* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Point
Computer chess wikipedia , lookup
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Computer Go wikipedia , lookup
Artificial intelligence in video games wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
History of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
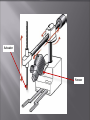
Artificial Intelligence ( AI ) Ahmed Ismail AIT 600 Spring 08 What is the Artificial Intelligence? What’s involved in Intelligence? Levels of Intelligence Goals in ( AI ) Brief History of ( AI ) ( AI ) Research approach Examples of AI What is the Artificial Intelligence? A.I. is the study of how to make computers do things at which, at the moment, people are better. AI is both the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science which aims to create it. Actuator Sensor What’s involved in Intelligence? Ability to interact with the world (speech, vision, motion, manipulation) Ability to model the world and to reason about it Ability to learn and to adapt AI Goals To build systems that exhibit intelligent behavior To understand intelligence in order to model it Why AI ? to use the power of computers to augment human thinking. to use a computer's artificial intelligence to understand how humans think. A Brief History of AI 1943 • McCulloch and Pitts propose a model of artificial neurons 1956 • The Dartmouth Conference and Agreement to name this new field of study: Artificial Intelligence 1956-1969 • Lots of work on neural networks 1969-1979 • Birth of expert systems 1980-1988 • R1 becomes first successful commercial expert system 1990s • Increases in computational power (computers are cheaper, faster, and have tons more memory than they used to) Computer Chess 2/96: Kasparov vs Deep Blue Kasparov victorious: 3 wins, 2 draws, 1 loss 3/97: Kasparov vs Deeper Blue First match won against world champion 512 processors: 200 million chess positions per second Computer science Linguistics Philosophy AI Psychology Mathematics Biology Reflex Weak AI Context aware Levels of Intelligence Goal seeking Strong AI Learning AI Research Approaches Performance oriented Simulation oriented Researcher tries to maximize the performance of the agents. Researcher tries to understand how the agents produce responses Just do it. Computer scientists approach Wait, let me figure what’s going on first Psychologists approach Computer Chess 2/96: Kasparov vs Deep Blue Kasparov victorious: 3 wins, 2 draws, 1 loss 3/97: Kasparov vs Deeper Blue First match won against world champion 512 processors: 200 million chess positions per second Robotics – Hopkins Beast 1964 Two versions of the Hopkins beast, which used sonar to guide it in the halls. Its goal was to find power outlets. http://www.frc.ri.cmu.edu/~hpm/book97/index.htm Robotics – Stanford cart •1971- Stanford cart. Remote controlled by person or computer. •1971- follow the white line •1975- drive in a straight line by tracking skyline •1979- get through obstacle courses. Cross 30 meters in five hours, getting lost one time out of four http://www.frc.ri.cmu.edu/~hpm/book97/ch2/index.html Phil, the drug robot, introduced in 2003 Moving Around and Picking Things Up Robot Evolution http://cosmos.bcst.yahoo.com/up/player/popup/ind ex.php?cl=7318200 Questions? http://www.ai.mit.edu/projects/humanoid-roboticsgroup/kismet/kismet.html Thank you