* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US breaks Japanese secret communications code
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in Japan during the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Pearl Harbor (film) wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Magic (cryptography) wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
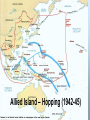
Unit 13: Part 2 Japan, Pearl Harbor and War Section 1 Japans ambitions in the Pacific “Co-Prosperity Sphere of Influence” • With the fall of France and Britain under siege, colonies in Pacific are unprotected. • July, 1941: Japan takes over French bases in Indochina (today Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos)… threatens move on Dutch East Indies • need oil, rubber, tin U.S Reaction to Japanese Aggression • FDR freezes Japanese assets in the U.S. • Places embargo on sales of scrap steel and aviation fuel to Japan U.S. breaks Japanese secret communications code Learns that Japan is preparing for a strike - Did not know from where attack would occur Peace talks fail - Dec. 6th: Japan rejects U.S Sec. Of State Cordell Hull’s proposal to release Japanese assets in return for Japan’s withdrawal from China and French Indochina… Japan Attacks the United States Pearl Harbor: Home of the U.S. Pacific Fleet Japanese planes prepare to take off for the Pearl Harbor attack Torpedo exploding into USS West Virginia, as seen from Japanese plane USS Utah took a torpedo hit and capsized early in the battle The wreck remains at Pearl Harbor U.S.S. Arizona “A date that live in infamy…” http://www.historyofwar.org/Pictures/PearlHarbor04.jpg • American casualties: 2403 killed, 1,178 wounded • 21 ships; 300 aircraft damaged or destroyed US Enters the War • December 8, 1941 US declares war on Japan • December 11, 1941 Germany declares war on the United States FDR http://dase.laits.utexas.edu/media/american_politics_collection/viewitem/000117156_400 . jpg Americans join war effort Demand for GI’s • 5 million volunteered • 10 million drafted • Labor shortage at home 6 million women join labor force 2 million minorities hired American Industry responds • Automobile plants were converted to build tanks, armored vehicles, etc. • Factories across nation convert to war production • Shipbuilder Henry J. Kaiser – Liberty ships, tankers, carriers The American Homefront • The United States government stirs patriotic feelings • Movies are used to build morale • Propaganda is used to keep war effort going: 1. Bugs Bunny Racist Propaganda • People rationed goods/supplies and started Victory Gardens http://www.ethicurean.com/wp-content/uploads/image/plant-victory-garden.jpg Continued War Effort http://z.about.com/d/politicalhumor/1/0/R/O/propaganda_quiet.jpg http://www.teacheroz.com/images/homes.gif http://www.usmm.org/p/looselips.jpg http://bss.sfsu.edu/tygiel/Hist427/1940sphotos/posters/ridewithhitler.jpg Women Enter the Workforce http://www.edupics.com/en-coloring-pictures-pages-photo-rosie-the-riveter-p7219.jpg http://www.rosietheriveterphotos.com/images/070705172615_Woman_Working_a_ War_Job_LG.jpg Japanese Americans Interned • Japanese-Americans (Nisei) • Thousands of Nisei were forced into internment camps in the West & Southwest http://peacecorpsonline.org/messages/imagefolder/japaneseinternment.jpg Internment Camp Poston, AZ http://education.eastwestcenter.org/asiapacificed/ph2006/PH2006projects/7_clip_image001.jpg End of Sec. 1 Notes • HW: read Sec 1 of Required Reading and do the worksheet…. • You can find both of these docs on my Web page With the U.S. now at war: • We’ll divide our study of the war into 2 geographic areas: Section 2 • The Eastern Theater of Operations (the ETO)…Europe and No. Africa Section 3 • The Pacific Theater of Operations (the PTO) The Nazis had broken their pact w/USSR: Operation Barbarossa (June 1941) By 1942 : War not going well for the Allies: – Germany controlled all of Europe and N. Africa and were deep into Russia Gloomy Prospects for the Allies The chain of spectacular victories disguised fatal weaknesses within the Axis alliance: Japan and Germany fought separate wars, they never coordinated strategies. The early defeats also obscured the Allies’ strengths: The manpower of the Soviet Union and the productive capacity of the United States. Turning Points of the War: The Battle of Stalingrad • The Pivotal battle in the war in Europe – Enemy at the