* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
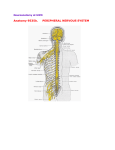
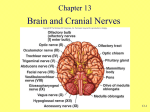
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves – 1 Human Neurobiology ANHB 2217 Avinash Bharadwaj Semester 1, 2006 Week 2 Brainstem and Cranial Nerves Two topics in one…? 10 out of 12 cranial nerves attached to brainstem. Anatomically and functionally inseparable! For ease of understanding : Lecture 1 : General features and important concepts. Lecture 2 : More details of cranial nerves and brainstem. Brainstem Rostral part of the brain Similarities with the spinal cord Attachments of nerves – cranial nerves Masses of grey matter inside Tracts of white matter Special features Other nuclei and their connections Central canal, fourth ventricle Distinct regional morphology Connections with the cerebellum Reticular formation And more…! Brainstem :Major Divisions Cerebellar peduncles Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Superior Middle Inferior Lab exercise! … And what are the other parts seen here? Cranial Nerves Unlike spinal nerves… No constant pattern Motor, sensory or mixed Special sensory nerves (vision, taste, hearing etc) Twelve pairs Attached to the brainstem except first two. Understanding of functions and pattern important! Names and Numbers… Understand the names! Olfactory I Facial VII Optic II Vestibulocochlear VIII Oculomotor III Glossopharyngeal IX Trochlear IV Vagus X Trigeminal V Accessory XI Abducens (t) VI Hypoglossal XII Attachments III IV I Cerebrum II Diencephalon III, IV Midbrain V Pons VI, VII, VIII Junction : Pons-Medulla IX, X, XI, XII Medulla oblongata V VI XII VII, VIII IX X XI Cranial Nerve Nuclei Motor nuclei Groups of neurons whose axons form a motor nerve Compare with cells of ventral horn of spinal grey matter. Sensory nuclei Groups of neurons that sensory nerve fibres synapse with. Axons from these nuclei go to other parts of the CNS. Compare with cells of spinal cord (dorsal grey matter) which give rise to tracts. Functional Components Efferent (Motor), Afferent (Sensory) Somatic : To / from “body wall” structures Visceral : To / from visceral structures (smooth/cardiac muscle, glands) General Special Special senses or developmentally “special” structures Such components are described for spinal nerves also, we shall understand them better with the ANS. Functional Components Nuclei (Neurone groups) SSA Alar Basal GSA SVE SVA GSE GVE GVA Brainstem Organisation Tracts Long tracts passing through Tracts beginning or terminating in the brainstem Tracts within the brainstem Nuclei Nuclei of cranial nerves Other nuclei Reticular formation But first, some general features of the brainstem! Medulla Oblongata IV Ventricle ICP P O Inf. cerebellar peduncle Pyramid and Olive G Cu Central canal Cuneate and gracile tubercles Pons Tegmentum Basilar Basilar part, tegmentum, MCP MCP Midbrain Tectum SC Tegmentum Crus Nerve III and Midbrain Oculomotor “Extrinsic” Muscles of the eyeball : GSE Nucleus close to the midline Constrictor of the pupil (smooth muscle) GVE Edinger-Westphal nucleus SC ST CP III RN SN C-Sp CP Nerve IV IC Trochlear nerve A muscle of the eyeball winds around a trochlea (pulley) GSE Exceptional course