* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BLOOD SPATTER
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Hemorheology wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
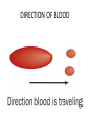
BLOOD SPATTER COHESION A KEY PROPERTY OF BLOOD • Blood is a water based substance, creates property of blood known as cohesion – Cohesion – molecules of the same substance attracting one another • Surface Tension- molecules do not want to separate from one another FACTOR EFFECTING SIZE OF SPATTER PASSIVE DROP • PASSIVE DROP – DROP THAT FALLS ON ITS OWN DUE TO ONLY GRAVITATIONAL FORCES – INITIAL SIZE OF DROP • Bigger drop = Bigger SPATTER – HEIGHT / VELOCITY OF DROP Effect of Height/Velocity of Pattern of Blood Spatter • Increase VELOCITY = Increase in DIAMETER of SPATTER in PASSIVE drops of blood – Passive drop increases velocity as it falls due to effects of gravity. – Spatter will not become larger at heights above 7 feet • Droplet reaches TERMINAL VELOCITY due to friction – Terminal velocity – maximum velocity • Increase VELOCITY also creates – Increased SPIKES – Increased SATELITES 4 PHASES OF IMPACT • CONTACT AND COLLAPSE – Blood droplet flattens on impact • DISPLACEMENT – Blood droplet spreads out • DISPERSION – Some particles fly off main drop at edges • RETRACTION – Particles not completely separated suck back into main drop due to adhesive forces SATELLITES AND SPIKES • Satellite droplets—drops that have been separated from main droplet – When blood falls from a height, or at a high velocity, – It overcomes its natural cohesiveness, and – Separates from the main droplet • Spiking patterns—drops that don’t make it completely away form main drop – Cohesion causes particles not completely separated to retract back into main drop – Form around the droplet edges Spikes and Satellites • Use terms collapse, displacement, dispersion, and retraction to describe how satellites and spikes seen below have formed. DIRECTION OF BLOOD EFFECT OF ANGLE ON SPATTER CALCULATING ANGLE using TRIGONOMETRY • ANGLE = INVERSE SIN (OPPOSITE/HYPOTENUSE) Distance A-B is OPPOSITE Distance B-C is HYPOTENUSE • IF OPPOSITE = 1.5 cm and HYPOTENUSE = 3.0 cm … – Calculate angle above • OPPOSITE / HYPOTENUSE = WIDTH / HEIGHTH – THEREFORE … CALCULATING ANGLE USING TRIGONOMETRY • THEREFORE ANGLE = INVERSE SIN (WIDTH / LENGTH) Lines of Convergence • Lines of convergence—two or blood splatters can pinpoint the location of the blood source – Circled area shows where lines converge = source