* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10 piercy fourth ed
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
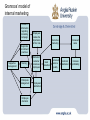
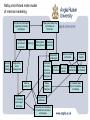
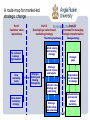
Implementation processes and internal marketing: Making it happen Lecture 11 A route-map for market-led strategic change Part I Customer value imperatives Part II Developing a value-based marketing strategy The strategic pathway Market sensing and learning strategy The Customer is always right-handed New marketing meets old marketing Value-based marketing strategy Strategic thinking and thinking strategically Strategic market choices and targets Customer value strategy and positioning Strategic relationships and networks Part III Processes for managing strategic transformation Change strategy Strategic gaps Organization and processes for change Implementation process and internal marketing Agenda - 1 • Why do we need to make an issue out of strategy implementation? • Implementation versus strategy • So, what is the thing about implementation? • Implementation denial • So, why doesn’t it work? • Building implementation strategies Agenda - 2 • Strategic internal marketing • Where does that leave us with strategy implementation? Why do we need to make an issue out of strategy implementation? • Many company change initiatives fail • Implementation capabilities • The need for internal marketing – getting employees on our side – getting managers on our side – getting collaborators on our side – changing culture How groups can block effective change in a company Energy High Low High The “yes … but”s or malicious obedience The ideal The dinosaurs The dangerous enthusiasts Understanding Low Implementation versus strategy • Traditional approaches: organization, resources action lists, control systems • Creates a dichotomy between strategy formulation and implementation • Need better ways of integrating strategy and implementation So, what is the thing about implementation? • Implementation failures associated with – separation of planning from management – hopeless optimism – implementation recognized too late – denial of implementation problems – implementation bolted-on at the end – fixation – implementation is a black-box Implementation denial • Failure to recognize the implementation problem • Need to recognize problems and prepare for change Recognising the implementation problem and preparing for change Perception that there is a problem High Low Ready to go Blissful ignorance Worried stayers/ frightened rabbits Closed minds High Willingness to change Low So, why doesn’t it work? • Strategy versus implementation skills – diagnosing implementation problems means comparing strategy (appropriate or inappropriate) with execution skills good or bad) Diagnosing the implementation problem Strategy Good Appropriate Inappropriate Success Roulette Trouble Failure Execution skills Bad So, why doesn’t it work? • Organizational stretch – what is the relationship between the fit of the strategy with company capabilities, systems and structures and the strategy itself (new or old)? Matching strategy to company capabilities Fit of strategy with company capabilities, systems, structures New Good Poor Synergistic strategies Stretch strategies Conventional strategies Obsolete strategies Market strategy Old So, why doesn’t it work? • Testing out the strategy versus blaming the salesperson • Lip-service to strategy caused by – management by assumption – structural contradictions – empty promises marketing – bunny marketing • Counter-implementation emerges Testing market strategies Test the strategy Is this really a coherent and complete strategy? No Results Reason No implementation This strategy does not tell us what to do No implementation Lip-service - we may agree with the strategy but we cannot put it into effect No implementation We do not accept this strategy - let’s see what counter-implementation can do! Yes Is this strategy capable of being implemented by this company at this time? No Yes Have we communicated the strategy - adapted it, won support for it? Yes No Implementation (maybe) So, why doesn’t it work? • What about execution skills and competences? – interacting skills – allocating skills – monitoring skills – organizing skills Building implementation strategies • • • • Screen strategies for implementation problems Isolate and evaluate priority implementation problems Evaluate key players in implementation Develop implementation strategies Screening strategies for implementation problems 1. Screen strategies for implementation problems early 2. Isolate and evaluate implementation problems in detail 3. Identify and evaluate key players 4. Develop credible, costed implementation strategies - or reject the strategy Internal and external marketing Strategy Plan Internal Targeted at key marketing groups in the programme company, alliance Product partner companies, Price and other influencers Communications Distribution External marketing programme Product Price Communications Distribution Targeted at key customers, segments and niches, and other external influencers Role of Internal Marketing • The managerial actions necessary to make all members of the organization understand & accept their role in implementation – internal products-marketing strategies – internal prices-changes that must be undertaken to implement the marketing strategy – internal distribution-how the strategies are communicated internally (training) – internal promotion-persuasive communications Models of internal marketing Source: Ahmed and Rafiq (2002) Internal Marketing Butterworth Heinemann Chapter 2 Berry’s model of internal marketing Employee involvement and participation Treating employees as customers Jobs as products Application of marketing techniques internally Employee