* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WORLD WAR ii
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Resistance in the German-occupied Channel Islands wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian resistance movement wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States Navy in World War II wikipedia , lookup
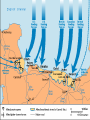
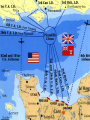
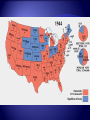
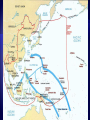
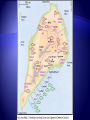
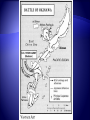
V. Victory in Europe 1. Allies target Italian island of Sicily as next step to invading Europe 2. Sicily (July 1943) – Allied forces led by U.S. Gen. George S. Patton and British Gen. Bernard Montgomery take control in less than a month 3. September 1943 – a) Italian king orders Mussolini’s arrest, Germans take him into hiding, eventually he reappears in northern Italy b) Italian government signs armistice with Allies, but Germans take over the fighting 4. January 1944 – Allied troops land at Anzio, near Rome – fierce fighting 5. June 1944 – Rome becomes first Axis capital to be taken by Allies 6. April 1945 – Mussolini is captured, shot and hung by his feet in Milan’s square 1. Operation Overlord a) Code name for the Allied invasion of France, led by Gen. Eisenhower b) Fortitude – Code name for fake operation led by Patton that would have landed at Calais, narrowest part of the English Channel c) June 6, 1944 (D-Day) – Description – 150,000 American, British and Canadian troops land along 50-mile stretch of Normandy coast, 25,000 paratroopers jump behind German lines German defenses – all heavily fortified Eisenhower unsure of mission’s chances Result – Germans caught off-guard, Hitler refused to send more troops, Allies advanced 15 miles in first week Very nearly failed, first units to land lost almost 90% of troops By nightfall 5,000 Allied troops were dead d) August 25, 1944 – Paris liberated by Allies e) September 1944 – first Allied troops enter Germany 1. November 1944 – FDR wins fourth term, beating New York Gov. Thomas Dewey 432-99 2. Liberation of Europe – Germany attacked from three directions – west (France), south (Italy), east (Eastern Europe led by Soviet Union) 1. Where? Heavily forested Ardennes region of Belgium, Luxembourg and France 2. What happened? 250,000 German troops attack unsuspecting Allied front in dead of winter, creating a bulge in the line 3. “NUTS!” – Gen. Anthony McAuliff’s response to German surrender demand 4. Result – Allied reinforcements push Germans back and restore line, last major German attack of the war 5. Casualties – 100,000 Germans killed, captured or wounded, 81,000 Americans 1. Yalta Conference (February 1945) a) What was it? Meeting between FDR, Churchill and Stalin to begin planning for postwar peace b) Result – Stalin pledges to declare war on Japan three months after Germany’s surrender Agree to divide and occupy Germany c) Creation of a new international peace organization 2. Race to Berlin a) Early 1945 – Air attacks take toll on German cities, Allied troops move in on Berlin from both sides Debate – Churchill wanted US and GB to take Berlin so Soviets wouldn’t try to claim seized territory, Eisenhower didn’t want military strategy decided by political concerns b) April 30 – Hitler commits suicide in his bunker deep under Berlin c) May 7 – Germans surrender unconditionally d) May 8 – V-E (Victory in Europe) Day VI. Victory in the Pacific 1. Air and naval forces played much larger role in Pacific than it did in Europe 2. Plan to take Japan – a) Island-hopping – troops would attack and seize only certain strategic Japanese-held islands and skip others b) Why? To cut off other Japanese islands from reinforcements and supplies 3. Battle of Leyte Gulf (Fall 1944) – a) The last, largest and most decisive naval fight of the war b) Result – Four Japanese carriers and two battleships sunk, Japanese navy no factor after this battle 4. February 1945 – MacArthur fulfills his promise to return to the Philippines