* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II - Loudoun County Public Schools / Overview
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
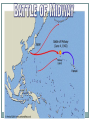
Topic 3: World War II Battles and Strategies EUROPE & NORTH AFRICA PACIFIC ISLANDS Sides and Strategies The Allies: Britain, Soviet Union (USSR), & the US The Axis Powers: Germany, Italy, & Japan - All Totalitarian regimes Strategies: Europe The Allies’ Strategy in Europe - Defeat Hitler First - Most of the resources were put into Europe Germany’s Strategy in Europe: Defeat the USSR quickly and defeat Britain using bombs and U-boats before the US can enter the war. (Germany easily beat France in 1939) Strategies: Pacific The US Strategy in the Pacific - Island hopping - Attacking islands close to Japan and jumping over fortified islands and cutting off their supply lines. Japan’s Strategy: After Pearl Harbor, Japan hopes to conquer Southeast Asia and the Pacific quickly Japan's War in the Pacific (39:00-49) Turning Points: Battles A) El Alamein (Egypt) Germany was poised to take Egypt and the Suez Canal which would have given them access to the oil fields in the Middle East and even attack the USSR from the South, but the British defeat them in a desert battle (Operation Torch). B) Stalingrad (August 1942 – February 1943). Germany wanted to seize Russian oil fields and capture Stalingrad. They are stopped by the brutal winter. German troops surrender to the Soviet Union due to starvation and cold. It was the turning point in the Eastern Front. Battle of Midway D) Normandy, France (D-Day June 6th 1944) - The Allies land in German-occupied France. There are heavy causalities for the US and its Allies, but the liberation of Western Europe begins vid clip beach landing Battles of Iwo Jima & Okinawa E) Iwo Jima & Okinawa (1945) - Though the Island Hopping victories are costly, American troops get closer to Japan – The Japanese soldiers fight heroically and many commit suicide rather than surrender http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2YedHaLF5So F) The atomic bombs on Hiroshima & Nagasaki (1945) -President Truman is told that an invasion of Japan might cost a million lives. Dropping the atomic bomb would be the quickest end to war Dropped on 2 Japanese cities: Hiroshima & Nagasaki About 140,000 Japanese civilians are killed in the blasts. More die from radiation later Japanese leaders surrender to the US. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t19kvUiHvAE Nagasaki: Before and After the Bomb Panoramic