* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Mittelbau-Dora wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
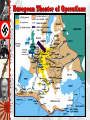
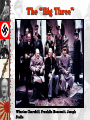
Poland Attacked: Sept. 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg German Troops March into Warsaw Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis, 1940 The Tripartite Pact European Theater of Operations The “Phony War” Ends: Spring, 1940 Dunkirk Evacuated June 4, 1940 France Surrenders June, 1940 A Divided France Henri Petain Battle of Britain: July – August, 1940 The Atlantic Charter: August, 1941 1941 FDR and Churchill approve the Atlantic Charter which supported self-determination, a new permanent system of general security (a new League of Nations), and the right of people to regain governments abolished by dictators. Operation Barbarossa: June, 1941 3,000,000 German soldiers 3,400 tanks The “Big Three” Winston Churchill, Franklin Roosevelt, Joseph Stalin Axis Powers in 1942 WWII was fought on two fronts: In the Pacific: Japanese forces reached their height of power in 1942. In Europe, most of the fighting in 1942 was between the Soviets and the Germans, as the Soviets attempted to repel the Nazi invasion. All sides engaged in civilian bombing. High tide for Axis ends in 1942, as US enters war and because the Soviets win at Stalingrad. Turning Point in the East: Stalingrad Battle of Stalingrad: Winter of 1942-1943 German Army Russian Army 1,011,500 men 1,000,500 men 10,290 artillery guns 13,541 artillery guns 675 tanks 894 tanks 1,216 planes 1,115 planes The North Africa Campaign: The Battle of El Alamein, 1942 Gen. Ernst Rommel, The “Desert Fox” Gen. Montgomery (“Monty”) Turning Point in North Africa: El Alamein: German forces out of N. Africa by May, 1943:Operation Torch After N. Africa, Then to Italy: The Allies Liberate Rome: June 5, 1944 Sicily was occupied in 1943, Mussolini removed from power, but Germans save him from mountaintop prison and return him to power in N. Italy, which is occupied by Germans until 1945. Casablanca, January, 1943: FDR and Churchill agree to step up Pacific war, invade Sicily, increase pressure on Italy and insist on an unconditional surrender of Germany. Teheran Conference, November, 1943: Allies agree to launch attacks from Russia on the east at the same time as US and Great Britain attack from west. Gen. Eisenhower Gives the Orders for D-Day “Operation Overlord” D-Day (June 6, 1944) The largest invasion by sea in history, the Allies secured several beachheads on the Normandy Coast. The Liberation of Paris: August 25, 1944 French Collaborators The Battle of the Bulge: Hitler’s Last Offensive Dec. 16, 1944 to Jan. 28, 1945 The Americans reorganized, won the Battle of the Bulge and move towards Germany. Horrors of the Holocaust begin to be uncovered as the Allies and Soviets each advance towards Berlin. Yalta: February, 1945 Stalin agreed that Poland would have free elections after the war and that the Soviets would attack Japan within three months of the collapse of Germany. Soviets receive territory in Manchuria and several islands; USSR agrees to join the United Nations on condition that she has three seats on the Security Council, along with USA, Britain, France and China. Mussolini & His Mistress, Claretta Petacci Hung in Milan, 1945 US & Russian Soldiers Meet at the Elbe River: April 25, 1945 Hitler Commits Suicide April 30, 1945 V-E Day (May 8, 1945) Pearl Harbor - Dec. 7, 1941 President Roosevelt Signs the US Declaration of War Pacific Theater of Operations Bataan Death March - April, 1942 76,000 prisoners [12,000 Americans] Marched 60 miles in the blazing heat to POW camps in the Philippines. Allied Counter-Offensive: “Island-Hopping” Lt. Col. Jimmy Doolittle: First U. S. Raids on Tokyo, 1942 Battle of the Coral Sea: May 7-8, 1942 Battle of Midway Island: June 4-6, 1942 Turning Point in the Pacific: Midway Japanese Kamikaze Planes: “The Divine Wind” Approximately 2,800 Kamikaze attackers sunk 34 Navy ships, damaged 368 others, killed 4,900 sailors, and wounded over 4,800 US Marines, Iwo Jima [Feb. 19, 1945] Potsdam Conference: July, 1945 Germany divided into four zones. Soviets to enter war against Japan. United Nations Created. The Manhattan Project: Los Alamos, NM Dr. Robert Oppenheimer Hiroshima – August 6, 1945 Nagasaki – August 9, 1945 V-J Day (September 2, 1945) V-J Day in Times Square, NYC