Troops succeed despite fierce Japanese resistance 5. Code-talkers – Native Americans who created a code of key terms in their native language, never broken by Japanese 6. Kamikaze – Japanese for “divine wind,” refers to suicide planes sent into U.S. carriers and battleships 1. Bombing Japan – island victories give U.S. new bases to launch B-29 bombers at mainland Japanese islands 2. March 1945 – Bombing raids destroy much of Tokyo, lowers civilian morale but government won’t quit 3. Battle of Iwo Jima (February 19-March 26, 1945) a) Significance – 750 miles south of Tokyo, small island allows planes closer access to home islands b) First days – More fierce resistance encountered Picture of flag-raising on top of Mount Suribachi is one of the most famous photos in American history c) Took six weeks to completely eliminate the Japanese threat Much longer than expected d) Result – only 212 of 22,000 Japanese soldiers taken prisoner, almost 7,000 Americans killed and 18,000 wounded 4. Battle of Okinawa (April 1945) a) Largest U.S. landing force in Pacific invades small island 350 miles from southern islands of Japan b) Result – Bloodiest battle of the Pacific war, 49,000 American casualties and over 100,000 Japanese killed 5. April 12 – FDR dies in Georgia, Harry S. Truman becomes President 1. Manhattan Project – started in 1942, code name for project by a group of scientists to build an atomic bomb started in basement of a building at Columbia University, thus “Manhattan” name 2. Enrico Fermi and Albert Einstein – scientists who had warned the U.S. government about the threat of an atomic bomb built by the Axis 3. Major research labs – Oak Ridge, Tennessee (U-235 uranium), Hanford, Washington (plutonium) and Los Alamos, New Mexico 4. J. Robert Oppenheimer – head of the Los Alamos lab who helped build the first atomic bomb 5. July 16, 1945 – first successful atomic bomb test at Alamogordo, New Mexico, flash seen 180 miles away 6. July 26 – Japan refuses Allied demand for unconditional surrender, Truman authorizes use of atomic weapons 1. Why did Truman make this decision? a) Military leaders estimated that a land invasion of Japan would cause 1 million U.S. casualties, even more Japanese b) Truman wanted to show USSR that the U.S. had a powerful new weapon 2. August 6 – Bomber Enola Gay drops “Little Boy” on Hiroshima at 8:15 a.m., 75,000 killed 3. August 8 – Soviet Union declares war on Japan, invades Manchuria 10. August 9 – “Fat Man” dropped on Nagasaki, everything within 1/8 mile vaporized 11. August 15 – Japan surrenders 12. September 2 – Formal surrender signed on board USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay 13. Total death toll from both bombings by end of 1945 – 200,000 VII. Costs of War 1. Genocide – The systematic annihilation of a political, racial, or cultural group. 2. Prejudice – a feeling directed at another person or group before you get to know them 3. Anti-Semitism – a feeling of hostility towards the Jewish people 4. Ethnocentrism – the feeling that your ethnic group is superior to others 5. Concentration Camps – used the Jews as a slave labor force to keep the German war machine going 6. Death Camps – included Auschwitz and Treblinka in Poland among others, place where Hitler’s “Final Solution” was carried out by killing Jews 7. Result – 6 million Jews killed, 2/3 of all European Jews, 5 million others including Gypsies, Poles, mentally disabled, religious and political prisoners Full extent of the Holocaust wasn’t discovered until after Germany was defeated 1. Unprecedented death toll and property damage 2. Nazi government and Japan’s military warlords destroyed 3. Towns, cities, buildings, artifacts and forests were destroyed 4. Millions lacked heat, running water, adequate food and the means to travel from one place to another Military Dead Military Wounded Civilian Dead Britain 373,000 475,000 93,000 France 213,000 400,000 108,000 Soviet Union USA 11 million 14 million 7 million 292,000 671,000 N/A Germany 3.5 Million 5 million 780,000 Italy 242,000 66,000 153,000 Japan 1.3 million 4 million 672,000