satisfaction Attitudes towards service mindedness Attraction and retention of customer conscious employees Perceived service quality Customer satisfaction Competitive advantage Gronroos’ model of internal marketing Pre-launch information regarding marketing campaign Employees realise the importance of their role Interactive marketing Increased sales Supportive recruitment practices Supportive management Training Participate management Employee discretion Motivated customer conscious employees Employees’ satisfaction Goal interaction Perceived service quality Customer satisfaction Increase profitability Rafiq and Ahmed meta-model of internal marketing Pre-launch information regarding marketing campaigns Supportive recruitment practices Training Employees realise the importance of their role Participative management Employee discretion Motivated employees Service quality strategy Supportive senior management Customer conscious/ customer orientated employees Jobs as products Application of marketing techniques internally Sales minded employees Employees’ satisfaction Attraction and retention of customer conscious employees Good interaction Word of mouth promotion Perceived service quality Customer satisfaction Increased loyalty Increased profitability Increased sales due to interactive marketing A framework for internal marketing of services Inter-functional Co-ordination and Integration Employee motivation Marketing-like approach Job satisfaction Customer orientation Service quality Customer satisfaction Empowerment The tools of internal marketing Source: Ahmed and Rafig Caveats • Employees as customers – products may be unwanted (e.g. new methods of working) – employees must accept the ‘product’ or be forced into acceptance under the threat of disciplinary action or dismissal Caveats – problem with idea of customer sovereignty – make impossible demands on organisation and its resources • In this approach employees do not know that they are customers even though they are treated as such INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • • • • Number of elements under the control of management are combined and integrated in order to produce the required response from the target market. Use extended seven P’s of service marketing Explicitly recognises inter-functional interdependence and the need for an integrated effort for effective service (or product) delivery Major aim of an internal marketing programme Levels of internal marketing Organizational levels Surface Structural Processual Critical questions What are the plans, systems and procedures in this business? Who runs things here? Who has influence here - sets the agenda, owns key processes, is an “expert”? Internal marketing levels Product: Plans and strategies Price: Opportunities given up Communications: Information, market research Distribution: Reports, presentations Product: New strategic direction Price: Loss of control, status, initiative Communications: Sponsorship, agenda-setting Distribution: Policies, participation Product: individual’s job, status, role Price: Adjustment to change, new culture Communications: Persuasion, image, influence, choice of criteria Distribution: informal communications network, social interaction Strategic internal marketing Programme Contents Examples Product The strategy and the plan, including the values, attitudes and behaviours needed to make them work What we are asking internal customers to “pay” – other projects abandoned, personal and psychological adjustment to change Media and messages to inform and persuade For example, the written plan, the new company initiative Physical and social venues for delivering the product and communications For example, meetings, work-groups, training sessions and workshops, informal meetings, social occasions Price Communications Distribution For example, stepping out of comfort zones for new types of operations For example, reports, plans, presentations, videos, roadshows INTERNAL MARKETING MIX PRODUCT • Strategic level refers to marketing strategies – sell values and attitudes needed to make a plan • Tactical level, e.g. – new performance measures – new ways of handling customers • Refer to services and training courses provided by HRM INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • Fundamental level – job – managers need to concentrate on the benefits of the product rather than its features – employees perspective and benefits they seek – consider: • training needs, • level of responsibility and involvement in decision making, • career development opportunities, • working environment – facilitate hiring retention and motivation of employees INTERNAL MARKETING MIX PRICE • Psychological costs of adopting new methods of working – projects have to be forgone in order to carry out new policies (i.e. opportunity cost) or to transfer pricing and expense allocation between departments – opportunity costs difficult to measure precisely – employees tend to overestimate costs of undertaking new practices and are inclined to resist change • Benefits of adopting new policies need to be clearly explained and any fears allayed by providing employees with appropriate information INTERNAL MARKETING MIX Internal communication/Promotion • • Need co-ordinated use of various techniques personal selling – face-to-face presentations to individuals and groups more effective than in external marketing – presenter has implicit authority behind what they are saying – face-to-face communication regarded has having far greater impact than other communication methods. INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • Incentives – – – – – • cash bonuses awards recognition programmes prize draws competitions used to overcome short-term resistance or to motivate employees toward consistent behaviour or to increase productivity. INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • • Advertising