* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 25-1 Mobilizing for Defense
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
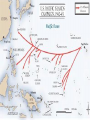
The United States in World War II Chapter 25 Essential Question Is there any ethical problem (is it wrong) to play war games of battles that really happened or watch movies like Saving Private Ryan for entertainment? Mobilizing for Defense 25-1 Selective Service and the G.I. G.I. – Government Issue The nickname given to enlisted WWII soldiers Selective Service – the draft Men who did not sign up for the military were called to military service Women in the Military George Marshall: Army Chief of Staff Started the Women’s Auxiliary Army Corps Organized women to do non-combat work for the army in WWII Discrimination in the Military African Americans, Mexican Americans, Native Americans, and Asian Americans were put into segregated troops and given the worst military jobs Huge groups of these soldiers volunteered for the war It was ironic to segregate troops while fighting to liberate people from unfair leaders Filipino Troops War Production Car factories in the US shut down and were used for making tanks, planes, boats, and command cars Many factories went from making household goods to things needed in the war With millions of men going to fight, millions of women took over work in the factories Women in Factories http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WhswqZ h2Rc4 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mgpvKX LTwr8 African Americans at Home Still given the worst jobs in factories Asa Philip Randolph: a labor leader who planned a huge march on Washington to protest poor treatment of African Americans in factories FDR said if Randolph called off the march he would work to end discrimination in the workplace War Science Office of Scientific Research and Development Created by FDR in 1941 Developed better sonar and radar Developed the use of DDT against insects Developed drugs like penicillin that saved soldiers Worked to develop the atomic bomb Manhattan Project Group of top scientists in New York who worked to create the atomic bomb Government Agencies Control the Economy (1942-1945) Office of Price Administration Fought inflation by freezing wages, prices, and rents Rationed foods such as meat, butter, cheese, veggies, sugar, and coffee Government Agencies Control the Economy (1942-1945) National War Labor Board Limited Wage Increases Allowed negotiated benefits (vaca, pensions, insurance) Kept unions stable by forbidding workers from changing unions Government Agencies Control the Economy (1942-1945) War Production Board Rationed fuel important materials Dept. of Treasury Issued War Bonds to raise $ Revenue Act of 1942 Extended income tax to raise $ Government Agencies Control the Economy (1942-1945) Smith-Connally AntiStrike Act (1943) Limited the right to strike in industries crucial to the war effort Gave President the power to take over factories that were in strike 25-2 The War for Europe and North Africa FDR and Churchill had an alliance so America focused on the War in Europe first. Battle of the Atlantic (’42-’43) Germans tried to stop food and materials from crossing from America to England or the Soviet Union Jan-Apr 1942: Germans sank 87 Am. Ships Apr-Aug 1942: Germans sank 594 more US ships started traveling in convoy’s surrounded by destroyers and airplanes This helped the US sink German U-Boats and win the Atlantic http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bB8GNHxf__A Battle of Stalingrad (In Soviet Union) Timeline: June 1941: Germany invades Soviet Union Nov. 1941: Bitter cold stops fighting Spring 1942: fighting starts back up June 1942: Germans winning in south Aug. 1942: Germans reach Stalingrad Battle of Stalingrad Fall/Winter 1942: Germans fight house to house combat; Winter sets in (bitter cold); Hitler orders them to stay there; they had destroyed all the houses The horrible winter kills many and they surrender to the Soviet Union Soviets Lost 1,100,000 soldiers at Stalingrad Battle in North Africa North African countries were under Axis control The Allies invaded N. Africa while Stalingrad was going on They won back N. Africa and called for unconditional surrender: they had to agree to whatever the Allies said Dwight Eisenhower: American General who commanded Allied Troops in N. Africa Battle in Italy While the battle in N. Africa was still happening, the Allies decided to attack Italy next. They quickly won Sicily and were successful in Italy at first They made Benito Mussolini resign and many Italian people were very happy Battle in Italy Germany stepped in and fought the Allies in Italy This kept Italy from being taken back by the Allies until 1945 (End of WWII) “Bloody Anzio”: a terrible battle just outside Rome that lasted 4 months 30,000 Axis and 25,000 Allied casualties Allied forces of all races fought for Italy Strategy of Operation Overlord Many troops parachuted behind German lines and thousands stormed the beaches of Normandy General Omar Bradley made a gap in the German line with a massive air and land bombardment General George Patton led The Third Army through the gap and advanced into Paris Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uP U4p7UQOtU The Battle of the Bulge October 1944 Americans/Allies were invading Germany Germans attacked the Belgium port of Antwerp December 1944 German tanks made it 60 miles into the Allied lines making a bulge in the lines The Battle of the Bulge SS Troopers: Elite Nazi Soldiers Captured 