* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - coach sambrooks
Survey
Document related concepts
French Revolutionary Wars wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the French Revolution wikipedia , lookup
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Vincent-Marie Viénot, Count of Vaublanc wikipedia , lookup
Louis XVI and the Legislative Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
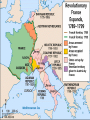
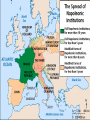
The French Revolution and Napoléon Section 1: The Roots of Revolution Section 2: The French Revolution Section 3: The French Republic Section 4: The Napoléonic Era Section 5: A Return to Peace The Roots of Revolution Objectives: –Describe how the Old Regime was structured. –Analyze why discontent began to grow in the mid-1700s. –Explain why Louis XVI wanted to call the Estates General. –Describe how the meeting of the Estates General pushed France toward revolution. The Old Regime The privileged estates – First Estate was clergy • Less than 1% – Second Estate was nobility • Less than 2% The Third estate – Bourgeoisie (urban middle class) • • • • • City workers Artisans Rural peasants Paid heavy taxes Paid a forced tithe to the church – 10% of income Growing Discontent Increased population and cost of living – The poor blamed the king for letting the cost of living get so high Bourgeoisie wanted liberty and equality – Resented paying taxes when nobility and clergy did not The Financial Crisis Assistance to United States during American Revolution led to France’s increased debts Louis XVI married Marie-Antoinette – Daughter of Austrian Empress – People resented her Austrian roots and political involvement Louis XVI tried to raise taxes – Hoped a meeting of all three estates would approve new taxes Banks refused to loan French government more money The Meeting of the Estates General The three estates had previously met separately – They would then come together and get 1 vote per estate Third Estate wanted representatives to vote as individuals – King refused Third estate declared themselves the National Assembly and asked the other two to work with them The French Revolution Objectives: –Explain why and how the French Revolution spread. –Analyze how a constitution changed French government. –Explain why the monarchy and the Legislative Assembly came to an end. The Spread of the Revolution Louis XVI allowed the three estates to meet together, but brought in troops to Paris – People thought he was going to force out the National Assembly so they took action Capture of Bastille prison led to formation of a new government (Video ) – General Lafayette lead National Guard – New flag of red, white, and blue replaced old French flag Peasants developed “Great Fear” – Feared what noble might do so they attacked manorial estates • Burn records • Pillaged supplies The End of the Old Regime The Declaration of the Rights of Man – Basic human rights and political powers • Similar to the Bill of Rights – Applied to men only Émigrés and royalists – Émigrés – French word for emigrants • Would cause trouble • Allowed nobles asylum in England, Germany, and Switzerland – Forced Louis XVI and family to return to Paris Reforms in government – Divided France in 83 equal districts called departments – Seized land owned by Catholic Church – Pope protested • Catholic Church was against revolution The Constitution of 1791 Limited powers of king – Could not make or block laws on his own Divided government into three branches: – Executive – king – Legislative – Legislative Assembly • If you were part of the National Assembly you could not be a part of this – Judicial King reluctantly agreed to this – Worked behind scenes with Émigrés to stop revolution – Tried to escape, but was caught – Made people distrust him and want a republic The Legislative Assembly and War Executive branch was weak Legislature was inexperienced – Divided into: • Conservatives – thought revolution had gone far enough • Radicals – wanted more drastic changes • Moderates – no extreme views Legislative Assembly united to wage war on Austria (video) – Other European monarch wanted a king on the throne of France – This united the Assembly – They prepared for war with Leopold II of Austria and Frederick William I of Prussia The End of the Monarchy Louis XVI plotted with foreign powers to overthrow Constitution of 1791 – Citizens realized this • Abolished monarchy • Imprisoned royal family • Defended Paris against Austrians Legislative Assembly ended National Convention drew up new constitution The French Republic Objectives: –Explain how the National Convention ruled France. –Describe how the Reign of Terror affected France. –Identify the Directory and explain how it