Companies need to take care of image projecting of themselves and the workforce in external advertising – seen be employees as well as customers – positive when positive customer-orientated attributes portrayed which employees can attempt to emulate Narrow casting developments – Business TV – Webcasting INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • • • Place/distribution Place and channels (or third parties) that are used to get to customers place is the locations where policies are announced : – meetings – conferences channels refers to third parties used to deliver training programmes – consultants and training agencies INTERNAL MARKETING MIX Physical/tangible evidence • • • • • Environment in which a product is delivered and where interaction takes place between contact staff and customers, as well as any tangible goods that facilitate delivery or communication if the product Physical evidence – essential or peripheral (tangible cues that a product has been delivered) Peripheral evidence e.g. memos, guidelines, training manuals Essential evidence - environment in which the product is delivered Special significance of particular policies may be signalled by holding conferences or by sending employees for special training to external agencies such as universities INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • • Tangible cues important Documentation of policies and changes in policies important – if employees are required to perform to certain standards then it is important that these standards are fully documented • Training sessions – tangible manifestation of commitment to standards or particular policies INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • • • • PROCESS How customer receives a product customer consciousness may be inculcated into employees by training (or retraining) staff Can refer to whether new policies are introduced through negotiations with unions or imposed unilaterally Also refers to delivery method e.g. – circulars, videos or line managers are sued to convey messages INTERNAL MARKETING MIX PARTICIPANTS • • • • • People involved in delivering product and those receiving the product who may influence the customers perceptions Source of internal marketing programme plays a crucial role in their effectiveness Inter-departmental or inter-functional communications are likely to be least effective Most effective means through immediate superior who needs to be motivated by strategic management. Direct contact between strategic management and contact staff would not by itself be sufficient for the implementation of internal marketing programmes. INTERNAL MARKETING MIX • • Market segmentation – process of grouping employees with similar characteristics and needs and wants – include types of benefits that employees want, and roles and functions that they perform – need to be segmented along motivational lines rather than departmental or other lines traditionally used in HRM Market research – identifying needs and wants of employees – monitoring the impact of HRM policies on employees – long history in HRM in form of employee attitude surveys. Implementing Marketing Activities • Good communication is key – upward communication from the front line – allows management to understand problems & needs of the employees • Employees must understand the implementation timetable – specific activities to be performed, time required, sequence, & who is responsible Implementing an Internal Marketing Approach • Conscientious recruitment, selection & training of employees • Top managers must be completely committed to the marketing strategy & overall plan • Employee compensation must be linked to marketing strategy implementation • Open communication must exist at all levels • Organizational structure, processes & policies must match the marketing strategy Strategic internal marketing • Operational internal marketing – service marketing and quality – brand ambassadors – internal communications – innovation management – corporate positioning – Internal markets instead of external markets Strategic internal marketing • Strategic internal marketing – internal market orientation – internal marketing strategy – the structure of SIM Strategic internal marketing • The internal marketing programme – internal market measurement – internal marketing targets – internal marketing evaluation • The hidden face of strategic internal marketing Causes of Improper Implementation • Marketing strategy is inappropriate or unrealistic • Implementation was inappropriate for the strategy or was simply mismanaged • Internal &/or external environment changed significantly between the development of the marketing strategy & its implementation Where does that leave us with strategy implementation? • Execution skills versus process management in strategy implementation – weak implementation – management-driven implementation – implementation-driven strategy – integrated strategy and implementation Execution skills versus process management in marketing strategy implementation Process management High Low Integrated ManagementStrong strategy and driven implementation implementation Execution skills ImplementationWeak Weak driven implementation strategy A route-map for market-led strategic change Part I Customer value imperatives Part II Developing a value-based marketing strategy The strategic pathway Market sensing and learning strategy The Customer is always right-handed New marketing meets old marketing Value-based marketing strategy Strategic thinking and thinking strategically Strategic market choices and targets Customer value strategy and positioning Strategic relationships and networks Part III Processes for managing strategic transformation Change strategy Strategic gaps Organization and processes for change Implementation process and internal marketing