricted submarine warfare Sink British ships without warning Sinking of the Lusitania German submarine sinks the Lusitania, a British passenger ship This angers the U.S. as Americans were on board Germany decides to end submarine warfare in 1915, but resumes it again in 1917. The Zimmerman Note Zimmerman note Telegram from Germany to Mexico Germany asks Mexico to join the fight on their side In return Mexico would regain the lands they had lost to the U.S. War affects the home front Governments begin to: wage total war- nations devote all resources to war Ration goods- people could only buy small amounts of items needed for the war Use propaganda- one sided information designed to keep up morale and support for the war. Propaganda Anti-German propaganda Rationing propaganda War bond propaganda Propaganda for women Enlistment propaganda Impact on Women Women took over jobs Manufactured weapons and supplies Nurses worked on the “front lines” Helped women’s rights The Allies win the war Russia withdraws in 1917 Communist leader Vladimir Lenin seizes power - offers Germany a truce called the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, ending the war between them The Central powers collapse Germany sends all of its forces to the Western Front, victory seems close Americans send 2 million more troops Advance toward Germany Central Powers begin to crumble. Bulgarians and Ottoman Turks surrender End of the war 1918 Kaiser Wilhelm steps down Germany is declared a republic French and German representatives meet and sign an armistice - an agreement to stop fighting Legacy of the war 8.5 Million soldiers dead Death of countless civilians by disease, starvations, and slaughter War devastates economy of European countries A Flawed Peace German cartoon: Versailles sends Germany to the guillotine. The Allies meet The Big Four: Woodrow WilsonUnited States David Llyod GeorgeBritain Vittorio Orlando- Italy George Clemenceau- France Wilson’s 14 Points End to secret treaties Freedom of the seas and free trade Reduced national armies and navies Adjustment of colonial claims with fairness toward colonial peoples Creation of new nations Self determination- allowing people to decide for themselves under which government they wished to live Treaty of Versailles Adopting Wilson’s 14th point, the treaty created the League of Nations- an international association whose goal was to keep peace among nations Germany punished harshly Lose territory Severe restrictions on military “war guilt” clause- places sole responsibility of the war on Germany. Germany was forced to pay war reparations. New nations form New nations emerged where Ottoman and Austrian empires stood Austrian Empire Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Austria and Hungary Ottoman Empire Palestine, Jordan, Syria, Turkey, and Lebanon Russia lost land as well Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia Poland established from Russia and Germany Treaty causes trouble Countries felt cheated by treaty African and Asian territories were not granted independence Italy and Japan gain less than what they had wanted War guilt clause left a bitterness in German people