* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fighting World War II
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
India in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
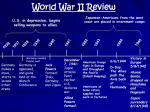
Fighting World War II 1941 – 1945 America Declares War 12/8/1941 – Declaration of war on Japan 12/11/1941 – Germany & Italy declare war on the U.S. U.S. and Great Britain decide to focus on Germany first Declaration of the United Nations (Grand Alliance) – 1/1/1942 – 26 countries met in Washington, D.C. – Pledged themselves to the principles of the Atlantic Charter – Promised no separate peace with common enemies Japan’s Empire U.S. lost islands of Guam, Wake Island, and Gilbert Island by the end of December, 1941 and the Philippines by March, 1942 – General MacArthur – “I shall return” Japan controlled: Singapore, Dutch East Indies, Malay peninsula, Hong Kong, & Burma by spring 1942 Resources – 95% of world’s raw rubber, 70% of tin, 70% of rice – Dutch East Indies supplied fuel “Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere” – “Asia for Asians” Recognition of independence for Burma, Vietnam, & Indonesia Nationalists fight back (Chiang kai-shek in China) Allied Defeats by mid 1942 Japan controls Guam, Wake Island, Hong Kong, Singapore, Burma, Dutch East Indies, & the Philippines – Bataan Death March – 85 mile forced march of U.S. soldiers who were tortured & eventually burned alive Doolittle Raid (April, 1942) – insignificant attack on Tokyo in response to Pearl Harbor German advances reach their peak – U-boats sink 8 million tons of allied supplies – Control Russia as far east as Stalingrad – Control North Africa as far east and south as El Alamein, Egypt Allied Turning Points (U.S.S.R.) Battle of Stalingrad (September, 1942) First major defeat of the Nazis on land Germany on the retreat until Russians reach Berlin in 1945 Stalin never forgives the Allies for not opening a 2nd front earlier (U.S. & Britain go to North Africa instead) Allied Turning Points (N. Africa) Operation “Torch” led by General Eisenhower (11/8/1943) British had been fighting General Irwin Rommel (“Desert Fox”) since 1941 Allies led by U.S. invade in Algeria & Morocco (Casablanca) Allied victory @ El Alamein Rommel pushed back to Tunisia, huge German casualties Germans retreat back to Europe Invasion of Italy Led by General George C. Patton 7/10/1943 – Allies land in Sicily, victory in a month Mussolini forced out of power by the Italians 6/4/1944 – Allies march into Rome Northern Italy remains under German control until spring of 1945 D-Day (June 6, 1944) “Operation Overlord” commanded by Eisenhower 120,000 troops land on 5 beachheads on the Normandy Coast of France – 800,000 men in 3 weeks, 3 million total – 2,245 Allied deaths, 1,670 wounded Significance: – Established a 2nd Front in Europe (U.S.S.R. happy) – Paris freed by August 25, 1944 – France, Belgium, & Luxemburg freed by end of summer D-Day Invasion of Germany Pre-invasion carpet bombing of major cities, factories, & oil refineries in Germany Allied invasion in September 1944 stopped by Germany at the Rhine River Battle of the Bulge (Dec/Jan – 1944/1945) – Ardennes forest in Belgium/Luxembourg – Germany’s last major offensive, stopped by the 101st Airborne Division & General Patton’s 110th Armored Division Battle of the Bulge Invasion of Germany (cont.) Dresden fire bombed by Allies (over 100,000 killed) April 1945 – – – – – U.S. approaches Berlin from the west, U.S.S.R. from the east Germany’s Italian resistance collapsing Mussolini caught by Italian resistance (killed) Roosevelt dies Hitler commits suicide V-E Day – May 7, 1945 – Germany’s unconditional surrender Japan Pushed Back Battle of Coral Sea (May 1942) – 1st all aircraft carrier battle – Prevents Japanese invasion of Australia Battle of Midway (June 4 – 7, 1942) – Turning Point in the Pacific! – Allies break Japanese Code – Japan loses 4 aircraft carriers and 7 ships – Prevents any chance of an invasion of the U.S. Island Hopping campaign – Goal = neatralize Japanese island strongholds and then move on closer to Japan – Battle of Guadalcanal (Solomon Islands) (Aug. 1942 – Feb. 1943) • 1st Japanese land defeat Japan Pushed Back (cont.) Iwo Jima (February 1945) – Incredibly bloody fighting, Japanese will fight to the last man – Needed for planes to be close enough to attack Japan Okinawa (April – June, 1945) – 50,000 American casualties – American leaders know it will take far more to invade Japan Begin bombing of Japan (starting March 1945) – Tokyo loses 60% of its buildings and hundreds of thousands of Japanese killed Election 1944 Roosevelt defeats Republican Thomas Dewey to win his 4th term in office – Harry Truman FDR’s running mate April 12, 1945 – FDR dies in Warm Springs, GA Truman becomes president The Atomic Bomb Manhattan Project begins in 1942 – Albert Einstein & Enrico Fermi warn FDR in a letter in 1939 that the Germans were working on a fission bomb – Conducted at various location throughout the U.S. – Headed by Dr. J. Robert Oppenheimer leads out of Los Alamos, New Mexico Successful test (“Trinity”) on July 16, 1945 near Alamogordo, New Mexico Potsdam Conference (July – August, 1945) – Truman (w/ Stalin there) warns Japan to surrender or suffer “complete utter destruction” Atomic Bomb (cont.) August 6, 1945 – Hiroshima – “Little Boy” dropped from the Enola Gay – @ 80,000 killed instantly and hundreds of thousands die later due to radiation sickness and cancer August 8, 1945 – U.S.S.R. enters the war against Japan August 9, 1945 – Nagasaki – “Fat Man” kills @ 60,000 instantly August 14, 1945 – Japan surrender (9/2/45 – official surrender on the U.S.S. Missouri) The Blasts Hiroshima Nagasaki Hiroshima Nagasaki Japanese Surrender Allied Diplomacy During WWII Casablanca Conference (1/14 – 25/43) – FDR & Churchill – Italy would be first target in Europe, not a 2nd front in France Moscow Conference (10/43) – Sec. of State Cordell Hull gets Soviet promise to join in war against Japan after Germany defeated Declaration of Cairo (12/1/43) – FDR meets with Chang Kai-shek – Chinese lands would be returned to China and Korea would be free Allied Diplomacy During WWII (cont.) Tehran Conference (11/28 – 12/1/43) – 1st Meeting of the “Big Three” (FDR, Churchill, & Stalin) – Allies agree to 2nd front in 1944 – Disagreement over carving up Germany and the types of government in Eastern Europe after the war is over Yalta Conference (2/4 – 11/45)* – “Big Three” discuss post-war Europe – Stalin agrees to the “Declaration of Liberated Europe” (free elections in eastern Europe) – Set-up basics of the United Nations – Germany to be divided up into occupation zones – Poland to have a coalition government of communist & non-communist Potsdam Conference (7/17 – 8/2/45) – – – – Truman, Stalin, & Clement Alliance breaking down Truman orders atomic bomb drop while at conference Start of the “Cold War” Tehran Conference Yalta Conference Potsdam Conference WWII Aftermath Casualties – @ 55 million dead, 35 million wounded, 3 million missing • @ 30 million soldiers killed (@300,000 Americans) • @ 25 million civilians killed (15 million in U.S.S.R.) Destruction – 4 million British homes destroyed, 7 million buildings in Germany, 1,700 towns in the U.S.S.R. Holocaust – @6 million Jews killed as part of the “final solution” – @6 million Gypsies, homosexuals, handicapped, Jehovah's witnesses, & political opponents also killed – U.S. response before & during the war • “Americanism” of the 1920s continued into the 1940s • German quota not met from 1933 to 1945, but Jews still turned away Normandy Cemetery Post-war Political Issues Allies and Ideology – WWII forced the “western” democracies and “eastern” communism to work together – Quickly turned to antagonism as the war ended Fate of Eastern Europe – By the end of the war the Soviet Union controlled: Bulgaria, Romania, & Hungary – Nazis driven from Poland and Czechoslovakia – Stalin promises free elections, west fears communism will win Germany’s Fate – Soviets want a weak Germany – U.S. & Britain want a strong economic Germany with a democracy Shift in the Balance of Power – Western Europe no longer the leader of world affairs – U.S. & U.S.S.R. become the two superpowers The Post-War World Nationalism – Colonies of Europe demand independence • India gains freedom from Great Britain • French Indochina (Vietnam) resists Europe – Formation of Israel Social Changes – African-Americans gain job opportunities (hope for more changes) – Many women find more opportunity, others return home – Population shift to the “sunbelt” Technology – Synthetic materials developed (due to rationing) – Improved technology (planes, communication, computers, etc.) – “Atomic Age” Cold War (1946 – 1992)