Gates • The German Army (“Wehrmacht”) had already lost 2 million men on the eastern front. • In 1942-43, a German army of over 300,000 was defeated and captured at the Battle of Stalingrad. • After losing a massive tank battle at Kursk, the Germans began a long retreat home… • The Red Army crossed into Poland in January 1944. Stalingrad House by house… Brick by brick North Africa: El Alamein • In 1942 German forces tried to seize Egypt and the Suez Canal • American invasion: “Operation Torch” • Yanks and Brits drove Germans out • Turning point in N. Africa: El Alamein Defeat of Italy (1943) • Invasion of Sicily opened door for invasion of Italy • Allies fought their way north up the “boot” • Mussolini forced to flee… captured , executed, and hung by his heels by anti-Mussolini Italians Sec. 3 The Doolittle Raid (April 1942) • Col. Jimmy Doolittle (related to me!) put together mission to bomb Tokyo & other targets IN Japan • Bombers taking off a carrier? • Military value? Not much • Psychological value? HUGE morale boost for American public • Movie Trailer: Thirty Seconds Over Tokyo The Pacific Theater: Early Battles • American Forces halted the Japanese advance in two decisive naval battles. – Coral Sea (May 1942) • U.S. stopped a fleet carrying Japanese troops to New Guinea • Japanese designs on Australia ended – Midway (June 1942) • Japanese Admiral Yamamoto hoped to capture Midway Island as a base to attack Pearl Harbor again • U.S. Admiral Chester Nimitz caught the Japanese by surprise and sank 3 of the 4 aircraft carriers U.S. strategy to defeat Japan: “Island-hopping” • No need to capture EVERY island… “hop” over some, leaving Japanese troops isolated • 1 island chain after another Allied Island – Hopping (1942-45) U.S. Marines assault an island Europe: Operation Overlord • Stalin had pressed FDR and Churchill for over a year to open a 2nd front against the Nazis…a cross-Channel invasion • All logistics in place for the invasion of Normandy, France in June, 1944 June 6, 1944: D - Day • Combined American, British, Canadian assault • Dwight D. Eisenhower: Supreme Allied Commander Invasion of Europe (con.t) • Allies cont. drive into France…by Aug., 1944: liberation of Paris The Allies Advance •Into Holland: “Operation Market Garden” •Into Belgium: •Nazis mount major counter-offensive •Battle of the Bulge Germany’s Defeat Americans advanced into Germany from the west while the Russians closed in on Berlin from the east American and Russian soldiers meet at the Elbe River Berlin 1945 Hitler’s Last Days In the underground bunker: committed suicide with companion Eva Braun With Berlin in ruins, the Nazis surrendered May, 1945 Victory in Europe at last Time Magazine cover - 1945 Allies learn of the Holocaust: A Nazi Labor Camp Somewhere in Germany From: Band of Brothers (HBO, 2001) The Allied Leaders met several times during the War to discuss goals and to map strategy : Yalta Conference: Feb. ‘45 The most important conference was at Yalta: Churchill, FDR, & Stalin The Allies were clearly winning the war and the end seemed near. The questions of what would happen once Germany was defeated were of huge importance: Stalin claimed that historically, Poland had been used as a corridor to invade Russia… He therefore believed it was critical that Poland become a “buffer zone” , meaning that a Polish gov’t friendly to Russia was necessary Translation: “friendly” gov’t = communist gov’t. The Big 3 agreed that free elections were to be held in Poland…let the people decide A 2nd point: USSR would enter war against Japan once Germany was defeated A 3rd point: Germany would be divided and occupied by the Allies Other points of agreement: War-crimes trials Further discussion on creating a United Nations In the Berlin suburb of Potsdam: Churchill Truman (FDR had died) Stalin Stalin balked at free elections in Poland Discussed specifics of Germany’s occupation after the war The capital city which lay entirely in the Russian zone of occupation was ALSO divided into 4 zones Focus turns to Japan US continues “island-hopping” strategy Goal: control of islands close enough to Japan to stage bombing raids FDR had died in office and new President Harry S. Truman learned of a new weapon. He ordered it to be used No surrender: Japanese military attempted a coup to seize power from the Emperor…wanted to continue to fight Aug. 9th: 2nd bomb on Nagasaki Quint's monologue (Jaws, 1976) The U.S.S. Indianapolis