* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Effects of IT on Strategy and Competition
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Resource-based view wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Business model wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer experience wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
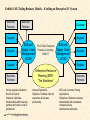
Exhibit 3.8 E-Tailing Business Models – E-tailing an Enterprise EC System
Business
Partners
Business
Partners
Customer
Supplier
Supplier
Supplier
B2B and
Supply Chain
Management
(SCM)
The E-Tailer Enterprise
Finance, Accounting,
HRM, IT
Supplier
Business
Partners
Facing supplier distributor/
Business Partner
Objective: Optimize
Relationships with business
partners and reduce cost of
goods sold
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
B2B and
Supply Chain
Management
(SCM)
Supplier
Supplier
Enterprise Resource
Planning (ERP)
“The Backbone”
Internal Operations
Objective: Facilitate internal
operations & increase
productivity
Business
Partners
B2C and Customer-Facing
Applications
Objectives: Optimize business
relationships with customers;
increase service
effectiveness and sales
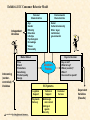
Exhibit 4.1 EC Consumer Behavior Model
Personal
Characteristics
Independent
Variables
Age
Gender
Ethnicity
Education
Lifestyle
Psychological
Knowledge
Values
Personality
Environmental
Characteristics
Social
Cultural/community
Other: legal,
institutional,
governmental
Buyer’s Decision
Market Stimuli
Intervening
(vendorcontrolled)
Variables
Price
Brand
Promotions
Advertising
Product quality
Design
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
Decision
Probes
Buy or not?
What to buy?
Where (vendor)?
When?
How much to spend?
EC Systems
Logistics
Support
Technical
Support
Payments
Delivery
Web design
and content
Intelligent
agents
Security
Customer
Service
Dependent
Variables
(Results)
Exhibit 4.5 The New Marketing Model - One-to-One Marketing and
Personalization in EC
Marketing/Advertising
Chose to Best
Server/Reach Customer
“Four P’s”
(Product, Place,
Price, and
Promotion)
Updated Uniquely
to Customer
[1]
Customer Receives
Marketing Exposure
Customer
Relationships
Customer Profile Based
on Behavior; Customer
Segmentation Developed
Database Update {…}
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
[2]
Customer decides
on marketing medium
for response
[3]
Customer makes
purchase decision
[4]
Detailed transaction/
Behavior Data Collected
Source: Linden, A. Management Update: Data Mining Trends Enterprises Should Know
About, Gartner Group, 2002
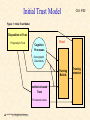
Initial Trust Model
Ch3. P.50
Figure 1: Initial Trust Model
Disposition to Trust
Propensity to Trust
Trust
Cognitive
Processes
Demographic
Dissimilarity
Trusting
Beliefs
Institution-based
Trust
Procedural Justice
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
Trusting
Intention
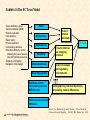
Exhibit 4.6 The EC Trust Model
Trust certificates, seals
Vendor evaluation (BBB)
Product evaluation
Free samples
Return policy
Privacy statement
Co-branding, alliances
Education efforts by vendor
stressing the use of security,
size and financial resources
Simplicity of shopping
Navigation, Web design
Seller
Competency
Trust in
internet
merchant
EC Trust
Benevolence
Reliability
Understandability
Security/payment
Business culture
Consumer protection
Effective law
Trust in internet
as shopping
channel
Trust in business
and regulatory
environments
Demographics, previous experience,
personality, cultural differences
Peers success stories
Referrals
Source: Lee, Matthew K.Q. and E. Turban, “A Trust Model for
Consumer Internet Shopping,” Vol. 6(1), M.E. Sharpe, Inc., 2001
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
Alternative Views of Strategy
The implicit Strategy Model of
the Past Decade
Sustainable Competitive
Advantage
• One ideal competitive position in the
industry
• Unique competitive position for the
company
• Benchmarking of all activities and
achieving best practice
• Activities tailored to strategy
• Aggressive outsourcing and partnering
to gain efficiencies
• Advantages rest on a few success
factors, critical resources, core
competencies
• Flexibility and rapid responses to all
competitive and market changes
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
• Clear trade-offs and choices vis-à-vis
competitors
• Competitive advantage arises from fit
across activities
• Sustainability comes from the activity
system, not the parts
• Operational effectiveness a given
Model of a Market-Directed Economy
Goods and Services
CONSUMERS
Information
Information
PRODUCTMARKET
Information
GOVERNMENT
Money (income)
Information
Informatio
n
Money (income)
Information
Information
Production resources
Money (expenditures)
Money (expenditures)
RESOURCE
MARKET
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
Information
Information
PRODUCERS
Primary direction
Secondary direction of feedback
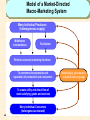
Model of a Market-Directed
Macro-Marketing System
Many Individual Producers
(heterogeneous supply)
Middlemen
intermediaries
Facilitators
Perform universal marketing functions
To overcome discrepancies and
separation of production and consumers
To create utility and direct flow of
need-satisfying goods and services
Many Individual Consumers
(heterogeneous demand)
Prentice Hall & Dr. Chen, Electronic Commerce
Monitoring by
Monitoring
bygovernment(s)
government(s)
and
groups
andpublic
publicinterest
interest
group