* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 17.2 Notes - Cloudfront.net
Operation Green (Ireland) wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
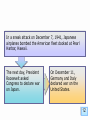
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
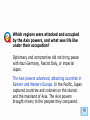
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
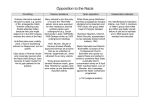
17.2 Notes: The Axis Advances Objectives • Describe how the Axis powers came to control much of Europe, but failed to conquer Britain. • Summarize Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union. • Understand the horror of the genocide the Nazis committed. • Describe the role of the United States before and after joining World War II. 1 Hitler used the tactic of blitzkrieg, or “lightning war,” to overrun much of Europe, starting with Poland. The German air force, the Luftwaffe, bombed airfields, factories, and cities in Poland. Then, fastmoving tanks and troops pushed their way in from the west. Meanwhile, Stalin’s forces invaded Poland from the east. Within a month, Poland ceased to exist. 2 Hitler waited out the winter. Then, in the spring of 1940, German forces overran Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Belgium. Next, German troops poured into France, trapping the retreating British forces at Dunkirk. British vessels crossed the English Channel and ferried more than 300,000 British troops to safety. 3 Germany continued to attack Western Europe. • German forces headed to Paris. With Italy attacking from the south, France was forced to surrender in June 1940. • Germany occupied northern France and set up a puppet government at Vichy in southern France. 4 • Next Hitler set his sights on Britain, calling this planned invasion “Operation Sea Lion.” • In September of 1940, the Luftwaffe began 57 straight nights of showering high explosives and firebombs on London. 5 London did not break under the Nazi blitz. • Citizens carried on with their daily lives, seeking protection in shelters and subways. • The Luftwaffe could not gain superiority over Britain. Operation Sea Lion was a failure. 6 Despite his failure to conquer Britain, Hitler seemed unstoppable. • German armies under the command of General Erwin Rommel pushed into North Africa. • In addition, Axis armies invaded Greece, Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, and Hungary. • By 1941, the Axis powers or their allies controlled most of Europe. 7 Who is this? “How long will the honeymoon last”? In June 1941, Hitler broke the Nazi-Soviet Pact when he attacked the Soviet Union. The attack stalled during the winter when thousands of unprepared Germans froze to death. Leningrad withstood a two-and-a-half-year siege. Stalin made an agreement to work with Britain. 8 Japan and Germany set out to build a “new order” in the lands they occupied. • Japanese troops seized crops, destroyed cities, and brutally treated local Chinese, Filipinos, and other conquered people. • The Nazis sent millions of Jews and political opponents to concentration camps. • The Nazis also targeted other groups they considered “inferior,” including Gypsies, Slavs, homosexuals, the disabled, and the mentally ill. 9 By 1941, Hitler had devised plans for his “Final Solution”—the extermination of all Jews in Europe. At special death camps in Poland, some six million Jewish men, women, and children were systematically murdered. 10 The scale and savagery of the Holocaust are unequaled in history. Young survivors of Auschwitz, the largest Nazi death camp. The United States declared neutrality, but Roosevelt wanted to be prepared for war. • In August 1941, he met secretly with British Prime Minister Winston Churchill to create the Atlantic Charter. Its goal was to destroy the Nazi reign. • Roosevelt persuaded Congress to pass the LendLease Act, allowing the United States to sell or lend supplies to Britain. • At the same time, tensions between the United States and Japan grew after the United States banned sale of war materials to Japan. 11 In a sneak attack on December 7, 1941, Japanese airplanes bombed the American fleet docked at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The next day, President Roosevelt asked Congress to declare war on Japan. On December 11, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States. 12 The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor brought the United States into World War II. As the United States mobilized for war, Japan expanded deeper into Asia. 13 Which regions were attacked and occupied by the Axis powers, and what was life like under their occupation? Diplomacy and compromise did not bring peace with Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, or imperial Japan. The Axis powers advanced, attacking countries in Eastern and Western Europe. In the Pacific, Japan captured countries and colonies on the islands and the mainland of Asia. The Axis powers brought misery to the peoples they conquered. 14 Terms and People • blitzkrieg – “lightning war” using improved tanks and airpower • Luftwaffe – German air force • Dunkirk – site of British troops stranded in France, and their rescue by sea • Vichy – location in France of Germany’s “puppet state” • General Erwin Rommel – German general known as the “Desert Fox” Terms and People (continued) • concentration camps – Nazi detention and killing centers for civilians considered enemies of the state • Holocaust – the systematic genocide of about six million European Jews by the Nazis during World War II • Lend-Lease Act – law allowing FDR to sell or lend war materials to those who were fighting for freedom