120 American GI’s Herded them into a field and shot them all The Battle of the Bulge After 1 month fighting, Germans were pushed back but had serious losses 120,000 Troops 600 Tanks 1,600 Planes Germans were forced to retreat from all combat Liberation of Death Camps Allies were working east into German and Soviets were working west through Poland July 1944: First death camp was liberated by the Soviets (Majdanek: name of camp) SS Guards tried to burn evidence, but they could not do it in time Soldiers found 1,000 starving people, the largest crematorium in the world, and 800,000 pairs of shoes from those who were killed V-E Day V-E Day: Victory in Europe Day April 25, 1945: Berlin was under attack Hitler Married Eva Braun Hitler wrote his last address to the German people Hitler’s Last Address Blamed Jews for starting WWII Blamed Generals for losing WWII Said that he and Braun would choose death over the disgrace of being captured by the Allies Both killed themselves the next day He shot himself, she drank poison V-E Day The Germans surrendered unconditionally on May 8, 1945 This was V-E Day, Victory in Europe Day FDR died on April 12, 1945 and never lived to see any of this Harry S. Truman (VP under FDR) took over as President of the United States at the end of WWII 25-3 War in the Pacific WWII in the Pacific Military Action Significance Philippines Japanese victory destroyed the myth of white supremacy in Asia. Doolittle’s raid American spirits lifted by the Tokyo bombing. Midway Damaged Japanese air power Leyte Gulf Reduced Japanese navy to minor role Okinawa Allowed attack on Japan itself Hiroshima America is first to use the atomic bomb. Nagasaki Led to Japan’s surrender Philippines The Japanese won the islands from the Americans This proved Japan’s power and it took away a major port for America Doolittle’s Raid April 1942 James Doolittle led a successful air raid on Tokyo (capital of Japan) Battle of the Coral Sea Americans and Australians stopped Japan from taking Australia One of the first times the allies were able to stop Japan Battle of Midway June 1942 US found out Midway Island was Japans next target and attacked their planes and ships before they attacked the island Many Japanese planes and ships were destroyed Was a turning point in the war Americans were attacking now, not defending Japanese Official: “Americans avenged Pearl Harbor” “Island Hopping” and Kamikaze Once they won Midway, Americans started attacking Japan one island at a time As soon as they got a new island, they would lay a cement airstrip and begin attacking the next island Kamikaze pilots tried to stop them Kamikaze pilots: Japanese suicide bombers who flew bomb-laden planes into American ships Battle of Iwo Jima General Macarthur: American General in the Pacific War Led attack on the island of Iwo Jima Iwo Jima was close enough to Japan that heavy bombers could take off there and reach Japan 6,000 US marines were killed 20,500 Japanese soldiers were killed (only 200 survived) Scenes from “Flags of Our Fathers http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ewIzAlm k8pQ&feature=related Battle for Okinawa April 1945 1,900 Kamikaze attacks and worse fighting than Iwo Jima 7,600 American casualties 110,000 Japanese casualties Two Generals committed suicide rather than surrender The fighting in Okinawa showed that an invasion of Japan would be horribly deadly Atomic Bomb Because Iwo Jima and Okinawa were really difficult battles, the Allies thought that an invasion of Japan would be a desperate struggle They decided instead to use the Atomic Bomb New technology developed by the Manhattan Project Atomic Bomb Manhattan Project led by J. Robert Oppenheimer It was first tested in the desert of New Mexico July 26, 1945: US warned Japan to surrender or it would face “prompt and utter destruction” Hiroshima August 6, 1945 B-29 Bomber (plane) named Enola Gay Atomic Bomb named Little Boy Hiroshima: city where Little Boy was dropped Hiroshima turned completely to dust after the bomb was dropped Nagasaki Japan did not surrender after the bomb was dropped on Hiroshima August 9, 1945: A second bomb was dropped on a city called Nagasaki Fat Man: Code name of second bomb This prompted Japan’s Emperor Hirohito to surrender 200,000 people were killed by the bombs The Yalta Conference A meeting in the Soviet Union to discuss how things should be in Germany after the war (how to prevent a WWIII) Feb 1945 The Big Three: Churchill, Stalin, FDR They decided to split Germany into four zones that would be governed by America, Britain, France, and the Soviet Union that would all eventually come together to be a united Germany again Soviet Union joined the war against Japan They would start the United Nations The Nuremberg Trials The trials of 24 surviving Nazi leaders for crimes against humanity, crimes against the peace, and war crimes Held in Southern Germany, a town called Nuremberg 12 were sentenced to death Most were sent to prison Nuremberg Trials Eventually almost 200 more were put on trial and sent to prison Some said this was not enough and many Nazi’s who were part of the Holocaust went free Trials set the principle that individuals are responsible for their actions during war If you do terrible things you cannot just say that you were following orders so it is okay Occupation of Japan After Japan surrendered, American forces stayed in Japan to control the country and to put leaders on trial for war crimes Led by Gen. Douglas MacArthur Lasted 7 years Started a new democratic government and a free market economy