* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Course of WWII
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
War Front: Turning Point wikipedia , lookup
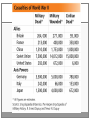
The Course of WWII CHAPTER 17 SECTIONS 2-4 Europe at War 1939: The invasion of Poland took just four weeks The Germans used a new style of war called Blitzkrieg “Lightning war” Germans also used something called the Panzer Divisions These were strike forces of about 300 tanks and soldiers support by airplanes By September 28, 1939 – Germany and the Soviet Union divided Poland 1940: Hitler invades Denmark then he attacks the Netherlands, Belgium, and France Maginot Line The fortified border between Germany and France France thought the Germans would go right through it However, Germany surprised the French by going around it June 22, 1940 The French sign an armistice with Germany Germany occupied 3/5 of France A French Authoritarian regime was set up by the Germans Only G.B. remained undefeated in Europe Great Britain Asked the U.S. for help The U.S. refused due to the strict policy of isolationism The U.S. did publically denounce the Germans But, the U.S. did nothing at first Overtime, laws relaxed and the U.S. shipped Food, ships, planes, weapons Hitler knew he could not attack G.B. by sea He had to control the air He began a major bombing offensive in England To retaliate, the British bombed Berlin Then the Germans began to bomb British cities Battle of Britain July 10, 1940 – October 31, 1940 This is the only battle in military history to be fought entirely in the air 2,936 pilots took part The British prevailed and prevented all of Europe from being taken over Hitler believed the British resisted because they were waiting for Soviet support So, Hitler invades the Soviet Union Early Winter in the Soviet Union German troops marched too far in Russia Low of supplies Strong Soviet resistance These factors helped the Soviets stop the Germans The first time the Germans were stopped Soviets then counter attack the Germans in December 1941 Japan at War December 7, 1941 Japan launches the surprise attack at Pearl Harbor By 1942, the Japanese controlled almost all of southeast Asia and most of the western Pacific Greater East-Asia Copropriety Sphere The entire Asia region was under Japanese control To make this sphere work they needed natural resources It treated the countries under their rule as conquered land Pearl Harbor The Japanese thought that the attack on a U.S. fleet would leave them as the dominate power in the Pacific However, this had the opposite effect The U.S. was now going to commit to war “They awoke a sleeping giant” Hitler Believed the U.S. would be too involved with Japan He would declare war on the U.S. four day later WWII was now a global war The Allies Advance The Grand Alliance Great Britain, Soviet Union, and the United States They focus mainly on military operations They also ignore political differences They all agree to fight the Axis Powers The Axis Powers Germany, Italy, and Japan 1942: The Germans are fighting in three spots Great Britain The USSR Africa Erwin Rommel - Germany Known as the Desert Fox Broke through British lines in Africa Helped the Germans gain an advantage in Africa Summer 1942 G.B. stops the German advances in Africa Fall 1942 U.S. and G.B. attack in French North Africa Germans surrender by May of 1943 The Eastern Front Hitler attacks Stalingrad Soviets cut off supply lines By May 1943, Hitler knew he would not defeat the Soviet Union Pacific Front Battle of Coral Sea, 1942 Americans save Australia from a Japanese Invasion The Battle at Midway Turning point for the Pacific front Led by General Douglas MacArthur U.S. destroyed 4 Japanese aircraft carriers This battle would establish U.S. supremacy in the Pacific Last Years of the War By 1943, the war had turned against the Axis powers The Allies will invade Italy Mussolini is removed from office Germany defends Rome in 1944 – many casualties are lost Winston Churchill British Prime Minister Referred to Italy as the “Soft underbelly of Europe” His refusal to give into Nazi Germany inspired the country He worked tirelessly throughout the war to build relations with U.S. President Roosevelt and the Soviets Normandy – P.584 June 6, 1944 Known as D-Day Allied invasion of France from across the English Channel Allies are led by Dwight D. Eisenhower Germans thought this was a diversion at first Slow to respond Allies break through German Lines 1945 – Hitler moves to an underground bunker April 30, 1945 – Russia outside Berlin Hitler commits suicide on April 30, 1945 Two days later Italian Resistance Fighters shoot Mussolini May 7, 1945 – WWII Ends May 8, 1945 – official end of WWII; V-E Day Asian Front War continued Harry S. Truman – U.S President Decides to drop the Atomic Bomb Hiroshima –Aug. 6, 1945:Nagasaki – Aug. 9, 1945 By the end of the war, 17 million people died Include civilians, it is closer to 50 million