* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Propaganda in Japan during the Second Sino-Japanese War and World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
American propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
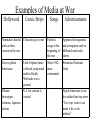
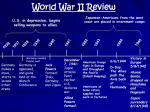
World War II U.S. Enters the War • After the attack on Pearl Harbor the U.S. enters the war-1941 Objectives of the War • The defeat of Germany was Top Priority • Unconditional surrender would be acceptedsurrender without any concessions • US would fight a defensive war against Japan • Allies fight to defeat the Nazis War at Home • Attack on Pearl Harbor ends the debate about intervention in World War II • Most people now believed the war was needed to fight for the FOUR FREEDOMS – Freedom of Speech and Expression – Freedom of Worship – Freedom from Want – Freedom from Fear GIs • American Soldiers called themselves GIs after the Government Issue stamp that was on all of their belongings • Many soldiers were drafted • Many volunteered after Pearl Harbor was bombed – Patriotism, anger towards Nazis, adventure, joblessness Women in the Army • Women were used in all areas except combat – Typists, clerks, control tower operators, radio operators, parachute riggers, mechanics, ferried planes around country, and towed targets from antiaircraft gunnery practice African Americans • Were officially segregated in the Military • Commanded by White Officers • Had jobs as cooks and laborers • Approximately 1 million served in the armed forces • Only at end of war, when there was a shortage of soldiers were they allowed to fight – General Dwight D. Eisenhower believed that integrated troops were more successful in combat Other Minorities • Hispanic-Americans – 350,000 served in the armed forces – Were the most decorated ethnic group from the war – Suffered from discrimination as well Minorities Continued • Native Americans were drafted and some volunteered – Navajo Code Talkersnative language was used by marines to transport messages by radio and phone – Outwitted Japanese by sending messages in code Minorities Continued – Japanese-Americans • Offered to fight despite discrimination suffered by families back home • 442nd Regiment became the most decorated unit in the war Improvements on the European Front • Battle for Stalingrad, Spring 1942 – – – – By September, Nazi troops begin major assault on Stalingrad Battle continues for 5 months: February 1943 Germans surrender Russia suffered more casualties than U.S. in entire war Stalin does not forgive Allies for failing to help • Didn’t want to face a winter deep within Russia • 1943-Allies now move into Italy via bases from North Africa thru Sicily – Italians overthrow Mussolini after the invasion of Sicily • September 8th unconditional surrender – Germans in Italy dug in and contested every Allied move • June 1944 Allies liberate Rome Africa Campaign • Operation Torch – North African Campaign 1942British gain victory at El Alamein, Egypt • Turning Point – Axis powers forced to surrender • May 1943 Atlantic Ocean • By late 1943 advances in SONAR technology allowed detection of submerged objects by means of sound waves – Allies have the edge on locating and sinking Uboats Pacific Improvements • May 1942 US forces begin to reverse the Japanese – Battle of Coral Sea: stop Japanese from advancing towards Australia • Midway Island – Last offensive Japanese operation in the war – U.S. won and reduce threat to Hawaii • Adopt a policy of “Island Hopping” – Surround Japanese strong holds and cut them off from supplies – Build bases from which to attack Philippines and eventually Japan itself st 1 US Offensive Battle • Guadalcanal – U.S. now has offensive in Pacific war – November of 1942- U.S gains control of waters around islands cutting of Japanese supply lines • Have to fight Jungle Warfare on the island • Battle enemy and jungle environment – Heat, humidity, rotting gear, poisonous insects, and tropical fevers – 1943 U.S. secures the island • 1st territory Japan loses Office of Civilian Defense • To raise and maintain the country’s morale, citizens were asked to contribute “An Hour A Day for the USA” Choose from a number of Civilian Defense Projects “Victory Gardens” • Some Americans helped by growing their own vegetables – Farmers were busy feeding the army – 40% of all vegetables grown, during the war, planted in Victory Gardens Materials for the War • Anything that could be turned into armaments was collected for the war effort – Newspapers, rubber, scrap metal, aluminum pots, tin cans, box springs • 1942-Paper collection temporarily called off b/c some so much was collected • Much of the steel, half the tin, and half the paper that was needed to fight the war was collected by citizens Media Goes to War • Government creates the Office of War Information – Function was to coordinate war news from various federal agencies – Encourage newspapers, radio stations, and movie industry to help