* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
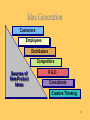
Topic 8 Product Issues in Channel Management By Dr. Songporn Hansanti 1 Objective 1: 10 Marketing Mix Resources By understanding how the other marketing mix variables interface with the channel variable, and the implications of such, the channel manager could coordinate all strategic components to create the synergy needed to meet customers’ needs. 2 Objective 2: 10 Product-Channel Management Interfaces New product planning & development The product life cycle 3 Major areas of product management Strategic product management 3 Objective 3: 10 New Product Planning 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What input, if any, can channel members provide into new product planning? What has been done to assure that new products will be acceptable to the channel members? Do the new products fit into the present channel members’ assortments? Will any special education or training be necessary to prepare the channel members to sell the new products effectively? Will the product cause the channel members any special problems? 4 10 Encouraging Member Input Solicit ideas for new products. Gather feedback on product size or on packaging. Solicit feedback during the test-marketing or commercialization stage. 5 10 Member Acceptance of New Products Determining Factors • How the product will sell • Whether the product is easy to stock & display • Whether the product will be profitable 6 10 Adding Products to the Assortment Key Considerations: Will existing channel members view the new product as appropriate to add to their assortments? Will channel members feel competent to handle the new product? 7 Categories of New Products New-To-The-World New Product Lines Product Line Additions Improvements/Revisions Repositioned Products Lower-Priced Products 8 The New-Product Development Process Long-Term Commitment New Product Strategy New Product Success Factors Capitalize on Experience Establish an Environment 9 New-Product Development Process New-Product Strategy Idea Generation Idea Screening Business Analysis Development Test Marketing Commercialization New Product 10 Idea Generation Customers Employees Distributors Competitors Sources of New-Product Ideas R&D Consultants Creative Thinking 11 Brainstorming Brainstorming The process of getting a group to think of unlimited ways to vary a product or solve a problem. 2 12 Idea Screening Screening The first filter in the product development process, which eliminates ideas that are inconsistent with the organization’s new-product strategy or are inappropriate for some other reason. 13 Concept Test Concept Test A test to evaluate a new-product idea, usually before any prototype has been created. 2 14 Business Analysis Demand Considerations in Business Analysis Stage Cost Sales Profitability 15 Development Creation of prototype Marketing strategy Packaging, branding, labeling Manufacturing feasibility Final government approvals if needed 16 Simultaneous Product Development Simultaneous Product Development A new team-oriented approach to newproduct development where all relevant functional areas and outside suppliers participate in the development process. 17 Introductory Stage • High failure rates • Little competition • Frequent product modification • Limited distribution • High advertising and production costs • Negative profits • Promotion focuses on awareness and information • Intensive personal selling to channels 18 Test Marketing Test Marketing The limited introduction of a product and a marketing program to determine the reactions of potential customers in a market situation. 19 Alternatives to Test Marketing • Single-source research using supermarket scanner data • Simulated (laboratory) market testing • Online test marketing 20 Commercialization Production Inventory Buildup Distribution Shipments Steps in Marketing a New Product Sales Training Trade Announcements Customer Advertising 21 10 Educating Channel Members Manufacturer goal: Method: To sell new products successfully Educate or train channel members in the product’s use and the special features to emphasize in sales presentations 22 10 Trouble-Free New Products Care in new product planning = New product problems 23 Product Life Cycle Growth Stage Maturity Stage Dollars Introductory Stage Decline Stage Sales Profits 0 Time 24 Growth Stage • Increasing rate of sales • Entrance of competitors • Market consolidation • Initial healthy profits • Aggressive advertising of the differences between brands • Wider distribution • Prices normally fall 25 Maturity Stage • Sales increase at a decreasing rate • Saturated markets • Annual models appear • Lengthened product lines • Service and repair assume important roles • Heavy promotions to dealers and consumers • Marginal competitors drop out • Prices and profits fall • Niche marketers emerge 26 Decline Stage • Long-run drop in sales • Large inventories of unsold items • Elimination of all nonessential marketing expenses • “Organized abandonment” 27 Objective 4: 10 Product Life Cycle Sales ($) Sales curve Introduction Growth Profit curve Maturity Decline Time 28 10 Introduction 1. Assure sufficient number of channel members for adequate market coverage 2. Assure adequate supply on channel members’ shelves 29 10 Growth 1. Assure sufficient number of channel member inventories for adequate market coverage 2. Monitor the effects of competitive products on channel member support 30 10 Maturity 1. Extra emphasis on motivating channel members to mitigate competitive impact 2. Investigate possibility for changes in channel structure to extend maturity stage & possibly foster new growth stage 31 10 Decline 1. Phase out marginal channel members 2. Investigate impact of product deletion on channel members 32 Objective 5: 10 Strategic Product Management Successful product strategies depend on: • Product quality, innovativeness, or technological sophistication • Capabilities of managers overseeing product line • Firm’s financial capacity & willingness to provide promotional support • Channel members’ role in implementing product strategies 33 Objective 6: 10 Product Strategies Product differentiation Product positioning Product line expansion & contraction Trading up & trading down Product brand strategy 34 10 Product Differentiation Creating a differential product involves getting consumers to perceive a difference. Implications for channel management: • Channel managers should try to select & help develop members who fit the product image when product differentiation strategy is affected by who will be selling the product. • Channel managers should provide retailers with the kind of support needed to properly present the product when this strategy is influenced by how the product is sold at retail. 35 10 Product Positioning The manufacturer’s attempt to have consumers perceive the product in a particular way relative to competitive products Implications for channel management: • Possible interfaces between the product positioning strategy and where the product will be displayed and sold to consumers should be considered before the strategy is implemented. • Elicit retailer support before attempting to implement strategy. • Maintain backup supply of retailer incentives 36 Product Line Expansion & Contraction 10 Manufacturers often engage in both expansion and contraction simultaneously. Implications for channel management: • Difficult to balance channel member satisfaction & Support for reshaped product lines • Channel members are making increasing demands on Manufacturers to have the right mix of products 37 10 Trading Down, Trading Up Adding lower-priced products or product lines, or higher-priced products or product lines, to a product mix Implications for channel management: • Whether existing channel members provide adequate coverage of high-end or low-end market segments to which trade-up or trade-down product is aimed • Whether the channel members have confidence in the manufacturer’s ability to successfully market the trade-up or trade-down product 38 10 Product Brand Strategy When manufacturers sell under both national and private brands, direct competition with channel members may result Implications for channel management: • Do not sell both national & private brand versions of products to the same channel members. • Sell national and private brand versions in different geographical territories. • Physically vary products enough to minimize direct competition. 39 Objective 6: 10 Product Service Strategy It is the role of the marketing channel to provide necessary service along with the product to the final user Manufacturers should provide after-sale service • by offering it directly at the factory • through their own network of service centers • through channel members • through authorized independent service centers • by some combination of the above 40