* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overview of the Day
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
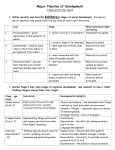
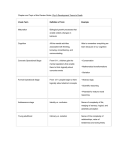
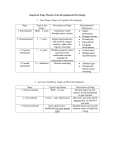
Overview of the Day Developmental Psychology - Part 2 Adolescence & young adulthood Middle age Old age Physical changes Adolescence: between the beginning of sexual maturity to independent adulthood Secondary sex characteristics Why are adolescents capable of having children when marriage is so much later? Why has onset of menarche occurring earlier in girls now (about 12-13, when in the past it was 13-15), even though marriage is much later? more fat in diet less physical activity Adulthood Physical capacity: heart, lung, energy expenditure, reaction time, sensory keenness all peak by early adulthood (mid-twenties ); because women mature earlier, their physical capacities peak earlier much of physical vigor is a function of regular exercise: use it or lose it (skiing 12 miles with PK who is mid 50s). people can still be extremely fit into their 60s and beyond, if they exercise regularly Menopause: secession of ability to bear children (onset typically occurs in late 40s) many women state that they feel better than they have in years after menopause grandmother hypothesis: care for their children’s offspring Cognitive changes Intelligence general intelligence does not decline much with age crystallized IQ (store of knowledge and reasoning strategies) increases and fluid IQ (general problem solving, free of content) decreases with age Memory? 20s is peak for memory but not all that bad when aging: recognition does not decline much with age (recall does); meaningful memory works well into old age (web of associations) same as with physical: use it or lose it (stay intellectually active) Senility (senile dementia) disturbance of higher order mental functions associated with age 5-20% of people become senile into 80s and 90s 50% of caused by Alzheimer (destroys neurons in the brain causing loss of memory, reasoning, and language impairment. Causes (genetic), loss of neurotransmitter acetylcholine (also myelin sheath); tangled neurons What is the relationship between age and performance at work? no relation At what developmental phase is a person’s age least predictive of her abilities and personality? Adulthood Social and moral development Kohlberg's theory of moral development stages of moral reasoning Erickson's theory of psycho-social development stages of social development Social clock: Culturally preferred timing for when one should leave home, marry, have children, and retire There is no rigid consensus on "social clock" cultural prescriptions. They vary by culture and subculture. Marriage and children 9 out of 10 adults marry; 75 % of those who divorce remarry (and are as happy as they were in 1st marriages) Marriage bonds are most likely to endure when . . . ? Couples maintain at least a 5 to 1 ratio of positive to negative interactions with each other When children grow up and leave home, mothers . . .? Report feeling happy Chance encounters Life course is not entirely predictable due to chance encounters Development: The bottom line Genes Peers Parents (neighborhoods, opportunities) Education; jobs Chance encounters Summary Development and maturation Conception and gestation Competent newborn Cognitive development Attachment Physical changes Social and moral development Marriage and children Chance encounters