Americans understand the progress of the war and government’s policies Examples of Media at War Hollywood Comic Strips Songs Advertisements Filmmakers hard at Characters go to war work on their version on the war Patriotic songs at the beginning of the war Appeared in magazines and newspapers and on billboards and radio shows Heroes-gallant Americans After 1942more sentimental Stimulated National Unity Little Orphan Annie collected scrap metal and her Daddy Warbucks was a general VillainsG.I. Joe cartoon is Stereotypes created Germans, Japanese, Italians Urged Americans to use less rather than buy more “Use it up, wear it out, make it do, or do without” New Markets and Methods • War Production Board – Helped to convert industries to war production • Convert factories from civilian to military production – Limit the production of materials not essential to the war effort » From shirts, toys and cars to uniforms, bombs, tanks, and aircraft New Plants and Over Production • Government paid companies to build new plants – Helped pay equipment as well – Granted relief from antitrust laws to war-related industries – Such a surplus of armaments that eventually asked plants to stop production Wartime Economy • Economy grows during the war – Gross National Product – Dollar value of all good and services produced annually • Rises from $90.5 billion to $211.9 billion – War creates 17 million new jobs – Farm production increases Economy Grows too Fast • FDR worries about inflation – General rise in wages and prices • 1st he freezes wages – Trade Unions oppose a wage freeze – Promise a No-Strike pledge during the war • FDR creates the National War Labor Board – Control wages and monitor inflation • Workers also want prices controlled – Office of Price Administration set a ceiling on all prices • Reasonable balance in achieved throughout the war Keeping Prices Down • Rationing – Distributing limited goods fairly – Reduces demand for goods • Controversial b/c even though people were earning more, they were restricted in their spending Paying For the War • Taxes met 40% of the war costs • 1942-Revenue Act passed – Increase corporate taxes and requires nearly all American to pay income taxes • 1943-Congress approves system for withholding taxes through monthly payroll deductions Paying for the War Cont. • Government borrows the rest of the money – War Bonds-certificates that promised that the government would pay the holder the amount borrowed plus interest • Also helped to control inflation • Hollywood stars helped to sell bonds • War stamps-children collected them and when they had $18.75 worth of stamps they received a bond for $25.00 in 10 years • Families of those who served in the armed forces bought war bonds to help them invest their money while they were away Women on the Home Front • Married women now working-6 million women joined the civilian labor force • Now working non-traditional roles – Factories • Defense Industries:Airplane Manufacturing and Shipbuilding • Increase in African American women in the work force Women’s Roles Continued • Problems – Restrictions imposed by managers, no fraternization between men and women – Women worried about leaving children – Low wages • 60% less then men – Little job security – End of the war women are urged to return home • 4 Million women either lost their job or left the workforce Japanese-American Internment • Rumors of sabotage after Pearl Harbor • Japanese were placed in internment camps – Citizens and non-citizens – Camps located in desolate areas – Wooden barracks covered with tar paper and protected by bared wire Road to Victory-Europe • Air attacks against Germany in 1943-44 softened German resistance • Operation Overlord-drive Germans out of France and defeat the the Third Reich • D-Day June 6, 1944 • Land, sea and air invasion – Beaches at Normandy, Eisenhower • August 1944 Paris is freed • Battle of the Bulge-December 1944 German counterattack • Last Offensive German Move Allies moved into Germany End of War in Europe • Final Assault on Germany early 1945 • April 12th FDR dies after 12yrs in office – Truman takes office • April 30, 1945 Hitler commits suicide in a Berlin bunker • May 2 Berlin Falls • May 7, 1945 Germany’s unconditional surrender • May 8, victory in Europe Day End of War in Pacific • • • • By 1944 bombers close enough to attack Japanese mainland Truman scheduled invasion for late 1945/46 By March of 1945 bombing Tokyo July 1945-J. Robert Oppenheimer successfully detonates 1st atomic bomb in New Mexico • Decision to bomb Japan – Invading Japan would result in high casualties figures • Up to a million deaths – Use of bomb in hopes of ending war without an invasion • August 6, 1945 – Enola Gay dropped “Little Boy” on Hiroshima • Killed 100,000 plus people instantly another 100,00 die later from burns, radiation, or other wounds • 4 square miles of city destroyed • August 9, 1945 – “Fat Man” dropped on Nagasaki killing 40,000 plus people – August, 1945 Japan formally surrenders