ruled. –Analyze why Napoléon was able to come to power. The National Convention Universal manhood suffrage – Every adult male could vote Three main groups – Girondins • Feared domination of France by Paris – Jacobins • Wanted Paris to dominate France • Lead by Georges-Jacques Danton and Maximilien Robespierre – Delegates who had no definite views One of the first acts of the national convention was to try and convict Louis XVI of endangering the nation – He was beheaded by the Guillotine (video) Exporting the Revolution Committee of Public Safety – Set up a tribunal to deal with any opponents of the revolution – Adopted the draft • Conscription – requiring military service Opposition – European monarchs formed an alliance against France – Didn’t want their people getting any revolutionary ideas The Reign of Terror Evolutionary Tribunal – Tried to suppress all opposition and revolts within France – Robespierre actually turned on Danton and had him executed – He himself was eventually sent to the guillotine Work of the National Convention Abolished slavery Planned public education Adopted metric system Created a new calendar – It did not survive The Directory Governed by five individuals from the government’s executive branch Bicameral legislature – Lower house had 500 representatives • Created legislation – Upper house had 250 representatives • Accepted or rejected legislation Eliminated universal manhood suffrage Weak, corrupt rulers – Paved the way for a military dictatorship of France Napoléon Bonaparte Personal Bio – Born in 1769 on island of Corsica – Great organizational skills – 5’2” with a strong personality – Married Josephine Beauharnais • French societal leader • Within weeks of marriage he was in Italy fight Austrians Rise of Napoléon – Strong military leader – Gained control of all northern Italy for France Napoléon takes power (video) – Coup d’état (stroke of state) due to unstable government The Napoléonic Era Objectives: –Identify the ways in which Napoléon’s government was successful. –Explain how France became an empire. –Describe how Napoléon reorganized Europe. –Analyze the events that led to Napoléon’s final defeat at Waterloo. Napoléon as Dictator 1799 – 1814 The Consulate – People accepted Napoléon as dictator – Gave people freedom as long as his orders were displayed – Allowed people to up or down vote his new laws – Napoléon gave himself unlimited power Accomplishments in government – Napoléonic Code – French Law – Bank of France – National Bank – Public education – included high schools – Concordat - agreement with Pope • Recognized that most French citizens were Catholic • Still granted religious freedom Napoléon as Emperor French people voted to become an empire Napoléon crowned himself – Took crown from Pope just before it was placed on his head Defeated Austria and Russia Blockade of British Isles The Reorganization of Europe Dissolved the Holy Roman Empire Increased nationalism – Napoléon placed members of his own family as monarchs of countries he conquered – Loyalty and patriotism The Peninsular War – Spanish and Portuguese revolt against French rule – Aided by Britain and Duke of Wellington – Won the revolt and continued the idea of the French revolution Catastrophe in Russia The Grand Army – Marched to Russia – Russians retreat using a scorched earth policy • Burned and destroyed everything in retreat – Were defeated through lack of proper housing and supplies, Russian winter Final defeat – Western European countries allied against France • Russia, Prussia, Great Britain, and Austria • Defeated Napoleon and put Louis XVIII The Hundred Days Napoléon led army into France and ruled for one hundred days until Britain, Prussia, and Netherlands were victorious and forced him into exile Sent to St. Helena – Small island in South Atlantic Tried to poison himself, but overdosed Eventually died there Failures forgotten, became legendary A Return to Peace Objectives: –Describe how the Congress of Vienna attempted to restore stability to Europe. –Explain why politicians practiced conservative policies. –Analyze how Metternich influenced conservative politics and stopped revolution. The Congress of Vienna Austria, Great Britain, Prussia, Russia and France attended The principles of the Congress of Vienna – Compensation – pay back countries Napoleon took from – Balance of power – no single nation could control Europe – Legitimacy – all former ruling families should be restored to their thrones Compensations – Countries were reshuffled Reactionary Alliances Restored balance of power Emphasized conservative view to prevent revolution Establish the quadruple Alliance – Early form of U.N. The Age of Metternich Secret police Military suppression – Against revolutionary ideals Underground resistance