* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII: The US War in Europe
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of the United Kingdom during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Wehrmacht forces for the Ardennes Offensive wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian resistance movement wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
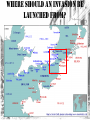
WWII: The US War in Europe War on Two Fronts • After Pearl Harbor, Germany and Italy declared war on the United States. • The USA now had to fight a war on two fronts… – Develop a “Europe First” policy with Great Britain. War in North Africa • November 1942 Allied troops land in Morocco and begin pushing east. • Under US General Dwight Eisenhower. • Why North Africa? – Gain Experience – Help British • 240,000 Italian and German troops surrender. – Rest flee to Italy. Meanwhile: War in the USSR • Frustrated by the stalemate in the Battle of Britain, Hitler turned his attention to the East. – June 22, 1941: Germany launches a Blitzkrieg on Russia. • German troops advance east. • Soviet army retreats to interior of USSR. – Stalin orders troops to destroy supplies the Nazis may find useful. – German advance is stalled between July 1942 to January 1943 at Stalingrad. • 90,000 German surrender • 330,000 Germans dead • Over 1 million Soviets dead – Stalin pleads with his new allies (US, British) to open a new front in Europe… The Invasion of Italy • “The soft underbelly of Europe” – Churchill. – Why? • July to September 1943 Allies invade Sicily followed by Italy. – As Allied forces invade, Italy declares war on Germany! • Mussolini is removed and arrested by King Victor Emmanuel. – Germans smuggle him to N. Italy as they retreat. • Progress stalls north of Rome - Allies will not take all of Italy until April, 1945. – Mussolini killed, 1945 Where to launch an invasion? 1943: The Soviets are still pleading with the USA and Britain to open up a second front against “Fortress Europe.” The Allies want to launch an attack, but where? Operation Overlord • Late 1943 – June, 1944 – Allies built up forces in southern England in preparation of a massive invasion. • Utilize carpet bombing – Scattering a large number of bombs over a large area. – Germans fortified the French coastline with machine-gun nests, barbedwire fences, land and water mines, and underwater obstructions. Where should an invasion be launched from? The Invasion of mainland Europe • June 6th, 1944 – “D-Day” – Operation Overlord – Establish foothold in mainland Europe. • Midnight: – Warships depart from Southern England » 1,000 RAF aircraft begin pounding German forces on Normandy coast. » 23,000 British and American “airborne” parachute behind enemy lines. • Dawn: – 150,000 Allied troops come ashore. – Intense fighting ensues. Paris Liberated! • Within a week, 2 million Allied forces were in Normandy. – Allied forces quickly moved south-east. • Paris was liberated, August 25th, 1944. Operation Market Garden • September 1944 – British plan to end the war by Christmas. – Drop paratroopers in Netherlands, capture bridges and move army quickly ahead. – Fails miserably. Battle of the Bulge • December 1944 Last-ditch effort by Germany to turn back the Allied advance. – Invade sections of Allied controlled Belgium. – Largest battle of the War. • 100,000 German loses • 80,000 Allied loses The Invasion of Germany and Battle of Berlin • Spring 1945 – – Allied forces invade Germany – Soviet Union takes Berlin. • Hitler commits suicide, April 1945. V-E Day: May th 8 , 1945