* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 Influencing Consumer Behaviors Approaches to
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
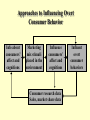
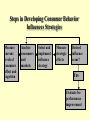
Chapter 10 Influencing Consumer Behaviors Approaches to Influencing Overt Consumer Behavior Info about consumers’ affect and cognitions Marketing mix stimuli placed in the environment Influence consumers’ affect and cognitions Consumer research data Sales, market share data Influent overt consumer behaviors Steps in Developing Consumer Behavior Influences Strategies No Measure current levels of consumer affect and cognition Analyze consumers and markets Select and implement influence strategy Measure strategic effects Desired influence occur? Yes Evaluate for performance improvement A comparison of views on marketing Marketing issues Behavior Approaches Cognitive Approaches Role of marketing Modify consumer behavior to achieve organizational objectives Role of marketing Investigate strategies for predicting Investigate strategies for & controlling consumer behavior influencing consumer affect and cognition & consumer research Satisfy needs of consumers at profit Two Types of Promotion • Overall, “sales promotion” refers to any marketing strategy directed at changing behavior. • Consumer Promotion - “Pull” strategy • Trade Promotion - “Push” strategy Pepsi offers a $5 rebate on the Home Alone video -- A type of consumer promotion Rebates are often effective at changing purchase probabilities, even for big-ticket items Types of consumer promotions Sampling. Consumers are offered regular or trial sizes of the product either for free or at a nominal price. America Online – 7, 500 hours free trial version. Price deals. Consumers are given discounts from the product’s regular price. For example, $1 off of Pepperidge Farm Raisin Bread. Bonus packs. Bonus packs consist of additional amounts of the product provided in the package or container. For example, 33% more free on Head and Shoulders. Consumer promotions, cont. Rebates and refunds. Consumers, either at purchase or by mail, are given cash refunds for purchasing products. For example, A 2000$ rebate on GM trucks in April. Sweepstakes and contests. Consumers are offered chances to win cash and/or prizes either through chance selection or games of skill. For example, Marriott Hotels teamed with Hertz Rent-ACar in a scratch-card sweepstakes that offered over $90 million in prizes. Consumer promotions, cont. Premiums. A premium is a reward or a gift that comes from purchasing a product. For example, P & G offered a free package of Diaperene baby washcloths with the purchase of any size Pampers. Coupons. Consumers are offered cents-off or added value incentives for purchasing specific products. For example, Lenscrafters offered newspaper coupons for $20 off the purchase of contact lenses from its stores. What can be influenced? • Purchase probability – try new product, position to purchase, brand switch, brand loyalty. • Purchase Quantity • Purchase Timing • Purchase Location Promotion effects on consumer behavior Premiums Sweepstakes 16 Bought - later 9 17 21 Rebates Coupons 47 17 Bought - sooner 46 70 23 17 Bought - more 48 59 41 26 Bought - dif. Brand 51 73 46 24 Bought - never tried 36 70 20 Bought - didn't need 12 17 22 Social Marketing • Usually focus on behavior. • Increase probability of desired behaviors (use car pools, save natural resources etc.) • Decrease probability of undesired behaviors (unsafe driving, illegal drugs etc.)