* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hand Foot and Mouth Disease
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
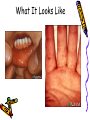
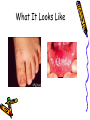
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease Dr. Carla Hoo Hand Foot Mouth Disease • Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness of infants and children. • Disease is caused by an enterovirus, usually Coxsackie A16 • The disease usually begins with a fever, poor appetite, malaise (feeling vaguely unwell), and often with a sore throat. Symptoms • One or 2 days after fever onset, painful sores usually develop in the mouth. They begin as small red spots that blister and then often become ulcers. The sores are usually located on the tongue, gums, and inside of the cheeks. Symptoms • A non-itchy skin rash develops over 1–2 days. The rash has flat or raised red spots, sometimes with blisters. The rash is usually located on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet; it may also appear on the buttocks and/or genitalia How it spreads • Infection is spread from person to person by direct contact with infectious virus particles. These are found in the nose and throat secretions, saliva, blister fluid, and stool of infected persons. • It is very contagious • It usually occurs in children less than 10 years of age • Infected persons are most contagious during the first week of the illness Diagnosis • HFMD is one of many infections that result in mouth sores. However, health care providers can usually tell the difference between HFMD and other causes of mouth sores by considering the patient’s age, the symptoms reported by the patient or parent, and the appearance of the rash and sores. What It Looks Like What It Looks Like Treatment • There is no specific treatment for HFMD. • Symptoms can be treated to provide relief from pain from mouth sores and from fever and aches: – Fever can be treated with antipyretics – Pain can be treated with acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or other over-the-counter pain relievers. – Mouthwashes or sprays that numb pain can be used to lessen mouth pain. • Fluid intake should be enough to Prevention • Good hygiene practices that can lower the risk of infection include – Washing hands frequently and correctly especially after changing diapers and after using the toilet Prevention – Cleaning dirty surfaces and soiled items, including toys, first with soap and water and then disinfecting them by cleansing with a solution of chlorine bleach – Avoiding close contact (kissing, hugging, sharing eating utensils or cups, etc.) with persons with HFMD Stay Healthy Recovery • Most persons recover within 7 to 10 days even without medical treatment • Usually there are no complications References • http://emedicine.medscape.com/artic le/1132264-overview • http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvrd/rev b/enterovirus/hfhf.htm