* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download War in the Pacific
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
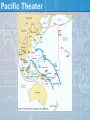
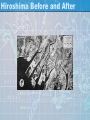
War in the Pacific 1941-1945 Pearl Harbor: December 7, 1941 •Japan attacked US Naval Base Pearl Harbor because: •US was boycotting Japanese goods because of China and Indochina (FDR had demanded Japan withdraw from both) •US stood between Japan and Pacific expansion •Greater victory than they had hoped: •Sank/disabled 19 ships, 188 airplanes, killed over 2400 and wounded 1100 •US aircraft carries out to sea, so they escaped damage •Roosevelt declared war the next day Victory in the Pacific (1942-45) •While European war occurring, Japan taking over much of the Pacific (wanted living space) •1942 Japan took Philippines, Malay States, Dutch East Indies, part of New Guinea •US halted their advance north of Australia at Coral Sea (May) and Midway (June, considered payback for Pearl Harbor) •August, under command of Douglas MacArthur, launched an attack at Guadalcanal •6 months to victory •Beginning of “island hopping” North to Japan, take some islands, skip others •1945 captured Iwo Jima and Okinawa, allowed US to launch air raids on Japan •Japan fought back with Kamikaze, suicide pilots Pacific Theater Back to Europe •Yalta Conference •Feb. 1945, the Big Three (Roosevelt, Stalin & Churchill) met in the Soviet Union to decide what to do with the world after the war •Decisions reached: •United Nations would be organized as a permanent international peacekeeping organization •Germany & Berlin would be divided into 4 zones of occupation by the US, Britain, Soviet Union, & France Victory Over Japan •General Hideki Tojo refused to surrender •July US issued an ultimatum, surrender or face “utter destruction” •Japan did not surrender •Japanese refused to surrender & President Harry S. Truman (FDR had died in April) knew an invasion of Japan could mean up to a 1 million American deaths, he ordered that a new defensive weapon be dropped on a Japanese city •August 6, 1945 first bomb dropped on Hiroshima •Japan still did not surrender •August 9 second dropped on Nagasaki •August 14 Japan surrendered Truman’s notes to Stalin At Potsdam Manhattan Project • Atomic bomb • • • • • • Bomb cloud over Hiroshima Invented in the Manhattan Project • Albert Einstein told FDR in 1939 that a a-bomb could be built and the Nazis were working on it US secret project led by Oppenheimer • Used people from US, GB, Canada, and refugees from Nazi-occupied Europe • Made Atomic Bomb containing 2 lbs of Uranium; explosive power of 20,000 tons of TNT • Bombs were known as “fat man” and “little boy” Hiroshima bomb killed or injured 130,000 destroyed 60% of city GB worked on it, Allies did not tell Stalin about a-bomb: led to resentment that leads to Cold War H-bombs, which we have today, several thousand times more powerful than a-bomb, can wipe out all life within a 60- to 100-mile radius Bad times Hiroshima Before and After Effects of the War • • • • 55 million people died in this war China, Japan, & Germany were in ruins from the bombing Millions of people were homeless & w/o families—known as displaced persons The US and Soviet Union would have major conflicts that would result in the Cold War